Infectious Disease
A Patient with Generalized Weakness – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8593CThe CT of the abdomen and pelvis showed evidence of a large subcapsular rim-enhancing fluid collection with multiple gas and air-fluid levels along the right kidney measuring 8 x 4 cm axially and 11 cm craniocaudally (blue outline) with mass effect on the right renal parenchyma (yellow outline). Another suspected fluid collection adjacent to the upper pole of the right kidney measuring 4 x 3.4 cm was noted (red outline). Bilateral pyelonephritis was suggested without hydronephrosis or nephrolithiasis. The findings suggested complicated pyelonephritis with emphysematous abscess and hematoma formation.
Flipping Tickborne Illnesses with Infographics
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83H12After participation in this module, learners will be able to 1) list the causative agents for Lyme Disease, Babesiosis, Tularemia, Ehrlichiosis, Anaplasmosis, Tick Paralysis, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, and Powassan Virus, 2) identify different clinical features to distinguish the different presentations of tickborne illnesses, and 3) provide the appropriate treatments for each illness.
Case Report of Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus with Concurrent Parotitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R93NThe presence of soft tissue stranding about the parotid gland suggested an underlying inflammatory or infectious process of the parotid gland. Cellulitis was considered as a possible diagnosis as well, given the presence of soft tissue stranding in the dermis that is adjacent to the parotid gland. Fortunately, no enhancement was seen in local muscles, fascia, or bones to suggest a myositis, fasciitis, or osteomyelitis. By using the anatomy of the patient and understanding the changes that occur on CT when inflammation is present, the appropriate depth and location of infection can be made, allowing for appropriate treatment regimens.
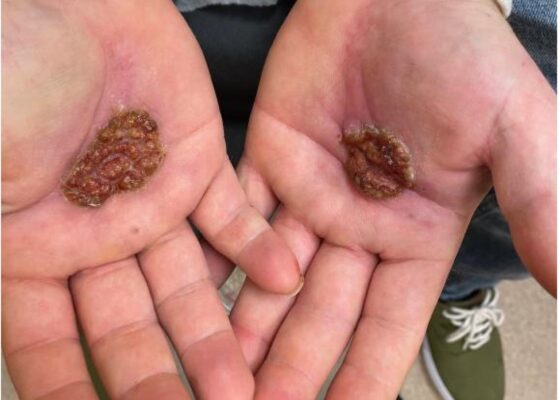
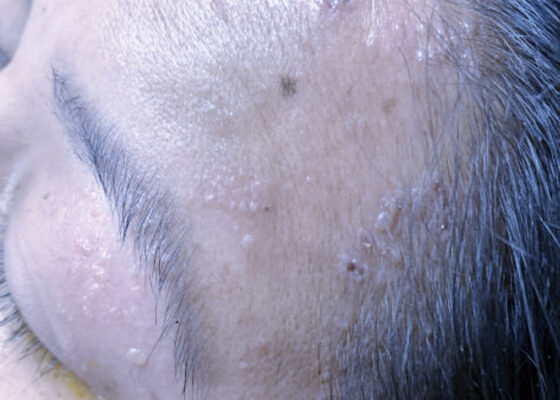
The Continued Rise of Syphilis: A Case Report to Aid in Identification of the Great Imitator
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R93NImages taken of the bilateral palmar skin lesions at our institution showed multi-centimeter, well-demarcated, friable, verrucous, crusted plaques with overlying fine yellow crust. Lesions such as these are suspicious for syphilitic gummas seen with cutaneous tertiary syphilis.
A Case of Community-Acquired Tuberculosis in an Infant Presenting with Pneumonia Refractory to Antibiotic Therapy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X07MChest radiographs during the initial presentation at seven weeks of life demonstrated right lower lobe (RLL) air space opacity on both PA and lateral views, compatible with pneumonia (referenced by yellow and green arrows, respectively). Repeat chest radiograph performed 12 days after the initial imaging revealed persistent right lower lobe opacity and right hilar fullness, seen as an opacified projection off of the mediastinal border as compared with the prior image, concerning for lymphadenopathy (designated by the aqua arrow). On the third presentation, computed tomography (CT) of the chest with intravenous contrast found persistent right lower lobe consolidation, innumerable 2-3 mm nodules, and surrounding ground glass opacities. This is best visualized as scattered areas of hyperdensity in the lung parenchyma. Axial images confirmed the presence of right hilar as well as subcarinal lymphadenopathy (indicated by white and pink arrows, respectively). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with IV contrast was performed which showed a punctate focus of enhancement in the left precentral sulcus compatible with a tuberculoma (denoted with red arrow).
A Case Report of Fournier’s Gangrene
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z356Physical exam revealed a comfortable-appearing male patient with tachycardia and a regular cardiac rhythm. The genitourinary exam indicated significant erythema and fluctuance of the bilateral lower buttocks with extension to the perineum. Black eschar and ecchymosis were also noted at the perineum. There was significant tenderness to palpation that extended beyond the borders of erythema. There was no palpable crepitus on initial examination. Physical exam was otherwise unremarkable.
Clinical and Radiologic Features of Fulminant Pediatric Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JW75The neurology service was consulted in the ED and multisequence MRI and MR angiography (MRA) of the brain were obtained without and with IV contrast. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and T2-weighted-Fluid-Attentuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) sequences showed multifocal small areas of diffusion signal abnormality in the brainstem and basal ganglia (red asterisks) suggestive of ischemia. Additional multifocal bilateral supra- and infratentorial foci of signal abnormality including subcortical white matter and deep grey matter were highly concerning for encephalitis or demyelinating disease. MRI was repeated on day 3 and day 7 during evolution of disease.
Meningococcal Meningitis with Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TH1KBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: (1) manage a patient with altered mental status (AMS) with fever while maintaining a broad differential diagnosis, (2) recognize the risk factors for meningococcal meningitis, (3) manage a patient with worsening shock and perform appropriate resuscitation, (4) develop a differential diagnosis for thrombocytopenia and elevated international normalized ratio (INR) in an altered febrile hypotensive patient with rash, (5) manage the bleeding complications from WFS, (6) discuss the complications of meningococcal meningitis including WFS, and (7) review when meningitis prophylaxis is given.