Issue 7:3
Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room for POCUS Pulmonary: Scan Your Way Out
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RM0MBy the end of performing the Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room, learners will be able to: 1) recognize sonographic signs of A-line, B-line, Barcode sign, Bat sign, Seashore Sign, Plankton sign, Jellyfish Sign, Lung point, lung lockets, and Lung pulse; 2) differentiate sonographic findings of pneumothorax, hemothorax, pneumonia, COVID 19 pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and pleural effusion from normal lung findings; 3) distinguish pneumonia from atelectasis by recognizing dynamic air bronchogram; and 4) recognize indications for performing POCUS pulmonary such as dyspnea, blunt trauma, fall, cough and/or heart failure.
High-Efficiency Ultrasound-Guided Regional Nerve Block Workshop for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84P8RThe objective of this workshop is to provide emergency medicine residents the confidence and skill sets needed to effectively perform five commonly used UGRNBs for conditions encountered in the emergency department. Through this one-day, accelerated workshop, residents will be given an opportunity to sharpen their UGRNB technique prior to applying them in the clinical environment. By the end of this workshop, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the clinical situations in which UGRNBs can be utilized and understand the associated risks, 2) list the commonly used local anesthetic medications and their proper dosing in respect to regional nerve blocks, 3) demonstrate proper ultrasound probe positioning and identify relevant anatomical landmarks for each nerve block on both standardized patients and cadavers, 4) describe the common steps involved to perform each nerve block, 5) perform the five UGRNB techniques outlined in this workshop.
Cyanide Poisoning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80W76After the completion of this simulation, participants will have learned how to: 1) identify clues of smoke inhalation based on a physical examination; 2) identify smoke inhalation-induced airway compromise and perform definitive management; 3) create a differential diagnosis for victims of fire cyanide poisoning, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide; 4) appropriately treat cyanide poisoning; 5) demonstrate the importance of preemptively treating for cyanide poisoning; 6) perform an initial physical examination and identify physical marks suggesting the patient is a fire and smoke inhalation victim; and 7) familiarize themselves with the Cyanokit and treatment with hydroxocobalamin.
Aortic Dissection Presenting as a STEMI
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W647At the conclusion of the simulation session or during the debriefing session, learners will be able to: 1) Verbalize the anatomical differences and management of Stanford type A and type B aortic dissections, 2) Describe physical exam findings that may be found with ascending aortic dissections, 3) Describe the various clinical manifestations of the propagation of aortic dissections, 4) Discuss the management of aortic dissection, including treatment and disposition.
Morphine Equianalgesic Dose Chart in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RD29By the end of this session, the learner will be able to: 1) define the term, “morphine milligram equivalents;” 2) describe the relative onset and duration of action of different pain medications often used in the emergency department; and 3) convert one opioid dose to another.
Residents Are Coming: A Faculty Development Curriculum to Prepare a Community Site For New Learners
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87D2NOur goal is to prepare community-based EM attendings to be outstanding educators to future residents by augmenting their knowledge of current educational practice and adult learning theory, literature review, and biostatistics.
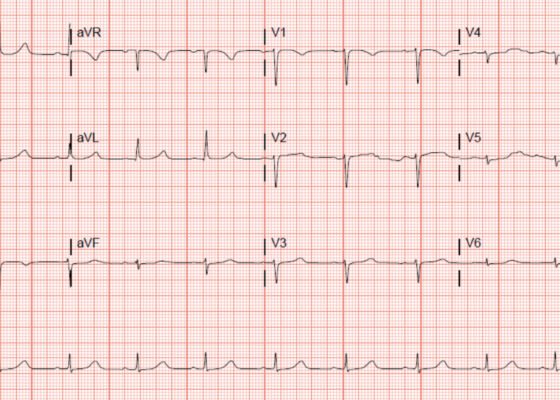
‘Cath’ It Before It’s Too Late: A Case Report of ECG Abnormalities Indicative of Acute Pathology Requiring Immediate Catheterization
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HW7VA 12 lead ECG performed at the time of emergency department (ED) admission revealed regular sinus rhythm with noted T-wave inversion (blue arrows on Figure 1) in Lead aVL new when compared to an ECG performed a few months prior (see Figure 3). Two days later a second ECG was done when the patient developed acute chest pain while in the ICU (Figure 2) that showed persistent inversion in Lead aVL (blue arrows) as well as new J point deviation (JPD) in Leads II, aVF, V5 and V6; and new JPD in Leads V1 and V2 (green arrows) from her previous ECG while in the emergency department. These focal repolarization abnormalities did not qualify as an ST-elevation myocardial infarction by current guidelines.
1›
Page 1 of 2