Issue 3:2
The Use of a Social Media Based Curriculum for Newly Matched Interns Transitioning into Emergency Medicine Residency
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8F92GThis curriculum is designed to bridge this gap by fostering an environment in which incoming interns can communicate, collaborate, and practice clinical reasoning with each other and faculty prior to their arrival in residency. The goals and objectives were tailored to the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) level 1 milestones in patient care. 1) Interpret basic ECGs; 2) Demonstrate ability to interpret basic radiographs; 3) Identify common visual diagnoses; 4) Identify common neurological emergencies on head imaging; 5) Recognize basic airway anatomy; 6) Demonstrate successful application of FOAMed resources to clinical cases; 7) Interpret common ultrasound images; 8) Describe common ED procedures; 9) Demonstrate fundamental knowledge of evidence-based medicine and biostatistics
High Fidelity In Situ Shoulder Dystocia Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88305DAt the end of this simulation, learners will: 1) Recognize impending delivery and mobilize appropriate resources (ie, both obstetrics [OB] and NICU/pediatrics); 2) Identify risk factors for shoulder dystocia based on history and physical; 3) Recognize shoulder dystocia during delivery; 4) Demonstrate maneuvers to relieve shoulder dystocia; 5) Communicate with team members and nursing staff during resuscitation of a critically ill patient.
Fainting Spells
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z91RABSTRACT: Audience: The target audience for this simulation is 4th year medical students, emergency medicine residents, pediatric residents, and family medicine residents. Introduction: Brugada syndrome is defined as the combination of specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes and clinical manifestations of a ventricular arrhythmia, including syncope and sudden cardiac arrest.1 Brugada syndrome is caused by a mutation in the phase-0 cardiac sodium channel. This
Guillain-Barrè
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TH06At the conclusion of the simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) Recognize the clinical signs and symptoms associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome, including muscle weakness and hyporeflexia. 2) Identify abnormal vital signs secondary to dysautonomia. 3) Discuss evaluation for impending respiratory failure, including bedside pulmonary function testing. 4) Discuss the management of Guillain-Barré, including management of dysautonomia and respiratory failure, as well as definitive management with plasmapheresis versus intravenous immunoglobulin. 5) Appropriately disposition the patient to the intensive care unit. 6) Effectively communicate with team members and nursing staff during resuscitation of a critically ill patient
Sepsis Secondary to an Abdominal Wound Infection
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PS60At completion of this case learners should be able to: 1) Recognize and differentiate between systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. 2) Prepare an appropriate differential diagnosis for a patient with sepsis. 3) Demonstrate appropriate fluid resuscitation and antibiotic therapy for a septic patient. 4) Demonstrate appropriate vasopressor therapy for a septic patient. 5) Understand and apply the Surviving Sepsis Guidelines.
Chest Pain with Acute Coronary Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8K04CAt the end of this case learners should be able to prepare a differential for patients with chest pain, provide appropriate medications for a patient with chest pain, recognize an ST segment elevation MI, and appropriately disposition a patient with acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
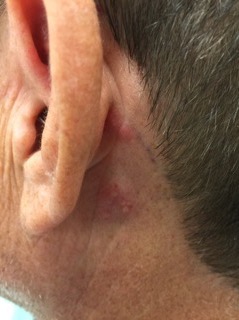
An Unusual Case of Pharyngitis: Herpes Zoster of Cranial Nerves 9, 10, C2, C3 Mimicking a Tumor
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B05KOn exam, the patient was sitting upright while holding an emesis basin filled with saliva. His voice was noticeably hoarse. Examination of the head and neck revealed vesicular eruptions on the left scalp in the V1 dermatome and on the left mastoid process (Images 1 and 2). Physical exam also shows vesicular eruptions on the left posterior oropharynx that did not cross midline (Image 3).