Issue 3:1
An OSCE Evaluation Tool for the Assessment of Emergency Medicine Resident Progression Performance of ACGME Patient Case and Interpersonal Communication Milestones
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J63ROur goal was to create a standardized OSCE based formative assessment tool that could be deployed with minimal resource utilization. The purpose of our tool is to provide data regarding Emergency Medicine Residents’ performance in ACGME patient care milestones as they progress longitudinally through their residency.
A Model Curriculum for an Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Rotation for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DD0FThe aim of this curriculum is to provide a robust learning experience for EM residents around prehospital care and EMS that fulfills the ACGME requirements and which can be easily replicated and implemented in a variety of EM residency training programs.
Hosting an eConference: Interactive video conference grand rounds between two institutions
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88P80Our objectives were to create and implement a novel virtual conference format through the integration of social media tools which allows for interdisciplinary and multi-site participation to enhance EM resident education. We wish to outline the steps required to reproduce this innovative session and share lessons learned.
A Brief Didactic Intervention to Improve Multiple-Choice Item-Writing Quality
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81633The primary objective of this training module is to provide emergency medicine residents and faculty the basic knowledge necessary to write high quality structured single-best answer examination items through a brief, independent study format.
Utilizing the Flipped Classroom, Simulation-Based Mastery Learning and Group Learning to Teach and Evaluate Lumbar Puncture Skills
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RW58The goal of the curriculum is to teach and evaluate senior medical students / emergency medicine residents on the performance of a lumbar puncture using a group learning protocol. At the completion of the training session, learners should be able to: 1) Demonstrate how to perform a LP on an adult patient by achieving the minimum passing standard on the checklist, 2) state the indications and contraindications of performing a LP, and 3) state the potential complications that can occur after performing a LP.
The Toxiscape Hunt: An Escape Room-Scavenger Hunt for Toxicology Education
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW58By the end of the activity, learners should be able to: 1) Calculate an anion and osmolal gap. 2) Recognize poisonings amenable to hemodialysis. 3) Interpret EKG changes related to a variety of ingestions, including beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers, digitalis, and tricyclic antidepressants. 4) Recognize poisonous plants and their clinical toxidromes. 5) Calculate loading dose of N-acetylcysteine as antidote for acute acetaminophen ingestion. 6) Collaborate as a team to arrive at solutions of problems. 7) Recognize poisons that have available antidotes 8) Know the clinical effect of various types of snake envenomations. 9) Recognize the toxicity associated with at least four household chemicals. 10) Know the antidotes for six common poisonings.
Severe Sepsis Manifesting as A-Fib with Rapid Ventricular Rate
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WG9WBy the end of this simulation session, the learner will be able to: 1) Recognize severe sepsis (please note – Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Sepsis-I and II definitions are used throughout the case, as Sepsis-III has not been adopted by any emergency medicine organizations), 2) recognize atrial fibrillation, 3) review the importance of a thorough history and physical exam, 4) discuss the sepsis spectrum, 5) discuss the acute management of severe sepsis, 6) discuss common and uncommon sources of sepsis, 7) discuss appropriate empiric antibiotic options, 8) discuss common causes of newly-diagnosed atrial fibrillation, 9) review the different emergency medicine-based treatment modalities for uncomplicated atrial fibrillation, specifically atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular rate.
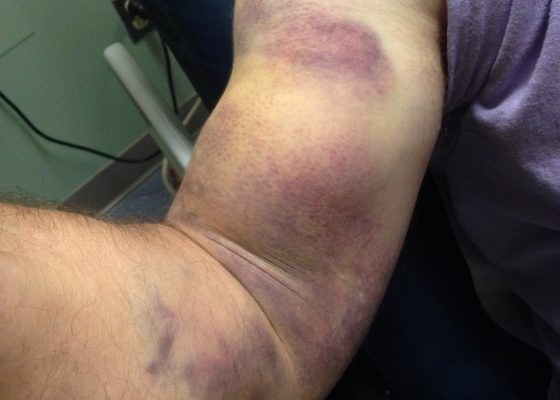
Biceps Tendon Rupture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RP8BPhysical exam was significant for ecchymosis and mild swelling of the right bicep. When the right arm was flexed at the elbow, a prominent mass was visible and palpable over the right bicep. Right upper extremity strength was 4/5 with flexion at the elbow.