Ultrasound
Hemorrhagic Renal Cyst
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C92VBedside renal ultrasound demonstrated a right renal cyst with echogenic debris consistent with a hemorrhagic cyst (red arrow). In addition, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis revealed a 4mm non-obstructing right renal stone and bilateral renal cysts. The CT also confirmed the ultrasound finding of a right renal cyst with mild perinephric stranding possibly consistent with a hemorrhagic cyst.
Bilateral Common Iliac Artery Aneurysm
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S73A bedside ultrasound of the aorta was performed. The proximal, middle, and distal aorta appeared normal in caliber, as demonstrated by the images; however there seemed to be some enlargement at the bifurcation. The bifurcation into the iliac arteries, as highlighted by the yellow arrow, demonstrates a slightly enlarged iliac artery on the left. The aorta was followed below the bifurcation as it divided into the iliac arteries, as shown in the video clip. The ultrasound demonstrated a left iliac artery aneurysm measuring 5.99 cm, as highlighted by the orange circle. There were aneurysms to the bilateral common and internal iliac arteries.
Atypical Presentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82W6FBedside ultrasound revealed an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) with concern for dissection vs thrombus/hematoma due to an area of echogenicity within the lumen of the vessel, since normal blood vessels (including the aorta) have lumens that are uniformly anechoic. An intimal flap concerning for dissection appears as a hyperechoic stripe within the lumen of the vessel on ultrasound, often with a hypoechoic and/or anechoic area appreciated underneath the flap, indicating a separate area of blood flow. If this visualized area is of significant size, color doppler can be used to confirm blood flow on both sides of the flap. Given his bedside ultrasound findings, the patient underwent emergent computed tomography scan and was found to have an enlarged infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm, with acute intramural hematoma, extending into bilateral common iliac arteries.
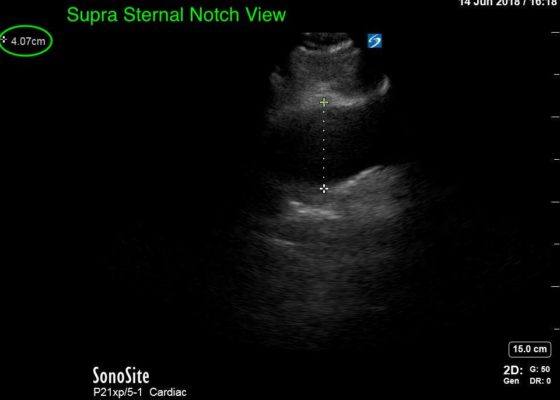
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Measured by Point of Care Ultrasound Suprasternal Notch View
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z64VPoint-of-care cardiac echocardiogram demonstrated a dilated ascending aorta (illustrated in red) measuring approximately 4 cm in the parasternal long axis (PLAX). A dilated aortic arch (illustrated in green) also measuring approximately 4 cm was appreciated using the suprasternal notch view (SSNV). A follow-up computed tomography angiogram (CTA) was performed, validating bedside ultrasound measurements.
Ultrasonographic Findings of Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8063SThe ultrasound video clip shows a longitudinal view of the AT during a dynamic exam. While the patient’s foot is gently passively dorsi/plantar flexed, the video demonstrates first a normal Achilles tendon (from the unaffected extremity) without disruption (highlighted by a yellow bracket on screen left). Then it shows an abnormal tendon (the patient’s affected side) with disruption of the typical linear tendon fibers (red arrow identifies area of rupture). Dynamic testing shows the movement of the distal stump of the AT is evident adjacent to hypoechoic fluid that is reactive edema or blood from the acute rupture.
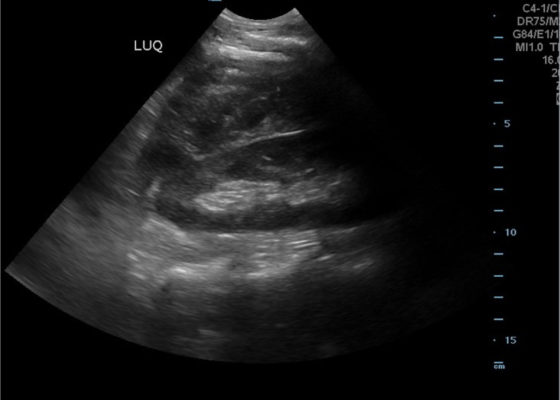
FAST Exam to Diagnose Subcapsular Renal Hematoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NP8DA bedside point of care ultrasound FAST exam was performed revealing a left subcapsular renal hematoma. The hematoma was a non-compressing hematoma, evidenced by preserved renal contour with the hematoma labeled with a red H and the normal renal contour labeled with a green K. Additionally, cortical necrosis and ischemia can be characterized by a dark, hypoechogenic renal cortex on ultrasonography with a decrease in flow to the cortex on color doppler which was not seen on this patient, providing further evidence that the hematoma was non-compressing. The hematoma was concluded to be an acute process due to its hypoechoic appearance with some mixed ultrasonographic echoes caused by the early deposit of fibrin.
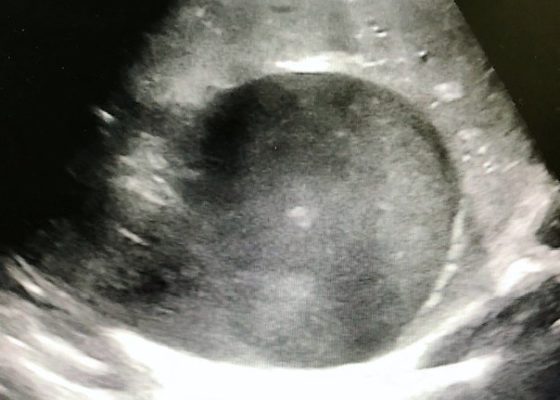
Right Upper Quadrant Pain in a World Explorer
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QP9DThe ultrasound images show the abscess, which is a large, circular, hypoechoic mass outlined in blue in the center of the image. The abscess is surrounded by the hyperechoic and heterogeneous liver tissue.
For better delineation of the abscess, a CT was ordered. The axial CT scan image shows the liver abscess, which appears as a hypodense, ovoid, intrahepatic fluid collection within the liver parenchyma. The size of the abscess has been annotated with a dotted line measuring 194.9 mm x 166.2 mm.
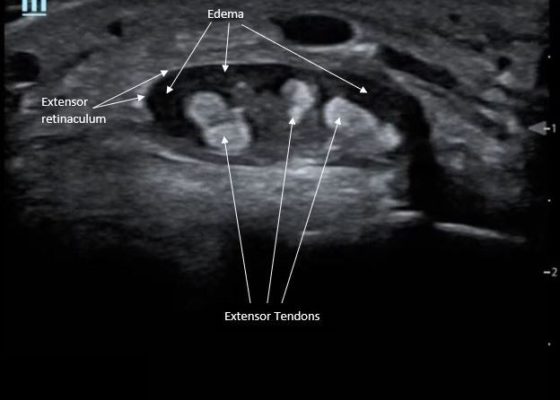
Point-Of-Care Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Extensor Tenosynovitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q050Point-of-care ultrasound of the dorsal aspect of the left hand reveals a heterogenous hypoechoic fluid collection surrounding the extensor tendons (axial view) within the retinaculum consistent with edema. Longitudinal view shows anechoic fluid within the tenosynovium which is located between the anisotropic extensor tendon and linear hyperechoic synovial sheath. Longitudinal view also shows some cobblestoning, or tissue edema, superficial to the anisotropic extensor tendon. The patient’s contralateral right dorsal hand was scanned in a longitudinal view and shows no cobblestoning or hypoechoic fluid under the synovial sheath. The patient was diagnosed with tenosynovitis, and started on intravenous antibiotics.