Issue 2:3
Choledocholithiasis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q62XComputed tomography (CT) was significant for two large gallstones measuring 1.1 centimeters impacted at the level of the pancreatic head with associated common bile duct (CBD) dilatation.
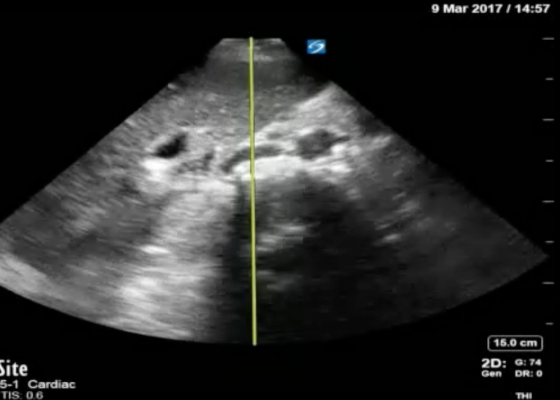
Using Bedside Ultrasound to Rapidly Differentiate Shock
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S047A RUSH exam demonstrated hyperdynamic cardiac contractility and collapse of the inferior vena cava (IVC) with probe compression more than 50% suggesting hypovolemia likely secondary to sepsis. Incidentally, Morrison’s pouch revealed a large right renal cyst but no signs of free fluid. A computed tomography of abdomen/pelvis showed a 10.8 x 9.5 cm right renal cyst and left lower lobe pneumonia.
Corneal Sparing Conjunctival Abrasion
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KG93Physical exam was significant for multiple broken teeth, multiple minor abrasions on the face, and fine shards of shattered glass on his face and hair. His right eye had conjunctival injection, with no signs of subconjunctival hemorrhage or ocular penetration. Vision, extraocular movement, and pupillary exam were grossly intact. Fluorescein staining with slit lamp exam with cobalt blue filter examination of the right eye revealed superficial bulbar conjunctival uptake of fluorescein dye staining an area of the conjunctiva inferior to the limbus 5 mm vertical by 2 mm horizontal (estimation by photo provided). No foreign bodies were visualized in the inferior fornix. These findings were consistent with superficial conjunctival abrasion. The exam noted sparing of the corneal epithelium.
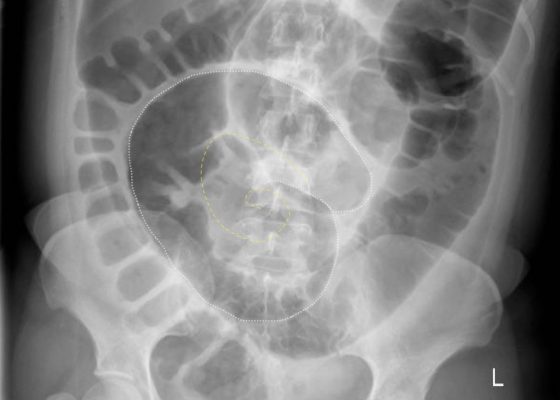
Volvulus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JH0QUpright and supine frontal radiographs of the abdomen demonstrate gas dilation of the large bowel from the level of the cecum to the sigmoid colon with air fluid levels (yellow arrows). There is a swirled configuration of the distal descending to sigmoid colon indicating the level of the volvulus (dashed yellow line) and giving rise to the classic “coffee bean” sign (dotted white tracing). Note the elevated left hemidiaphragm on the upright view reflecting abdominal distention with increased intra-abdominal pressure (red arrow).
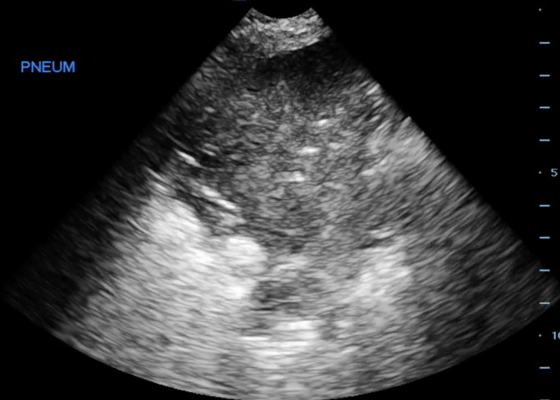
Pneumonia Diagnosed by Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XP64Point-of-care ultrasound of the left lower lobe demonstrates lung hepatization, a classic finding for pneumonia. In addition, a shred sign is present with both air bronchograms and focal B-lines—all suggestive of poorly aerated, consolidated lung. The patient was started on antibiotics and admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia.
Re-expansion Pulmonary Edema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WS6VInitial chest X-ray (chest X-ray 1) showed a right-sided pleural effusion with compressive atelectasis of the mid to lower right lung. Repeat chest X-ray immediately after evacuation (chest X-ray 2) shows improvement of the pleural effusion and a new trace apical right pneumothorax measuring 6.7 mm. When the patient became tachypneic, a third X-ray (chest X-ray 3) showed persistent trace apical right pneumothorax measuring 6.7 mm.
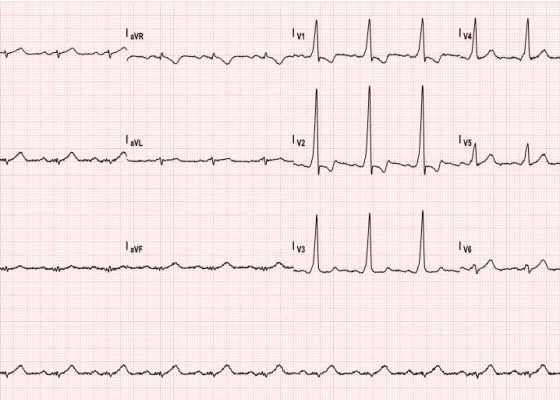
Asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome: Incidental EKG
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T05XThe ECG shows slurred up-stroking of the QRS complexes characteristic of a delta wave. The PR interval is normal; however, the QT interval is greater than 110ms.
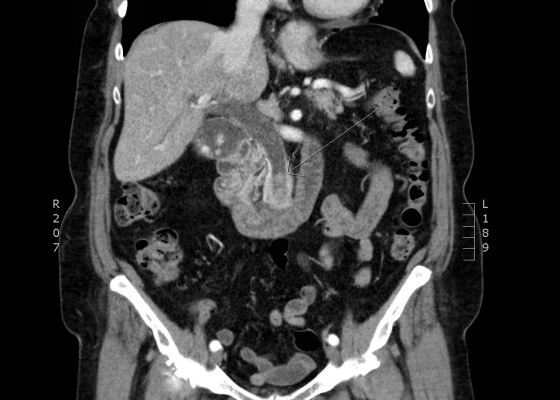
Renal Infarction from Type B Aortic Dissection
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HG9GInitial abdominal images demonstrated a dissection flap; therefore, a CTA of the chest was also obtained. These images revealed a Stanford type B aortic dissection beginning just distal to the left subclavian artery and extending to the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery. The right renal artery arose from the true lumen of the dissection while the left renal artery arose from the false lumen. This case is interesting as imaging shows the lack of perfusion to the left kidney, residing in the retroperitoneum, which correlates with her non-descript abdominal and left flank pain.