Search By Topic
Found 26 Unique Results
Page 1 of 3
Page 1 of 3
Page 1 of 3
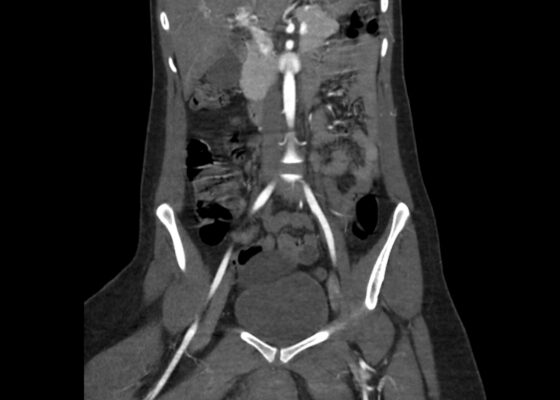
Computed Tomography Findings in Non-Obstetric Vulvar Hematoma: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8194HBedside ultrasound was first used to evaluate for evidence of abscess or cyst formation. Ultrasound demonstrated a hypoechoic area within the right labia without evidence of a cyst or abscess wall. Based on these findings, an angiogram CT of the pelvis was obtained which revealed a vulvar hematoma with evidence of active arterial extravasation. In both the coronal and axial view, there is an asymmetric area of isodensity in the right labia representing a hematoma (blue circled area). Angiography may show areas of active extravasation, which appears as hyperdensity within the area of hematoma (see red arrow in coronal plane).
High-Fidelity Simulation with Transvaginal Ultrasound in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8606QBy the end of the session, learners should be able to 1) recognize the clinical indications for transvaginal ultrasound in the ED, 2) practice the insertion, orientation, and sweeping motions used to perform a TVPOCUS study, 3) interpret transvaginal ultrasound images showing an IUP or alternative pathologies, and 4) understand proper barrier, disinfection, and storage techniques for endocavitary probes.
Septic Abortion Complicated by Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8GH1GAt the conclusion of the simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) Obtain a relevant focused history including pregnancy history, medication use, and past medical history. 2) Develop a differential for fever and vaginal bleeding in a pregnant patient. 3) Discuss management of septic abortion, including empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics and obstetric consultation for source control with dilation and curettage (D&C). 4) Discuss expected laboratory findings of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). 5) Discuss management of DIC, including identification of underlying etiology and supportive resuscitation with blood products. 6) Review the components of blood products. 7) Identify appropriate disposition of the patient to the intensive care unit (ICU).
Vaginal Bleeding Due to Iatrogenic Uterine Perforation – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83643The bedside transabdominal US of the pelvis showed a heterogeneous mixture of hypoechoic and hyperechoic endometrial thickening extending to the lower uterine segment (blue arrow), which was thought to represent active hemorrhage. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis showed evidence of a large amount of endometrial hyperdensity (red arrow) suggestive of hemorrhagic contents within a grossly enlarged uterus. There was relative decreased enhancement of the uterine body and fundus, concerning for devascularization. There was also active extravasation along the left lateral uterus (yellow arrow).
A Homemade, Cost-Effective, Realistic Pelvic Exam Model
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HM0FAfter utilizing this pelvic examination model, the learner will be able to: 1) demonstrate ability to perform a pelvic examination comfortably and safely, 2) demonstrate ability to obtain a cervical swab on female patients, and 3) show proficient understanding of female anatomy.
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZS9MBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) initiate a workup of a pregnant patient who presents with syncope, 2) accurately diagnose peripartum cardiomyopathy, 3) demonstrate care of a gravid patient in respiratory distress due to peripartum cardiomyopathy, 4) appropriately manage cardiogenic shock due to peripartum cardiomyopathy.
Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Diagnose Molar Pregnancy: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82W7TA transabdominal point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was initiated to determine whether an abnormality to the pregnancy could be identified. Curvilinear probe was used. Our transabdominal POCUS, in the transverse plane, showed a heterogenous mass with multiple anechoic areas in the uterus. The white arrow on the ultrasound identifies these findings. The classic “snowstorm” appearance was concerning for molar pregnancy.
Syncope Due to a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86M0NAt the conclusion of this simulation, the learner will be able to: 1) review the initial management of syncope; 2) utilize laboratory and imaging techniques to diagnose a ruptured ectopic pregnancy; and 3) demonstrate the ability to resuscitate and disposition an unstable ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
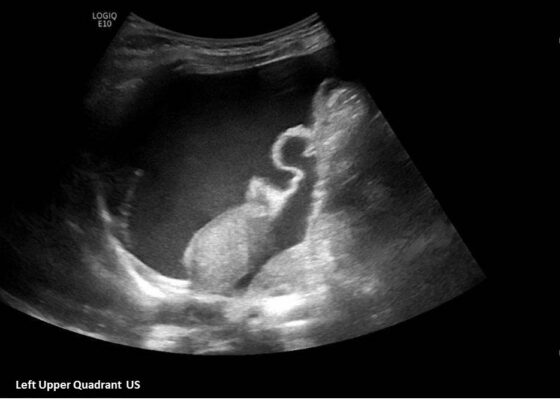
Ovarian Juvenile Granulosa Cell Tumor Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8035HA focused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) exam was performed initially to evaluate for intra-abdominal injury given the clinical picture. A phased-array ultrasound transducer was placed in sagittal orientation along the patient’s right and left flank, demonstrating extensive heterogenous fluid collections in Morrison’s pouch (red arrow), subphrenic space (solid green arrow), and splenorenal recess (dashed green arrow). To further evaluate, a phased-array transducer was placed over her pelvic area in transverse orientation, demonstrating, a large, heterogeneous mass (outlined in yellow arrows). The surgical team was promptly consulted and blood products were ordered. Although there was concern for impending hemorrhagic shock due to patient’s presenting tachycardia, the patient was hemodynamically stable enough for a CT scan of her chest, abdomen, and pelvis. The CT scan showed large-volume ascites, which exerted mass effect on all abdominal organs with centralization of bowel loops. Additionally, there was a large, 6.4 x 6.8 x 10.9-centimeter, midline pelvic mass (outlined in blue arrows).
Eclampsia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PS8RBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) demonstrate care of a gravid patient with altered mental status; 2) demonstrate care of a gravid patient with seizures; 3) recognize care involved in assessment of fetal status; 4) execute appropriate subspecialty consultation; 5) recognize the clinical signs and symptoms of eclampsia; 6) distinguish different treatment options for eclampsia; 7) identify magnesium toxicity and reversal agent; and 8) differentiate the spectrum of preeclampsia.