ECG
Severe Hyperkalemia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KH1DThe initial ECG obtained upon arrival shows what is commonly referred to as a sine wave pattern. This patient does have a biventricular pacemaker which would ordinarily create a wide QRS complex mimicking an intraventricular conduction delay. However, the QRS complex here is exceptionally wide, in excess of 400 milliseconds (normal: less than 120 milliseconds). As the QRS widens, alongside other deflections present on the ECG, it morphologically mimics a mathematical sine wave.
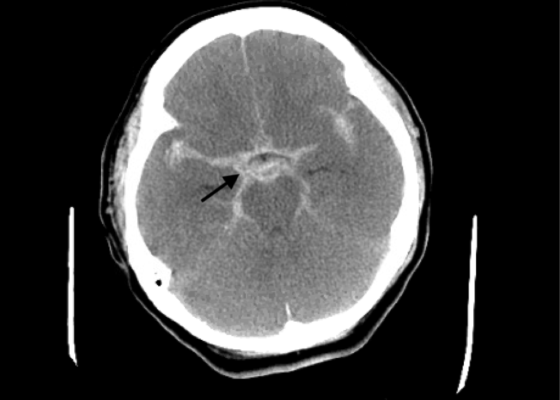
Post-Coital Sudden Cardiac Arrest Due to Non-Traumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8663NThe electrocardiogram demonstrated sinus tachycardia with ST segment elevation in lead aVR (black arrows) and diffuse ST depressions concerning for possible ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Given the events reported and the patient’s neurologic exam without sedation, non-contrast CT of the head was ordered; imaging showed evidence of a large subarachnoid hemorrhage, mostly at the level of the Circle of Willis (black arrow) concerning for an aneurysmal bleed as well as mild generalized white matter density suggestive of cerebral edema.
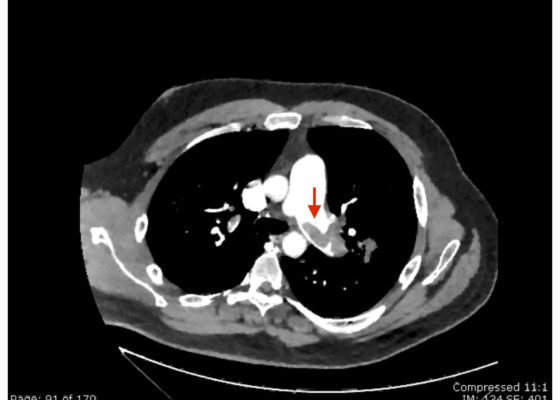
Saddle Pulmonary Embolus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8N63PAn electrocardiogram (ECG) showed evidence of right heart strain with an incomplete right bundle branch block, S1Q3T3 (see red arrow [S1], blue arrow [Q3], and black arrow [T3]), and ST-segment elevation in the septal leads (green arrows). Bedside echocardiography showed a dilated right ventricle with ventricular wall akinesis (red arrow) sparing the apex (purple arrow), which is known as McConnell’s Sign. It also showed a mobile hyperechoic mass (yellow arrow). These ultrasound findings were concerning for pulmonary embolism (PE), so computed tomography (CT) angiogram of the chest was ordered and confirmed massive bilateral obstructive filling defects (red arrows) consistent with saddle pulmonary embolism. Additionally, noted is flattening of the interventricular septum (blue arrow) consistent with right heart strain. Laboratory studies were notable for a troponin-I of 0.29 ng/mL, a B-type natriuretic peptide of 792.3 pg/mL, lactic acid of 5.30 mmol/L, and a creatinine of 2.0 mg/dL, consistent with end organ dysfunction. All other lab work was within normal limits.
Wellens’ Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FS8KInitial electrocardiogram (ECG) revealed the classic biphasic T waves in V2 and V3 of Wellen’s syndrome (see red outlines). A second EKG demonstrated an evolving deeply inverted T wave (see blue outlines).
Guilty as Charged: Jailed Coronary Vessel Presenting as Wellens’ Syndrome Type B
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DS6HEvolving changes to electrocardiograph (ECG) were noted during serial ECG monitoring involving leads V2 and V3, along with some T-wave inversion in V4 and V5 that were concerning for a Wellens’ syndrome type B on second ECG. She was admitted and subsequently taken to cardiac catheterization suite where it was revealed that the previously placed stent in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery was patent. Unfortunately, the stent blocked off an adjacent side branch vessel off the LAD in proximal two-third region of the stent (as seen in the cartoon).
Clinical Evaluation and Management of Pediatric Pericarditis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HP85An electrocardiogram (ECG) was concerning for ST segment elevation in leads II, III, aVF, and V4, with subtle ST elevations in V5 and V6 (see black arrows). There is also ST segment depression in aVL (see blue arrows).
Don’t Forget the Pacemaker – A Rare Complication
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8GS7HThe ECG demonstrated the presence of pacemaker spikes without appropriate capture (green arrows) and a ventricular escape rhythm which can be identified by an absence of P waves prior to the QRS complex (purple arrows). The portable chest X- demonstrated displaced pacemaker leads (red arrows) that were coiled around the pulse generator (blue arrow).
Propafenone Overdose-induced Arrhythmia and Subsequent Correction After Administration of Sodium Bicarbonate
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D925The first ECG in this case showed sinus tachycardia with a widened QRS (black arrow), a rightward axis, prolonged corrected QT interval (QTc), and terminal R wave in AVR (white arrow). There are several potential causes for these ECG findings, but put together with the patient’s history, we were suspicious of sodium channel blockers being the most likely cause. The second ECG, after sodium bicarbonate was administered, demonstrated a normal QRS (black arrow) and no rightward axis deviation, reduction of the QTC and resolution of the terminal R wave (white arrow). We later learned that the patient’s cardiologist recently increased her propafenone dose.