Issue 3:2
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85S7QLeft-sided cranial nerve VII palsy with flattened forehead creases, inability to keep the left eye open, and drooping of the corner of mouth. Vesicular lesions were found in and posterior to the left ear in a unilateral, dermatomal distribution.
Retinal Detachment
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8204QBedside ocular ultrasound revealed a serpentine, hyperechoic membrane that appeared tethered to the optic disc posteriorly with hyperechoic material underneath. These findings are consistent with retinal detachment (RD) and associated retinal hemorrhage.
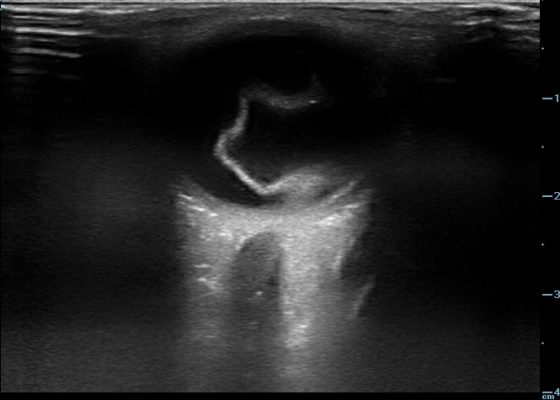
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X92TComputed tomography (CT) of the abdominal and pelvis with intravenous (IV) contrast revealed inflammatory changes, including gas and fluid collections within the ventral abdominal wall extending to the vulva, consistent with a necrotizing soft tissue infection.
Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum: Hamman Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NS72The initial CT scans showed extraluminal gas surrounding the distal esophagus as it traversed the posterior mediastinum, concerning for possible distal esophageal perforation that prompted surgery and GI consultations. There was no evidence of a drainable collection or significant fat stranding. The image also showed an intraluminal stent traversing the gastric antrum and gastric pylorus with no indication of obstruction. Circumferential mural thickening of the gastric antrum and body were consistent with the patient’s history of gastric adenocarcinoma. The shotty perigastric lymph nodes with associated fat stranding, along the greater curvature of the distal gastric body suggested local regional nodal metastases and possible peritoneal carcinomatosis.
The thoracic CT scans showed extensive pneumomediastinum that tracked into the soft tissues of the neck, which given the history of vomiting also raised concern for esophageal perforation. There was still no evidence of mediastinal abscess or fat stranding. Additionally, a left subclavian vein port catheter, which terminates with tip at the cavoatrial junction of the superior vena cava can also be seen on the image.
Intussusception
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SH0WA segment of bowel within the right abdomen that measured approximately 1.6 x 1.5 cm transaxially. It demonstrated a hypoechoic edematous outer loop of bowel (blue arrow) and hyperechoic compressed loop of bowel telescoping within (red star), this is known as the "target sign."
Lateral Epicondyle Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J05FRadiographs of the right elbow revealed an acute fracture through the lateral epicondyle with dislocation of the radial head inferiorly. Radiographs of the left elbow revealed a slightly angulated fracture through the lateral epicondyle.
Propafenone Overdose-induced Arrhythmia and Subsequent Correction After Administration of Sodium Bicarbonate
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D925The first ECG in this case showed sinus tachycardia with a widened QRS (black arrow), a rightward axis, prolonged corrected QT interval (QTc), and terminal R wave in AVR (white arrow). There are several potential causes for these ECG findings, but put together with the patient’s history, we were suspicious of sodium channel blockers being the most likely cause. The second ECG, after sodium bicarbonate was administered, demonstrated a normal QRS (black arrow) and no rightward axis deviation, reduction of the QTC and resolution of the terminal R wave (white arrow). We later learned that the patient’s cardiologist recently increased her propafenone dose.
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88H07Physical exam was significant for an erythematous maculopapular rash in the right ophthalmic nerve (V1) region, a crusted vesicle at the right upper eyelid, and surrounding eyelid edema. Visual acuity remained at baseline and intraocular pressure was within normal limits. External slit lamp exam with fluorescein staining was remarkable for pseudodendrites in the inferior-temporal cornea approximately 1.5 mm from the limbus. Ophthalmology was consulted and completed an in-depth evaluation of the corneal lesions. They found no evidence of anterior chamber reaction and performed a complete dilated fundus examination which demonstrated no retinal involvement. The patient was then discharged on acyclovir and erythromycin ointment with close follow-up.