Search By Topic
Found 39 Unique Results
Page 1 of 4
Page 1 of 4
Page 1 of 4
Innovative Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Nerve Block Model for Training Emergency Medicine Physicians
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PW7DThis innovation model is designed to facilitate hands-on training of the ultrasound-guided ESP nerve block using a practical, realistic, and cost-effective ballistics gel model. By the end of this training session, learners should be able to: 1) identify relevant sonoanatomy on the created simulation model; 2) demonstrate proper in-plane technique; and 3) successfully replicate the procedure on a different target on the created training model.
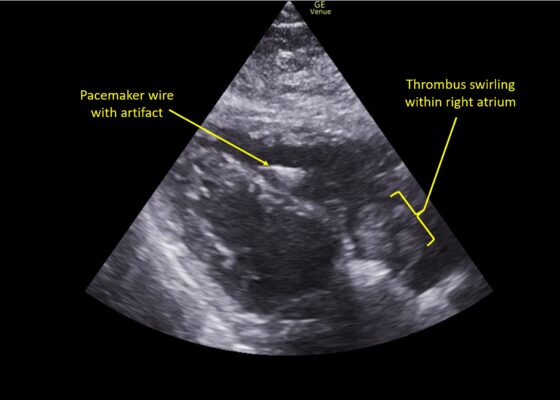
A Case Report of Right Atrial Thrombosis Complicated by Multiple Pulmonary Emboli: POCUS For the Win!
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TM07Pulmonary POCUS was performed by the ED physician (GE Venue, C1-5-RS 5MHz curvilinear transducer), and lung examination was unremarkable with no pleural effusion, pneumothorax, or infiltrate. Subxiphoid views (GE Venue, 3Sc-RS 4MHz phased-array transducer) were obtained because this patient’s COPD with severe pulmonary hyperexpansion made parasternal and apical 4-chamber views suboptimal. A large thrombus can be seen within the right atrium (movie 1, images 1, 2). This has a serpiginous, rounded appearance and is mobile, appearing to swirl within the right atrium with intermittent extrusion through the tricuspid valve. A pacemaker wire is also visible within the right ventricle as a non-moving, hyperechoic, linear structure with posterior enhancement artifact. Pericardial effusion is not present.
E-FAST Ultrasound Training Curriculum for Prehospital Emergency Medical Service (EMS) Clinicians
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S060By the end of these training activities, prehospital EMS learners will be able to demonstrate foundational ultrasound skills in scanning, interpretation, and artifact recognition by identifying pertinent organs and anatomically relevant structures for an E-FAST examination. Learners will differentiate between normal and pathologic E-FAST ultrasound images by identifying the presence of free fluid and lung sliding. Learners will also explain the clinical significance and application of detecting free fluid during an E-FAST scan.
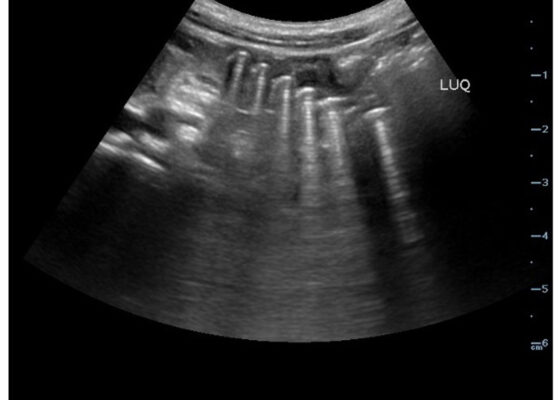
Point-Of-Care Ultrasound Use for Detection of Multiple Metallic Foreign Body Ingestion in the Pediatric Emergency Department: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83D2DBedside POCUS was performed on the patient’s abdomen using the curvilinear probe. The left upper quadrant POCUS image demonstrates multiple hyperechoic spherical objects with shadowing and reverberation artifacts concerning multiple foreign body ingestions. Though the patient and mother initially denied knowledge of foreign body ingestion, on repeated questioning after POCUS findings, the patient admitted to his mother that he ate the spherical magnets he received for his birthday about one week ago. The patient swallowed these over the course of two days. The presence of multiple radiopaque foreign bodies was confirmed with an abdominal X-ray.
Sonographic Retrobulbar Spot Sign in Diagnosis of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8735PThe bedside ocular ultrasound (B-scan) was significant for small, hyperechoic signal (white arrow) in the distal aspect of the optic nerve, concerning for embolus in the central retinal artery. Subsequent direct fundoscopic exam was significant for a pale macula with cherry red spot (black arrow), consistent with central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO).
Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room for POCUS Pulmonary: Scan Your Way Out
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RM0MBy the end of performing the Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room, learners will be able to: 1) recognize sonographic signs of A-line, B-line, Barcode sign, Bat sign, Seashore Sign, Plankton sign, Jellyfish Sign, Lung point, lung lockets, and Lung pulse; 2) differentiate sonographic findings of pneumothorax, hemothorax, pneumonia, COVID 19 pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and pleural effusion from normal lung findings; 3) distinguish pneumonia from atelectasis by recognizing dynamic air bronchogram; and 4) recognize indications for performing POCUS pulmonary such as dyspnea, blunt trauma, fall, cough and/or heart failure.
High-Efficiency Ultrasound-Guided Regional Nerve Block Workshop for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84P8RThe objective of this workshop is to provide emergency medicine residents the confidence and skill sets needed to effectively perform five commonly used UGRNBs for conditions encountered in the emergency department. Through this one-day, accelerated workshop, residents will be given an opportunity to sharpen their UGRNB technique prior to applying them in the clinical environment. By the end of this workshop, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the clinical situations in which UGRNBs can be utilized and understand the associated risks, 2) list the commonly used local anesthetic medications and their proper dosing in respect to regional nerve blocks, 3) demonstrate proper ultrasound probe positioning and identify relevant anatomical landmarks for each nerve block on both standardized patients and cadavers, 4) describe the common steps involved to perform each nerve block, 5) perform the five UGRNB techniques outlined in this workshop.
Vitreous Hemorrhage Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88D3BPoint of care ultrasound (POCUS) revealed hyperechoic material in the vitreous consistent with a vitreous hemorrhage. On the ultrasound images, there is visible hyperechoic debris seen floating in the vitreous as the patient moves his eye. Since the vitreous is typically anechoic (black) in color on ultrasound, turning up the gain on the ultrasound machine makes these findings easier to see and often highlights abnormalities, such as this hemorrhage (see annotated still).
Ureteral Obstruction and Ureteral Jet Identification—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8206GA point-of-care ultrasound of the urinary tract was performed, evaluating the kidneys and bladder. When imaging her kidneys, right-sided hydronephrosis was noted with a normal appearance to the left kidney. To further evaluate, a curvilinear probe was placed on her bladder with color doppler to assess for ureteral jets. Ureteral jets are seen as a flurry of color ejecting from each of the ureters as urine is released from the ureterovesical junction. In a healthy patient, this finding should be seen ejecting from both ureters every 1-3 minutes as the kidneys continue to filter the blood and create urine to be stored in the bladder. In our patient, however, ureteral jets were only noted on the left side (arrow), which was significant in further verifying our suspicion of right ureteral obstruction.
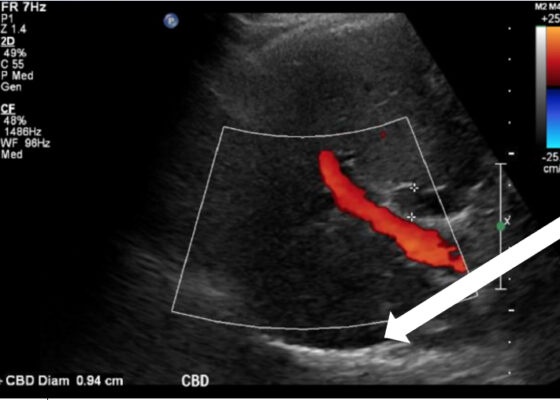
A Case Report on Detecting Porcelain Gallbladder form Wall-Echo-Shadow Sign on Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8164GPoint-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was performed by the emergency physician. Gallbladder ultrasound (US) should be performed using a curvilinear probe. If the patient’s body habitus does not allow for the use of a curvilinear probe, a phased array probe may be used. To find the gallbladder with ultrasonography, two approaches are commonly used. Many physicians prefer the “subcostal sweep” in which the probe is placed on the xiphoid process in a sagittal plane and swept along the inferior costal margin until the gallbladder is visualized. If this does not adequately locate the gallbladder, the “X minus 7” approach may be used. In this approach, the probe is placed on the xiphoid (X) process in a transverse view and moved 7 centimeters (minus 7) to the patient’s right. This technique is useful for patients with a larger body habitus. If the gallbladder is still not visualized, placing the patient in left lateral decubitus position or asking them to take a deep breath and hold may help the ultrasonographer locate the gallbladder. The US revealed mild hepatic biliary duct dilation with cholelithiasis and sludge, but no additional evidence to suggest cholecystitis. The US image showed a dilated common bile duct at 0.94 cm and calcifications. Visualization of the gallbladder wall is essential in differentiating between a positive wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign and a porcelain gallbladder. While a hypoechoic gallbladder wall is indicative of a WES sign, a hyperechoic wall layer will indicate a calcified gallbladder wall, suggesting a porcelain gallbladder. In image 1, the hyperechoic gallbladder wall can be visualized (white arrow), suggesting the presence of porcelain gallbladder and distinguishing it from a positive WES sign.