Infectious Disease
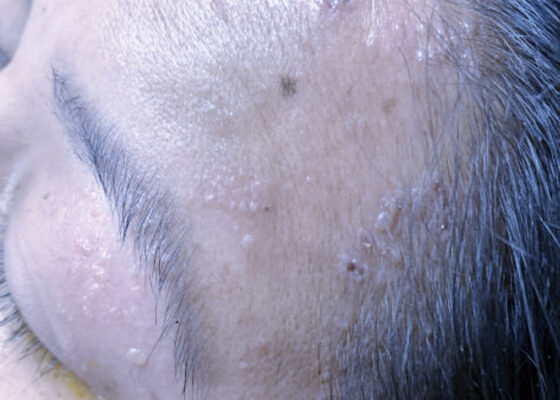
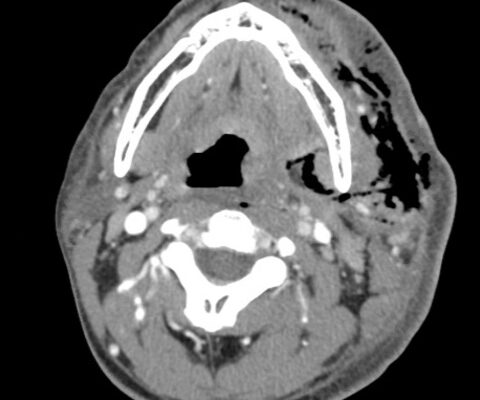
Case Report of Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus with Concurrent Parotitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R93NThe presence of soft tissue stranding about the parotid gland suggested an underlying inflammatory or infectious process of the parotid gland. Cellulitis was considered as a possible diagnosis as well, given the presence of soft tissue stranding in the dermis that is adjacent to the parotid gland. Fortunately, no enhancement was seen in local muscles, fascia, or bones to suggest a myositis, fasciitis, or osteomyelitis. By using the anatomy of the patient and understanding the changes that occur on CT when inflammation is present, the appropriate depth and location of infection can be made, allowing for appropriate treatment regimens.
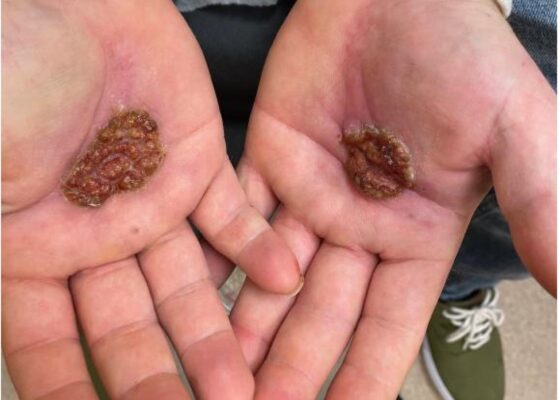
The Continued Rise of Syphilis: A Case Report to Aid in Identification of the Great Imitator
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R93NImages taken of the bilateral palmar skin lesions at our institution showed multi-centimeter, well-demarcated, friable, verrucous, crusted plaques with overlying fine yellow crust. Lesions such as these are suspicious for syphilitic gummas seen with cutaneous tertiary syphilis.
A Case of Community-Acquired Tuberculosis in an Infant Presenting with Pneumonia Refractory to Antibiotic Therapy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X07MChest radiographs during the initial presentation at seven weeks of life demonstrated right lower lobe (RLL) air space opacity on both PA and lateral views, compatible with pneumonia (referenced by yellow and green arrows, respectively). Repeat chest radiograph performed 12 days after the initial imaging revealed persistent right lower lobe opacity and right hilar fullness, seen as an opacified projection off of the mediastinal border as compared with the prior image, concerning for lymphadenopathy (designated by the aqua arrow). On the third presentation, computed tomography (CT) of the chest with intravenous contrast found persistent right lower lobe consolidation, innumerable 2-3 mm nodules, and surrounding ground glass opacities. This is best visualized as scattered areas of hyperdensity in the lung parenchyma. Axial images confirmed the presence of right hilar as well as subcarinal lymphadenopathy (indicated by white and pink arrows, respectively). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with IV contrast was performed which showed a punctate focus of enhancement in the left precentral sulcus compatible with a tuberculoma (denoted with red arrow).
A Case Report of Fournier’s Gangrene
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z356Physical exam revealed a comfortable-appearing male patient with tachycardia and a regular cardiac rhythm. The genitourinary exam indicated significant erythema and fluctuance of the bilateral lower buttocks with extension to the perineum. Black eschar and ecchymosis were also noted at the perineum. There was significant tenderness to palpation that extended beyond the borders of erythema. There was no palpable crepitus on initial examination. Physical exam was otherwise unremarkable.
Clinical and Radiologic Features of Fulminant Pediatric Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JW75The neurology service was consulted in the ED and multisequence MRI and MR angiography (MRA) of the brain were obtained without and with IV contrast. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and T2-weighted-Fluid-Attentuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) sequences showed multifocal small areas of diffusion signal abnormality in the brainstem and basal ganglia (red asterisks) suggestive of ischemia. Additional multifocal bilateral supra- and infratentorial foci of signal abnormality including subcortical white matter and deep grey matter were highly concerning for encephalitis or demyelinating disease. MRI was repeated on day 3 and day 7 during evolution of disease.
Meningococcal Meningitis with Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TH1KBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: (1) manage a patient with altered mental status (AMS) with fever while maintaining a broad differential diagnosis, (2) recognize the risk factors for meningococcal meningitis, (3) manage a patient with worsening shock and perform appropriate resuscitation, (4) develop a differential diagnosis for thrombocytopenia and elevated international normalized ratio (INR) in an altered febrile hypotensive patient with rash, (5) manage the bleeding complications from WFS, (6) discuss the complications of meningococcal meningitis including WFS, and (7) review when meningitis prophylaxis is given.
Using Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Expedite Diagnosis of Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85051A consultative scrotal ultrasound was performed, which was read as showing a small right hydrocele, small bilateral scrotal pearls, and normal-appearing testes. Although present, there was no mention of subcutaneous air suggestive of NF, seen in figure 1 as punctate hyperechoic foci (arrowhead) with ring-down artifact known as dirty shadowing (arrow). Also, subcutaneous thickening (asterisk) and free fluid (arrow) were seen as shown in figure 2, although their clinical relevance was not recognized in the radiologist's final report. Figure 3 shows an abdominal and pelvic CT that re-demonstrates subcutaneous air in the scrotum and lower abdomen (arrow) as well as fascial thickening of the perineum and free intra-abdominal air. After these images, the patient was transferred to our hospital for further management. Almost immediately after the patient's arrival, POCUS was employed. As seen in figures 4, we were able to identify in just a few minutes extensive subcutaneous air accompanied by dirty shadowing, as well as re-demonstration of subcutaneous thickening, fluid collections, and a right hydrocele. Even without the outside hospital's CT, the sonographic findings were highly suggestive for the diagnosis of NF of the perineum, also known as Fournier’s gangrene.
Auricular Perichondritis after a “High Ear Piercing:” A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WH16On physical examination, there was erythema, swelling, warmth, and general exquisite tenderness of the superior aspect of the left pinna (the outer ear) but excluding the ear canal, lobe, tragus, and crus. There was no facial involvement. There was no fluctuance about the ear and no drainage of fluid. The preauricular lymph nodes were enlarged and tender, but the anterior cervical lymph nodes were not tender. There was no mastoid tenderness, protrusion of the ear, or interruption of the postauricular crease.
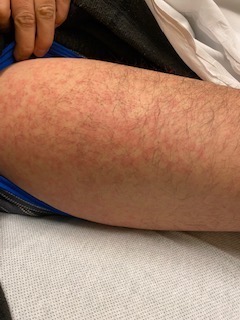
Case Report of COVID-19 Positive Male with Late-Onset Full Body Maculopapular Rash
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86W72The images demonstrate a diffuse, flat, maculopapular exanthema along the torso, bilateral upper and lower extremities, and neck without edema consistent with reported cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19. There are no surrounding bullae, vesicles, or draining. On palpation, there was blanching of the rash. Sensation to light touch was intact in all extremities. The findings were also apparent on the face with no mucosal involvement.
Necrotizing Fasciitis and Mediastinitis after Wisdom Tooth Extraction: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XW7KComputer tomography (CT) imaging of soft tissues of the neck and of the chest/abdomen/pelvis revealed extensive swelling and subcutaneous air (see red arrows) on the left side of the face and neck extending to the left shoulder, as well as parapharyngeal/retropharyngeal spaces and posterior/superior mediastinum.