CT
Meckel’s Diverticulum Causing Small Bowel Intussusception in Third Trimester Pregnancy
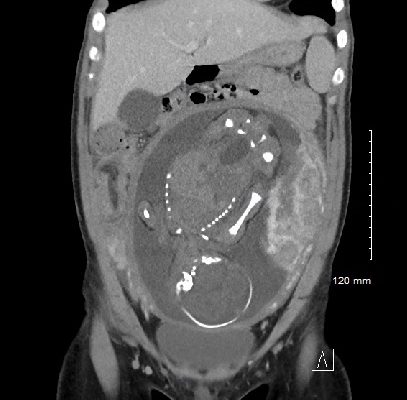
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87H19A CT scan was obtained which demonstrated distal small bowel intussusception with focal dilation suggestive of a small bowel obstruction in a pregnant female in her third trimester of pregnancy. The fetus can be seen in the uterus. The yellow arrow identifies the area of small bowel intussusception shown by telescoping intestines with associated bowel wall edema.
Bilateral Common Iliac Artery Aneurysm
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S73A bedside ultrasound of the aorta was performed. The proximal, middle, and distal aorta appeared normal in caliber, as demonstrated by the images; however there seemed to be some enlargement at the bifurcation. The bifurcation into the iliac arteries, as highlighted by the yellow arrow, demonstrates a slightly enlarged iliac artery on the left. The aorta was followed below the bifurcation as it divided into the iliac arteries, as shown in the video clip. The ultrasound demonstrated a left iliac artery aneurysm measuring 5.99 cm, as highlighted by the orange circle. There were aneurysms to the bilateral common and internal iliac arteries.
Case Report: Acute Supraglottitis
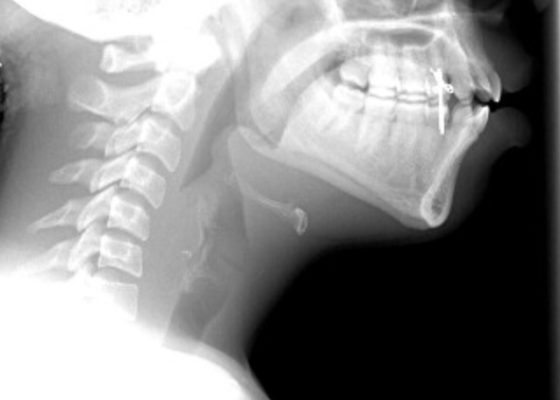
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8006VOn arrival, radiographs of the neck soft tissues were obtained, which showed a markedly enlarged epiglottic shadow (red arrow) concerning for epiglottitis. A computed tomography scan of the neck soft tissues with contrast was then obtained which revealed edematous mucosal thickening of the oropharynx (blue arrow) and supraglottic larynx (green arrow) including the epiglottis (purple arrow) concerning for acute infectious pharyngitis and supraglottic laryngitis with severe narrowing of the supraglottic laryngeal lumen, as well as associated extensive inflammation and edema of the superficial and deep left neck spaces. The patient’s white blood cell count was elevated to 25.7x109/L with 87% neutrophils. Her rapid strep test was positive. Otolaryngology was consulted and performed a bedside flexible laryngoscopy which showed significant edema of the epiglottis (orange arrow), vocal cords (white arrow), and arytenoids (black arrow), left greater than right. Based on the findings and concern for impending respiratory failure, the patient received an awake fiberoptic intubation by anesthesia at the bedside.
Case Report of the Unusual Presentation of Stridor in an Elderly Patient Following a Cervical Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V926The cervical CT was significant for a transverse fracture through the C4 vertebral body (see red arrow), lateral facet (green arrow), spinous process (blue arrow), and right lamina (purple arrow) as well as surrounding edema and retropharyngeal thickening (yellow line), best appreciated on sagittal view.
Atypical Presentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
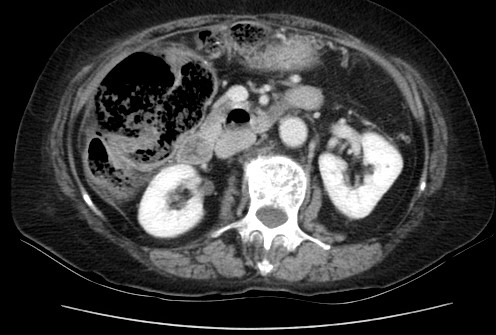
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82W6FBedside ultrasound revealed an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) with concern for dissection vs thrombus/hematoma due to an area of echogenicity within the lumen of the vessel, since normal blood vessels (including the aorta) have lumens that are uniformly anechoic. An intimal flap concerning for dissection appears as a hyperechoic stripe within the lumen of the vessel on ultrasound, often with a hypoechoic and/or anechoic area appreciated underneath the flap, indicating a separate area of blood flow. If this visualized area is of significant size, color doppler can be used to confirm blood flow on both sides of the flap. Given his bedside ultrasound findings, the patient underwent emergent computed tomography scan and was found to have an enlarged infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm, with acute intramural hematoma, extending into bilateral common iliac arteries.
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Measured by Point of Care Ultrasound Suprasternal Notch View
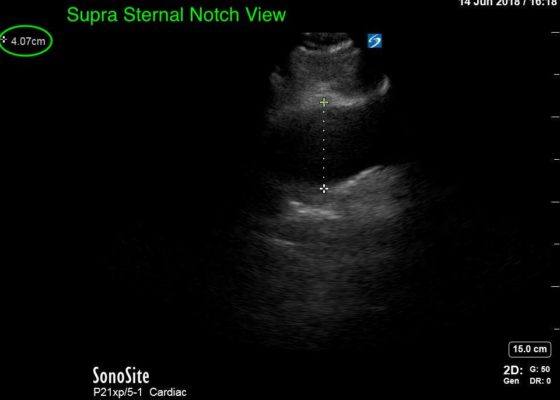
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z64VPoint-of-care cardiac echocardiogram demonstrated a dilated ascending aorta (illustrated in red) measuring approximately 4 cm in the parasternal long axis (PLAX). A dilated aortic arch (illustrated in green) also measuring approximately 4 cm was appreciated using the suprasternal notch view (SSNV). A follow-up computed tomography angiogram (CTA) was performed, validating bedside ultrasound measurements.
Incarcerated Ventral Hernia of T-colon Resulting in Colon Perforation and Intraabdominal Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83W74History of present illness: A 75-year-old female with a remote history of rectal cancer presented to the emergency department with acute right upper abdominal pain. The pain had begun suddenly after lunch. On review of systems, the patient had mild nausea. Initial vital signs were within normal limit. She denied fever, chills, or vomiting. The physical examination revealed a distended,
Bezoars: An Interesting Case of Abdominal Pain
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VD1VComputed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and intravenous contrast was ordered to evaluate her symptoms. The CT showed three large collections of ingested material seen as hypodense material with circular rings surrounded by the hyperdense oral contrast (see red outlines). These findings are consistent with bezoars, the largest of which measured 11.5 x 7.8 cm. There was also thickening of the gastric wall (see blue outline), most notably at the pylorus, consistent with partial obstruction.