X-Ray
A Case Report of Lateral Subtalar Dislocation: Emergency Medicine Assessment, Management and Disposition
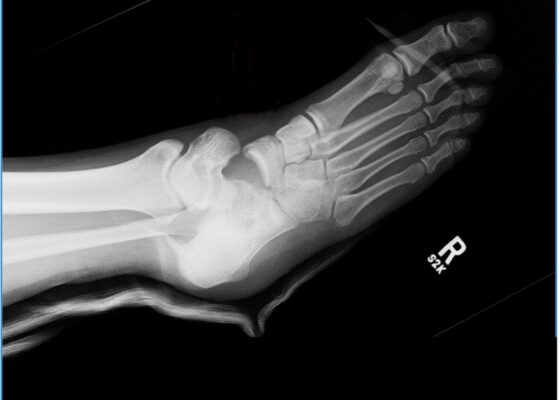
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SS8PIn a lateral subtalar dislocation, the navicular bone (red bone in 3D anatomy image) and the calcaneus (yellow bone in 3D anatomy image) dislocate laterally in relation to the talus (lavender bone in 3D anatomy image). Plain film oblique and lateral X-rays demonstrate the initial dislocation (talus in red, navicular in blue). It is clear in the initial lateral view that there is loss of the talar/navicular articulation (noted by red arrow). The anterior-posterior x-ray is more challenging to discern the anatomy; however, the talus (red dot) is laterally displaced in comparison to the navicular (blue dot).
A Case Report of Acute Compartment Syndrome
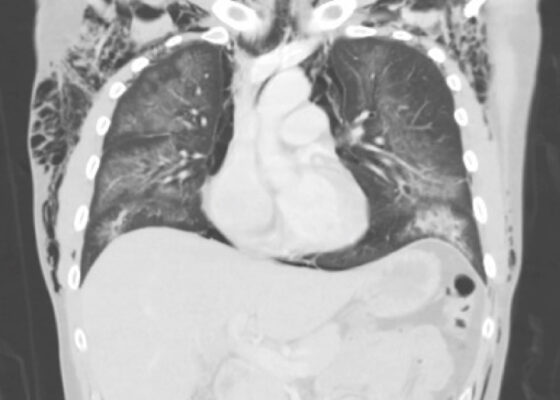
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87061Inspection of the extremity revealed significant swelling with dark discoloration and multiple bullae (pre-operative photograph). Furthermore, notable swelling of the right foot was noted, which felt cold to palpation. Radiographs of pelvis, bilateral knees, tibia, fibula, and feet demonstrated no fractures or dislocations. The bilateral tibia and fibula X-ray revealed soft tissue swelling in the proximal legs, particularly evident in the right leg's AP view, which also showed numerous ovoid radiodensities in the anterior compartment, likely related to soft tissue injury. Post operative images are also provided demonstrating the patients’ four compartment fasciotomies which were loosely closed using staples.
Case Report of a Child with Colocolic Intussusception with a Primary Lead Point
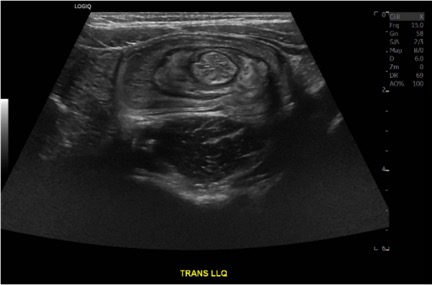
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8564QOn the initial ED visit, an abdominal ultrasound (US) was ordered which showed the classic intussusception finding of a target sign (yellow arrow), or concentric rings of telescoped bowel, on the transverse view of the left lower quadrant (LLQ).
A Case of Community-Acquired Tuberculosis in an Infant Presenting with Pneumonia Refractory to Antibiotic Therapy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X07MChest radiographs during the initial presentation at seven weeks of life demonstrated right lower lobe (RLL) air space opacity on both PA and lateral views, compatible with pneumonia (referenced by yellow and green arrows, respectively). Repeat chest radiograph performed 12 days after the initial imaging revealed persistent right lower lobe opacity and right hilar fullness, seen as an opacified projection off of the mediastinal border as compared with the prior image, concerning for lymphadenopathy (designated by the aqua arrow). On the third presentation, computed tomography (CT) of the chest with intravenous contrast found persistent right lower lobe consolidation, innumerable 2-3 mm nodules, and surrounding ground glass opacities. This is best visualized as scattered areas of hyperdensity in the lung parenchyma. Axial images confirmed the presence of right hilar as well as subcarinal lymphadenopathy (indicated by white and pink arrows, respectively). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with IV contrast was performed which showed a punctate focus of enhancement in the left precentral sulcus compatible with a tuberculoma (denoted with red arrow).
Electronic Cigarette or Vaping-Associated Lung Injury Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S65PThe CT of the chest with contrast showed subcutaneous emphysema (green star), pneumomediastinum (yellow arrow), and pneumopericardium (purple asterix) without an identifiable tracheal tear. Extensive air was visualized as hypodense areas within the chest wall within the soft tissue. The image also detailed a hypodense area surrounding the heart consistent with pneumopericardium. No disruption of the trachea was present. Additionally, the CT of the chest also showed bilateral ground glass airspace opacities (red stars) with subpleural sparing that is consistent with EVALI findings.2,5 These specific findings have been seen in many of the EVALI cases.5 This image is interesting because there is extensive pneumomediastinum with no clearly identifiable cause. The imaging shows no esophageal or tracheal or lung injury, so it is important to note relevant information collected during interview regarding patient’s recent history of vaping THC, especially when establishing a differential diagnosis.
Case Report of a Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture
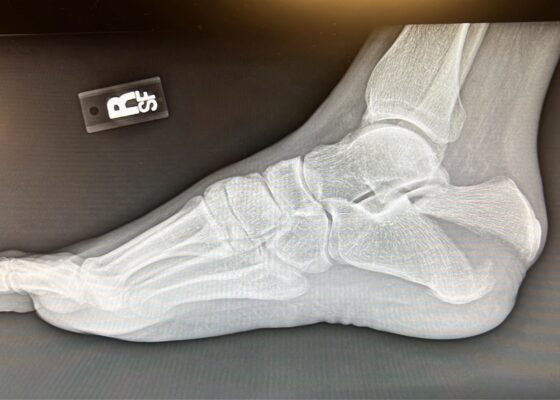
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NH11Examination of the right ankle demonstrated a large deformity of the superior talus with bruising and blanching of the overlying skin in the area of the Achilles tendon (see images 2,3). The remaining bones of the foot were not tender to palpation and the foot was neurovascularly intact throughout with only mild numbness in the area of the tented skin. Completing the trauma exam, the patient had no signs of head injury and no midline spinal tenderness to palpation. Inspection of the remaining long bones and joints showed no other injuries. There were mild skin scrapes on the right flank from the fall. X-rays of the right foot and ankle showed a longitudinal fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity from the articular surface to the posterior surface (see red outline) with extension into the subtalar joint (blue lines) and roughly 1.8 cm displacement between the fracture segments (yellow double arrow). These findings represented a tongue-type calcaneal bone fracture.
High-Pressure Injection Injury to the Hand – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D64WPlain radiographs of the left hand and forearm demonstrated extensive subcutaneous emphysema. The air can be seen as lucent striations tracking along the second and third fingers as well as along the dorsum of the hand and wrist. There is also diffuse soft tissue emphysema surrounding the metacarpophalangeal joints. Lab analysis did not show any significant acute abnormalities.
A Case Report of the Rapid Evaluation of a High-Pressure Injection Injury of a Finger Leading to Positive Outcomes
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TD2XOn exam the patient was noted to have a punctate wound to the ulnar aspect of his right index finger, just proximal to the distal interphalangeal joint. The finger appeared pale and taut, with absent capillary refill. The patient displayed diminished range of motion with both extension and flexion of the joints of the finger. Sensation was absent and no doppler flow was appreciated to the distal aspects of the finger. X-ray of the hand was obtained and showed many small foreign bodies in the soft tissue and extensive radiolucent material consistent with gas or oil-based material to the palmar aspect of the index finger tracking up to the level of the metacarpal heads.
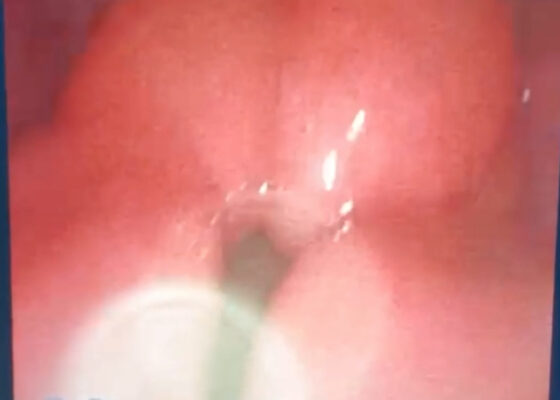
A Case Report of Epiglottitis in an Adult Patient
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QM09At the time of presentation to the ED, laboratory results were significant for leukocytosis to 11.8 x 109 white blood cells/L and a partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 52 mmHg on venous blood gas. Computed tomography (CT) of the soft tissue of the neck with contrast showed edematous swelling of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic fold with internal foci of gas (blue arrow) and partial effacement of the laryngopharyngeal airway and scattered cervical lymph nodes bilaterally (Figure 1). Findings were consistent with epiglottitis containing nonspecific air. Additionally, the pathognomonic “thumbprint sign” (yellow arrow) was found on lateral x-ray of the neck (Figure 2). The CT findings as shown in figure 3 illustrate lateral view of the swelling of the epiglottis, gas, and blockage of the airway.
A Case Report of a Large Goiter Resulting in Tracheal Deviation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80645In the image, one can see significant tracheal deviation around the right side of the mass (black arrows). This degree of deviation would make ventilation in a paralyzed patient extremely difficult, if not impossible.