Infectious Disease
A Case Report of an Atypical Presentation of Fournier’s Gangrene
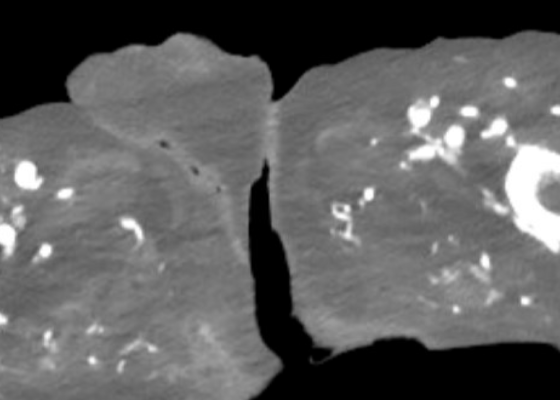
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/M5.52203A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis was significant for scrotal fluid and punctate gas locules (red arrow) without discrete evidence of invasion into the adjacent soft tissues, suspicious for Fournier’s gangrene. There was also fluid collection centered around the seminal vesicles suggestive of an abscess.
Open Chest Wound with Sternal Fracture in the Emergency Department, a Case Report
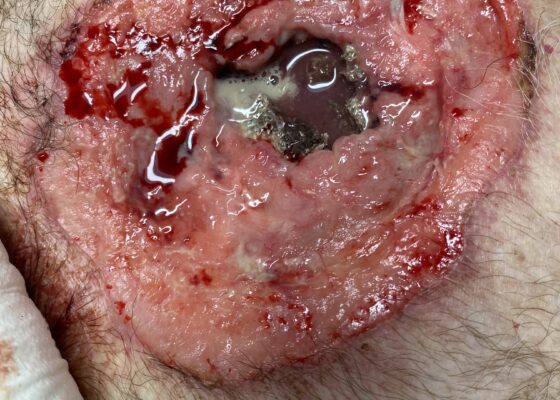
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/M5.52202The image demonstrates the large chronic-appearing wound of the patient’s anterior chest as well as the visible fractured segments of the patient’s exposed sternum. The sternum is necrotic appearing concerning for a chronic process including osteomyelitis and malignancy. Purulent drainage is visible on the wound consistent with an infectious process.
A Low-Cost Task Trainer Constructed from Silicone Nipple Covers
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52244Educational Objectives: By the end of this training session, learners will be able to anesthetize an abscess, perform incision and drainage, develop manual dexterity maneuvering instruments to break up the abscess, and place packing using both the linear incision and loop techniques.
Pizza and Paintballs: A Cost-Effective Model for Incision and Drainage Simulation Training
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52047Upon completing this lab session, the participant should have the capability to: 1) describe the indications, contraindications, and reasons for performing I&D of an abscess, 2) select the necessary equipment for performing I&D of an abscess, 3) demonstrate the necessary steps for performing
an I&D procedure on a simulated abscess.
A Case Report of Calciphylaxis
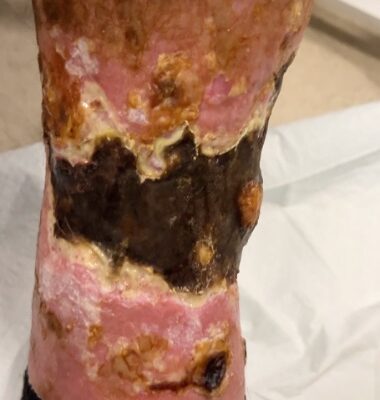
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW8VOn arrival for this visit, the patient was nontoxic appearing with stable vital signs. The physical exam was notable for deep, ulcerated, bilateral anterior leg wounds with purulent drainage and large areas of eschar (see photographs).