Neurology
Eye-Opener: A Case Report of Eyelid Taping as Presenting Symptom of Myasthenia Gravis
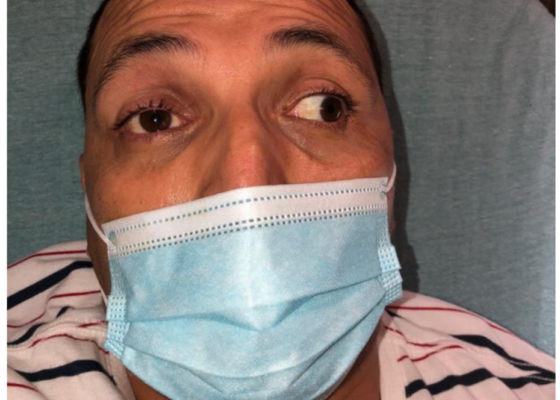
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW8GPhysical exam was significant for a very pleasant, well-appearing female in no acute distress, noted to have clear plastic tape attached to her bilateral eyelids and brows (Image 1). When the tape was removed, she had bilateral ptosis, more significantly in the left eye (Image 2). She had no conjunctival injection or pallor. Her airway was patent and protected. She had no neck masses or carotid bruits. Her heart and lung exams were normal, with no evident respiratory distress. Her neurologic exam was further significant for limited extra-ocular movement (EOM). Her most notable deficits were with lateral and upward gaze (Video 1) indicative of weakness at the muscles innervated by cranial nerves III and VI. Her pupillary response was symmetric and brisk bilaterally. She had no additional cranial nerve deficits, slurred speech, or asymmetry in her strength or sensation throughout.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causing a Seizure: An Assessment Simulation for Medical Students
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XH1HAt the conclusion of the simulation leaners will be able to: 1) efficiently take a history from the patient and perform a physical exam (including a complete neurological exam); 2) identify red flag symptoms in a patient complaining of a headache; 3) order and interpret the results of a CT of the head and either a CT angiogram of the brain or a lumbar puncture to make the diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage; 4) demonstrate appropriate management of a seizure; and 5) utilize the I-PASS framework to communicate with the inpatient team during the transition of care.
The Clue is in the Eyes. A Case Report of Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DP9MThere was no appreciable esotropia or exotropia noted on straight gaze (yellow arrows). On extraocular muscle examination, patient was noted to have a complete left medial rectus palsy consistent with a left internuclear ophthalmoplegia (red arrow). This was evidence by both eyes easily gazing left (green arrows); however, with rightward gaze, her left eye failed to gaze past midline (red arrow).
Headache Over Heels: CT Negative Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ND2CBy the end of this case, the participant will be able to: 1) construct a broad differential diagnosis for a patient presenting with syncope, 2) name the history and physical exam findings consistent with SAH, 3) identify SAH on computer tomography (CT) imaging, 4) identify the need for lumbar puncture (LP) to diagnose SAH when CT head is non-diagnostic > 6 hours after symptom onset, 5) correctly interpret cerebral fluid studies (CSF) to aid in the diagnosis of SAH, and 6) specify blood pressure goals in SAH and suggest appropriate medication management.
Epilepsy Caused by Neurocysticercosis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81P96In our patient, two lesions were most notable on CT in the frontal and occipital lobes. The lesion in the left frontal lobe (blue circle) was an approximately 1.5 centimeter (cm) rounded area with rim enhancement and surrounding hypodensity, consistent with vasogenic edema. A similar sized low-density area in the left occipital lobe (red circle) was noted, with increased peripheral density at the 3 o’clock position representing calcification. There were no areas of apparent hemorrhage or midline shift. The final radiology report concluded there were multiple cystic lesions, one with surrounding vasogenic edema in the left frontal lobe.
A Case Report of a Man with Burning Arm and Leg Weakness
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V659A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) of the head and neck was performed, followed by an MRI of the cervical spine. The CT demonstrated congenital narrowing of the cervical spinal canal, with posterior disc osteophyte complex and disc bulge at C3-4 and C4-5 (arrow). The T2-weighted MRI additionally demonstrated obliteration of the anterior and posterior subarachnoid space at the level of C3-C5, with associated patchy central cord signal abnormality (arrow).
Transverse Myelitis in Naloxone Reversible Acute Respiratory Failure—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B659Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine without contrast was obtained and revealed increased signal throughout the spinal cord from C-1 to the conus medullaris with mild expansion consistent with transverse myelitis.
Acute Flaccid Myelitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8MP9GAt the end of this oral board session, examinees will: 1) demonstrate the ability to obtain a complete pediatric medical history; 2) demonstrate an appropriate exam on a pediatric patient including a neurological exam; 3) investigate the broad differential diagnoses for neuromuscular weakness in a pediatric patient; 4) order the appropriate evaluation studies including an MRI; 5) interpret the use of a negative inspiratory force in determining the need for intubation and level of care upon admission; and 6) demonstrate effective communication with parents and caregivers.
An Unusual Case Report of a Toddler with Metastatic Neuroblastoma Mimicking Myasthenia Gravis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G35VWhile still in the ED, MRI with and without gadolinium contrast of the brain, orbits, and cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine were obtained to evaluate for possible CNS lesions including encephalitis, myelitis, or demyelination. Imaging, however, demonstrated multiple unexpected findings: a T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense and heterogeneously enhancing right adrenal mass measuring 2.7 x 2.1 x 3 cm (yellow asterisk) along with heterogenous enhancement at the clivus, C6, C7, T7, T8, T12, and L3 vertebral bodies (red asterisks). There were otherwise no significant intracranial signal or structural abnormalities and normal orbits.
Case Report of a Man with Right Eye Pain and Double Vision
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW7GABSTRACT: A 39-year-old previously healthy male presented with three days of right eye pressure and one day of binocular diplopia. He denied history of trauma, headache, or other neurological complaints. He had normal visual acuity, normal intraocular pressure, intact convergence, and no afferent pupillary defect. His neurologic examination was non-focal except for an inability to adduct the right eye past midline