Search By Topic
Found 67 Unique Results
Page 1 of 7
Page 1 of 7
Page 1 of 7
A Case Report of Acute Compartment Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87061Inspection of the extremity revealed significant swelling with dark discoloration and multiple bullae (pre-operative photograph). Furthermore, notable swelling of the right foot was noted, which felt cold to palpation. Radiographs of pelvis, bilateral knees, tibia, fibula, and feet demonstrated no fractures or dislocations. The bilateral tibia and fibula X-ray revealed soft tissue swelling in the proximal legs, particularly evident in the right leg's AP view, which also showed numerous ovoid radiodensities in the anterior compartment, likely related to soft tissue injury. Post operative images are also provided demonstrating the patients’ four compartment fasciotomies which were loosely closed using staples.
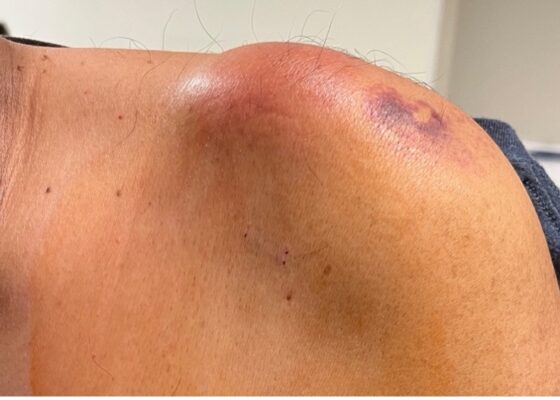
Septic Arthritis of the Acromioclavicular Joint: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP9NMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast was obtained of the shoulder and ankle, and results from both scans showed findings consistent with septic arthritis complicated by intraarticular abscesses. The MRI of the patient’s left acromioclavicular joint is shown as both a T1-weighted sequence in sagittal view and T2-weighted sequence in coronal view. The images show effusion (the dark fluid denoted by the red arrow) with an adjacent fluid collection (blue arrow). A T2-weighted MRI in coronal view of the patient’s right ankle showing multiple effusions (green arrows) and a fluid collection along the medial tibial cortex and subcutaneous tissues (yellow arrow).
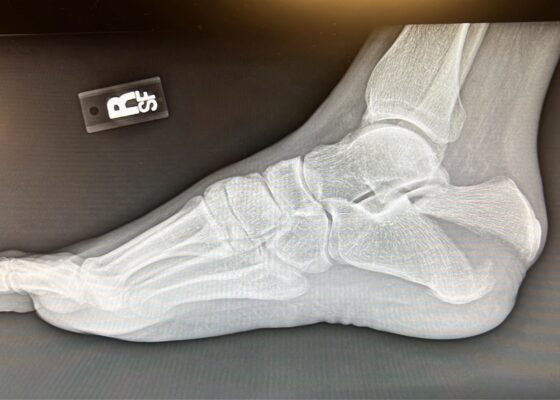
Case Report of a Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NH11Examination of the right ankle demonstrated a large deformity of the superior talus with bruising and blanching of the overlying skin in the area of the Achilles tendon (see images 2,3). The remaining bones of the foot were not tender to palpation and the foot was neurovascularly intact throughout with only mild numbness in the area of the tented skin. Completing the trauma exam, the patient had no signs of head injury and no midline spinal tenderness to palpation. Inspection of the remaining long bones and joints showed no other injuries. There were mild skin scrapes on the right flank from the fall. X-rays of the right foot and ankle showed a longitudinal fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity from the articular surface to the posterior surface (see red outline) with extension into the subtalar joint (blue lines) and roughly 1.8 cm displacement between the fracture segments (yellow double arrow). These findings represented a tongue-type calcaneal bone fracture.
High-Pressure Injection Injury to the Hand – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D64WPlain radiographs of the left hand and forearm demonstrated extensive subcutaneous emphysema. The air can be seen as lucent striations tracking along the second and third fingers as well as along the dorsum of the hand and wrist. There is also diffuse soft tissue emphysema surrounding the metacarpophalangeal joints. Lab analysis did not show any significant acute abnormalities.
A Case Report of the Rapid Evaluation of a High-Pressure Injection Injury of a Finger Leading to Positive Outcomes
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TD2XOn exam the patient was noted to have a punctate wound to the ulnar aspect of his right index finger, just proximal to the distal interphalangeal joint. The finger appeared pale and taut, with absent capillary refill. The patient displayed diminished range of motion with both extension and flexion of the joints of the finger. Sensation was absent and no doppler flow was appreciated to the distal aspects of the finger. X-ray of the hand was obtained and showed many small foreign bodies in the soft tissue and extensive radiolucent material consistent with gas or oil-based material to the palmar aspect of the index finger tracking up to the level of the metacarpal heads.
Jefferson Fracture and the Classification System for Atlas Fractures, A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88P9CComputed tomography (CT) revealed a burst fracture (Jefferson) of the anterior arch (white arrows) and of the posterior arch (yellow arrows) of the first cervical vertebrae (C1). There was also a fracture of the right lateral mass (blue arrow) of C1 with mild lateral subluxation of the lateral masses (curved arrows).
Posterior Sternoclavicular Dislocation: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8363QChest X-ray revealed an inferiorly displaced right clavicle at the right sternoclavicular joint (blue arrow). A computed tomography angiogram (CTA) of the chest was therefore obtained and revealed a right posterior sternoclavicular dislocation with resultant compression of the left brachiocephalic vein (purple arrow). Even though the right clavicle is displaced, the anatomy of the brachiocephalic vein is such that it is positioned to the right of midline, placing the left brachiocephalic vein posterior to the right clavicle. The right brachiocephalic and common carotid artery were normal in appearance. The CTA also revealed a comminuted fracture of the left anterior second rib at the costochondral junction that had not been previously seen on the x-ray.
Adult Clavicular Fracture Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FM0TThe patient's chest and clavicular radiographs showed a comminuted displaced acute fracture of the right mid-clavicle (green, blue, yellow). The clavicular fracture was also visible on the chest computed tomography (CT). The remainder of his trauma workup was negative for acute findings.
Case Report of Distal Radioulnar Joint and Posterior Elbow Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89S6KRadiographs of the left elbow and wrist were obtained. Left elbow radiographs showed simple posterolateral dislocation of the olecranon (red) without fracture of the olecranon (red) or trochlea (blue). Left wrist lateral radiographs demonstrated DRUJ dislocation with dorsal displacement of the distal ulna (green) without fracture or widening of the radioulnar joint (purple). Post-reduction radiographs demonstrated appropriate alignment of the elbow with the trochlea seated in the olecranon and improved alignment of the DRUJ.
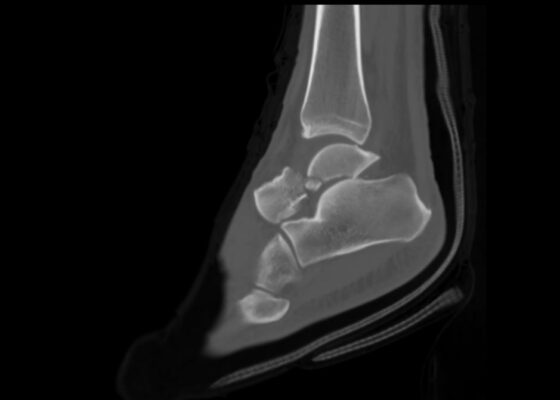
Case Report: Talar Neck Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FP75ABSTRACT: This report demonstrates a case of a severe talar neck fracture. Although rare, talar neck fractures have a high potential for morbidity. Typically caused by a high energy injury, this patient’s mechanism of injury was relatively minor, and presentation was not immediately concerning for such a severe fracture. Initial x-rays provided a gross demonstration of the fracture, but a