CT
Acute Dysphagia in a 25-Year-Old Male
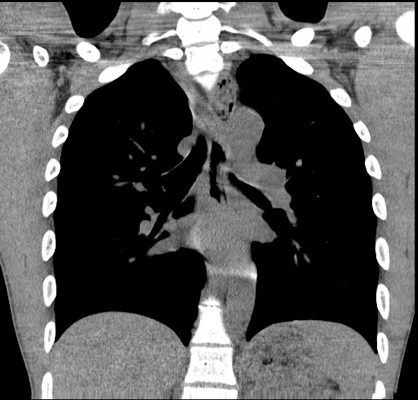
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83P8FAfter an unremarkable chest radiograph was obtained, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest was obtained due to possible co-ingestion of bones to rule out perforation. The CT scan demonstrated focal distention of the mid-esophagus due to an impacted food bolus (white arrow). An aberrant right subclavian artery (yellow arrow) was located just distal to the impaction site with partial compression of the esophagus (red arrow).
Achalasia: An Uncommon Presentation with Classic Imaging
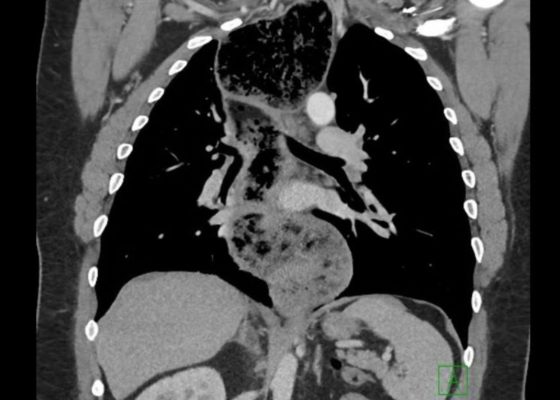
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86D2BThe chest X-ray demonstrated a markedly widened mediastinum (red brackets), raising concern for thoracic aortic aneurysm/aortic dissection, which prompted labs and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the chest. The CT revealed a dilated proximal esophagus that narrowed distally (yellow tracing and red arrow), with particulate material, mass-effect on the trachea (purple outline), and bilateral patchy opacities suggesting aspiration. Barium esophagram showed a drastically dilated esophagus filled with contrast (yellow arrow), terminating into the classic “bird’s beak sign” (red arrow) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Esophageal manometry later confirmed achalasia, proving that widened mediastina can have unexpected etiologies.
An Unusual Case of Pharyngitis: Herpes Zoster of Cranial Nerves 9, 10, C2, C3 Mimicking a Tumor
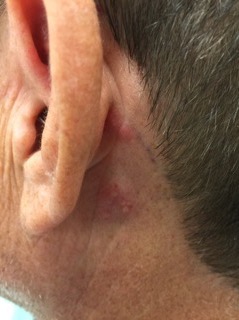
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B05KOn exam, the patient was sitting upright while holding an emesis basin filled with saliva. His voice was noticeably hoarse. Examination of the head and neck revealed vesicular eruptions on the left scalp in the V1 dermatome and on the left mastoid process (Images 1 and 2). Physical exam also shows vesicular eruptions on the left posterior oropharynx that did not cross midline (Image 3).
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X92TComputed tomography (CT) of the abdominal and pelvis with intravenous (IV) contrast revealed inflammatory changes, including gas and fluid collections within the ventral abdominal wall extending to the vulva, consistent with a necrotizing soft tissue infection.
Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum: Hamman Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NS72The initial CT scans showed extraluminal gas surrounding the distal esophagus as it traversed the posterior mediastinum, concerning for possible distal esophageal perforation that prompted surgery and GI consultations. There was no evidence of a drainable collection or significant fat stranding. The image also showed an intraluminal stent traversing the gastric antrum and gastric pylorus with no indication of obstruction. Circumferential mural thickening of the gastric antrum and body were consistent with the patient’s history of gastric adenocarcinoma. The shotty perigastric lymph nodes with associated fat stranding, along the greater curvature of the distal gastric body suggested local regional nodal metastases and possible peritoneal carcinomatosis.
The thoracic CT scans showed extensive pneumomediastinum that tracked into the soft tissues of the neck, which given the history of vomiting also raised concern for esophageal perforation. There was still no evidence of mediastinal abscess or fat stranding. Additionally, a left subclavian vein port catheter, which terminates with tip at the cavoatrial junction of the superior vena cava can also be seen on the image.
Procedural Sedation for the removal of a rectal foreign body
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81332Axial and coronal views on CT showed evidence of a large, tube-shaped foreign body in the rectum (see arrows) without evidence of acute gastrointestinal tract disease.
A Case of Otomastoiditis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RK89The patient underwent computed tomography (CT) of the head which revealed opacification of the left middle ear (red arrow) and mastoid air cells (red circles). Additionally, there was thickening of the soft tissues of the external auditory canal (blue arrowhead), likely reflecting concurrent otitis externa. Based on the imaging, he was admitted for findings consistent with acute otomastoiditis.
Large Ventral Hernia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86K9QComputed tomography (CT) scan with intravenous (IV) contrast of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated a large pannus containing a ventral hernia with abdominal contents extending below the knees (white circle), elongation of mesenteric vessels to accommodate abdominal contents outside of the abdomen (white arrow) and air fluid levels (white arrow) indicating a small bowel obstruction.