X-Ray
Classic Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD16The pelvis X-ray demonstrates a widened right capital femoral epiphysis (more than 2 mm) that is typical of a slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).1 The yellow highlight outlines this area of widening.
The classic Klein’s line (orange lines) is often inaccurate and even difficult to draw with certainty.1 Nevertheless, in this X-ray, one has a sense that the right capital femoral epiphysis does not align with the femoral neck in the same way as it does on the left side, suggesting slippage.
Asymptomatic CT Iodinated Contrast Extravasation of the Upper Extremity
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VK87The two radiographs demonstrate extravasation of radiopaque iodinated contrast in the lower left upper extremity with most seen in the left antecubital fossa and left proximal forearm. Extravasation is seen in the subcutaneous and subfascial tissue.
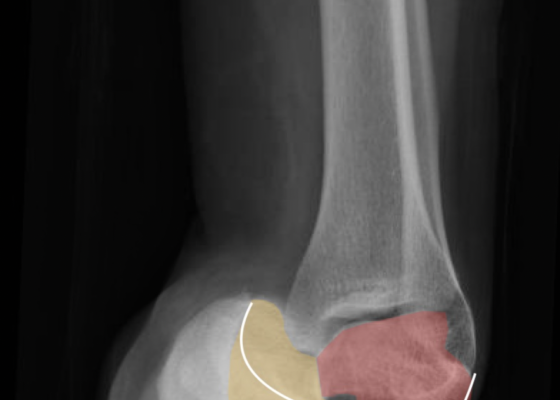
Open Fracture of the Patella
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BK9ZX-ray of the right knee showed evidence of an acute comminuted fracture of the patella (red arrows) with a suprapatellar joint effusion with gas (blue arrow). There was no evidence of joint dislocation or other osseous lesions.
Gastric Volvulus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8335FPoint of care ultrasound of his abdomen showed a large fluid filled structure with well-defined borders containing gastric contents extending from the xiphoid process to the umbilical region. No free fluid was noted on focus assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination. A computed tomography (CT) scan was performed emergently and it was noted that the patient had a significantly distended stomach and gastric volvulus (blue arrows) noted in the area of his paraesophageal/hiatal hernia.
Diagnosis and Treatment of an Anterior Shoulder Dislocation with Bedside Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z924Bedside ultrasound with the transducer placed on the posterior right shoulder revealed an anterior dislocation of the right humerus. This is evident by displacement of the humeral head further away from the posteriorly placed ultrasound transducer, and appears deep to the glenoid cavity. In a posterior shoulder dislocation, the humeral head would appear closer to the transducer (and the near field of the ultrasound image) than the glenoid. Note that a hypoechoic, heterogeneous fluid collection is within the joint space, compatible with a hematoma. A right shoulder X-ray confirmed the anterior dislocation with no evidence of fracture. Under direct ultrasound guidance the glenohumeral joint space was injected with 10 mL of 2% lidocaine as an intraarticular anesthetic block. The right shoulder was reduced using continual traction. Post-reduction ultrasound demonstrated a successful shoulder reduction, depicted by the humeral head being relocated to its anatomical location, adjacent to the glenoid cavity, as noted on the ultrasound image. A hematoma remains present within the joint space. Successful shoulder reduction was further confirmed by X-ray. The patient’s arm was placed in a sling and she was discharged home with orthopedics follow-up.
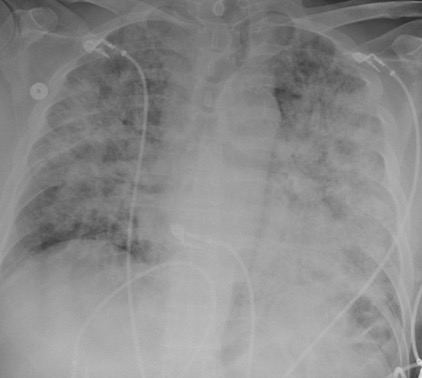
Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) Pneumonia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RW6NChest X-ray showed diffuse, patchy interstitial and alveolar infiltrates bilaterally concerning for Pneumocystis jirovecii(previously Pneumocystis carinii) pneumonia (PJP). The AP radiograph (top left figure) showed the classic “bat-wing” distribution on the left side. Repeat radiograph (bottom figure) one day after admission showed worsening of the infiltrates.
Bilateral Shoulder Dislocation after Ski Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86929An anteroposterior chest X-ray demonstrates bilateral shoulder dislocations. Both the right and left humeral heads (blue lines) are displaced medially, anteriorly, and inferiorly from their normal positions in the glenoid fossae (red lines), thus signifying bilateral anterior dislocations. There is also a fracture of the left humeral head at the greater tubercle (green arrow).
Talonavicular Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PG91The X-rays were significant for a subtalar dislocation. The calcaneus (red) is laterally displaced with respect to the talar head (orange), and the white lines indicate the normal articular surface. Additionally, there was a talonavicular dislocation, as seen in the fourth image: the talus (green) and navicular bone (purple) overlapping suggests a dislocation. In a normally aligned foot, the boundaries of the two bones create a point of articulation.