Pediatric Foreign Body Aspiration
History of present illness:
A 10-month-old male presented after choking on a carrot. Mom reported coughing with perioral cyanosis. On examination, the child had no retractions, but wheezing was heard in the right lung fields particularly when coughing.
Significant findings:
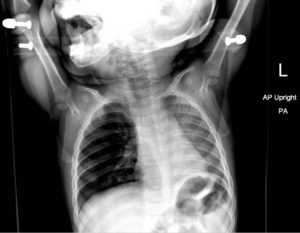
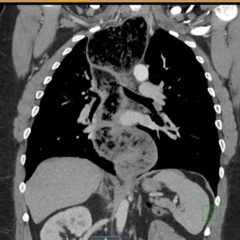
Chest radiograph showed increased radiolucency (red arrow) and flattening of the diaphragm on the right side (blue arrow) consistent with hyperinflation of the right lung, as well as left mediastinal shift (green arrow), indicating obstruction.
Discussion:
Foreign body aspiration is a common condition in pediatrics and can be life- threatening. It happens most commonly in children younger than 2 years due to a natural curiosity for putting objects in their mouth and an immature swallowing mechanism.1 Most foreign bodies are located in the right main bronchus due to its wider diameter and more direct extension of the trachea.2 Witnessed choking has the highest sensitivity and specificity for this pathology (sensitivity 75.4% and specificity 92.1%).3 These children will often present with coughing, wheezing, and/or decreased lung sounds that suggest an aspiration.4
Chest radiographs are excellent in detecting radiopaque objects. However, most aspirations are from radiolucent organic matters such as nuts or seeds.3 Radiographs that show focal area of hyperinflation, mediastinal shift, and atelectasis are highly specific for aspiration. Pathological findings on chest radiography showed an 86.1% sensitivity and 63.2% specificity.3 However, it is possible that these finding may not be seen on initial imaging.
It is important to keep a high index of suspicion as undiagnosed foreign body aspiration can lead to chronic pulmonary infections, bronchiectasis, pneumothorax, asphyxia, and death.3 This child had both physical and radiographic findings of a foreign body aspiration in addition to a witnessed choking episode. He was taken to the operation room by the pediatric surgery team for bronchoscopy and a piece of carrot was removed from the right mainstem bronchus.
Topics:
Foreign body aspiration, pediatric foreign body, pediatric pulmonology, respiratory.
References:
- Shlizerman L, Mazzawi S, Rakover Y, Ashkenazi D. Foreign body aspiration in children: the effects of delayed diagnosis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2010;31(5):320-324. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2009.03.007
- Cevik M, Gokdemir MT, Boleken ME, Sogut O, Kurkcuoglu C. The characteristics and outcomes of foreign body ingestion and aspiration in children due to lodged foreign body in the aerodigestive tract. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29(1):53-57. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e31827b5374
- Heyer CM, Bollmeier ME, Rossler L, et al. Evaluation of clinical, radiologic, and laboratory prebronchoscopy findings in children with suspected foreign body aspiration. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41(11):1882-1888. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.03.050
- Mortellaro VE, Iqbal C, Fu R, Curtis H, Fike FB, St Peter SD. Predictors of radiolucent foreign body aspiration. JPediatr Surg. 2013;48(9):1867-1870. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.03.050