Search By Topic
Found 27 Unique Results
Page 1 of 3
Page 1 of 3
Page 1 of 3
Alcohol Withdrawal
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87S8QAt the end of this oral boards session, learners will: 1) demonstrate the ability to perform a detailed history and physical examination in a patient presenting with signs and symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, 2) investigate the broad differential diagnoses, including electrolyte abnormalities, trauma in the intoxicated patient, mild alcohol withdrawal, and delirium tremens, 3) list appropriate laboratory and imaging studies to include complete blood count (CBC), complete metabolic panel (CMP), magnesium level, computed tomography (CT) scan of the brain; 4) understand the management of hypoglycemia with concurrent administration of thiamine to prevent Wernicke’s encephalopathy and subsequent Korsakoff syndrome, 5) appropriately treat acute alcohol withdrawal with intravenous (IV) hydration and benzodiazepines, phenobarbital, or alternative medications, and 6) understanding the need for the complex management of these patients, appropriately disposition the patient to the intensive care unit after consulting with critical care specialists.
Acetaminophen Toxicity
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8435RAt the end of this practice oral board session, examinees will be able to: 1) demonstrate an ability to obtain a complete medical history in an oral boards structured interview format, 2) review appropriate laboratory tests and imaging to evaluate abdominal pain, 3) investigate a broad differential diagnosis for right upper quadrant abdominal pain, 4) recognize chronic acetaminophen toxicity, 5) initiate the appropriate treatment for chronic acetaminophen toxicity, 6) demonstrate effective communication with the patient, consultants, and the admitting team.
Development and Design of a Pediatric Case-Based Virtual Escape Room on Organophosphate Toxicity
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DH1VBy the end of the activity, learners should be able to: 1) recognize risk factors, symptoms, and presentation for organophosphate poisoning; 2) understand the radiologic and laboratory findings in organophosphate poisoning; 3) distinguish and differentiate electrocardiogram findings in common toxic ingestions; 4) explain the pathophysiology of organophosphate poisoning; 5) understand the importance of decontamination of the patient and personal protective equipment for staff for organophosphate poisoning; 6) describe the airway management of organophosphate poisoning; 7) describe the medical management of organophosphate poisoning, including antidotes and the correct dosing and 8) demonstrate teamwork through communication and collaboration.
Calcium Channel Blocker Overdose
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CQ07At the end of this oral board session, examinees will: (1) demonstrate ability to evaluate a patient with undifferentiated shock with bradycardia and discuss the differential diagnosis, (2) recognize the signs and symptoms of calcium channel blocker overdose, (3) demonstrate ability to manage treatment of a patient with calcium channel overdose.
Alcohol Withdrawal with Delirium Tremens
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S35NBy the end of the session, learner will be able to 1) discuss the causes of altered mental status, 2) utilize CIWA scoring system to quantify AW severity, 3) formulate appropriate treatment plan for AW by treating with benzodiazepine and escalating treatment appropriately, 4) treat electrolyte abnormalities by giving appropriate medications for hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia, and 5) discuss clinical progression and timing to AW.
Infant Botulism
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88350At the end of this oral board session, examinees will: 1) demonstrate an ability to obtain a complete pediatric medical history, 2) perform an appropriate physical exam on a pediatric patient, 3) investigate a broad differential diagnosis for neuromuscular weakness in a pediatric patient, 4) recognize the classic presentation of infant botulism and implement treatment with botulinum specific antitoxin before confirmatory testing, 5) recognize impending airway failure and intubate the pediatric patient with appropriately dosed medications and ET tube size, and 6) demonstrate effective communication with healthcare team members and parents.
Botulism due to Drug Use
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q93BABSTRACT: Audience: This scenario was developed to educate emergency medicine residents on the diagnosis and management of wound botulism secondary to injection drug use. Introduction: Botulism is a relatively rare cause of respiratory failure and descending weakness in the United States, caused by prevention of presynaptic acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction. This presentation has several mimics, including myasthenia gravis
Anticholinergic Toxicity in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D07ZBy the end of this simulation case, learners will be able to: 1) describe the classic clinical presentation of anticholinergic toxicity, 2) discuss common medications and substances that may lead to anticholinergic toxicity, 3) recognize the electrocardiogram (ECG) findings in anticholinergic toxicity that require specific therapy, and 4) review the management of anticholinergic toxicity.
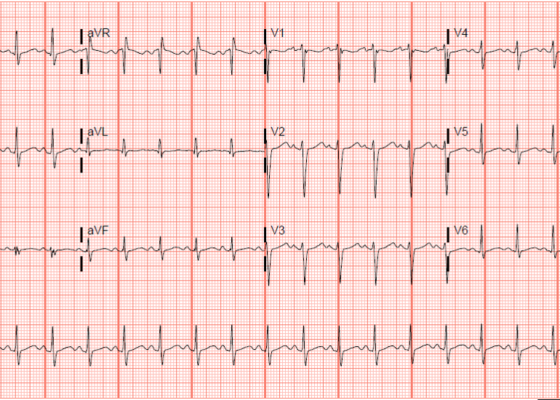
Electrocardiogram Abnormalities Following Diphenhydramine Ingestion: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85H1PThe blue arrow points to one of the terminal R waves in aVR, and the green arrow points to one of the large S waves in lead I, indicating right axis deviation. These findings are pathognomonic for sodium channel blockade. Due to the specific ECG findings and knowledge of diphenhydramine overdose, it was evident that these ECG findings were due to a cardiac sodium channel blockade. Sodium channels are essential within myocardial tissue to ensure the rapid upstroke of cardiac action potential, as well as rapid impulse conduction throughout cardiac tissue. Therefore, sodium channel blockers tend to exhibit significant dysrhythmic properties due to severe conduction disturbances.2 The blockage of the cardiac sodium channels appears as terminal R waves in aVR as well as terminal S waves in lead I due to delaying, and possibly blocking, the electrical conduction pathway of the heart. The orange arrows show resolution of terminal R wave in aVR and terminal S wave in lead I, after administration of sodium bicarbonate.
Methemoglobinemia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PH1BAt the end of this simulation case, participants should be able to: 1) recognize shortness of breath, cyanosis and respiratory distress, and the difference between all of them based on the clinical presentation 2) identify the underlying cause of the condition by conducting a thorough history and physical 3) know how to identify and treat methemoglobinemia by ordering necessary labs and interventions and understand the pathophysiology leading to methemoglobinemia 4) recognize patient’s response to treatment and continue to reassess.