Genitourinary
Point-of-care Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Bladder Hematoma vs. Hemorrhage
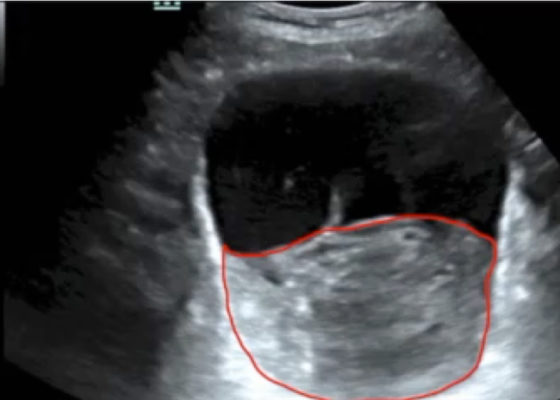
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8092FBladder POCUS demonstrated 500mL of post void residual fluid, indicative of retention. Half of the volume is hyperechoic (red circle); this is likely the bladder wall hematoma. Could also consider sonographic artifact, bladder mass, or cystitis.1-2
Bedside Ultrasound for the Rapid Diagnosis of Fournier’s Gangrene
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CP99Point of care ultrasound (POCUS) utilizing a high-frequency linear probe revealed heterogeneous debris with subcutaneous air within the scrotal wall extending into the perineum consistent with necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier’s gangrene (FG). The video shows multiple foci of gas that appear as echogenic dots with “dirty shadows” posteriorly from reverberation artifact arising from gas within the soft tissue.
Priapism Team-based Learning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80K9VThe primary goal of this curriculum is to teach EM interns critical thinking; clinical decision making; and presentation, communication, documentation and procedural skills. The secondary goal is to identify interns who might not be performing at the expected level for potential early intervention. In addition, we wanted to ensure that all interns have achieved Level 1 milestones in the patient care, systems-based practices, and interpersonal and communication competencies.
Chancre of Primary Syphilis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83342Physical examination revealed a non-tender, erythematous lesion on the glans penis, two similar adjacent satellite lesions, as well as tender inguinal lymphadenopathy. No penile discharge was noted.
Novel Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing Self-Directed Learning and the Flipped Classroom Method: Genitourinary Emergencies Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89S56We aim to teach the presentation and management of genitourinary emergencies through the creation of a flipped classroom design. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.