Search By Topic
Found 39 Unique Results
Page 2 of 4
Page 2 of 4
Page 2 of 4
An Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Elective for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TP9BABSTRACT: Audience: This ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia elective is designed for emergency medicine residents. Length of Curriculum: The proposed length of this curriculum is over one week. Introduction: Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia (UGRA) is a useful tool in the emergency department (ED) for managing painful conditions, and many programs have identified that these are useful skills for emergency providers; however, only about
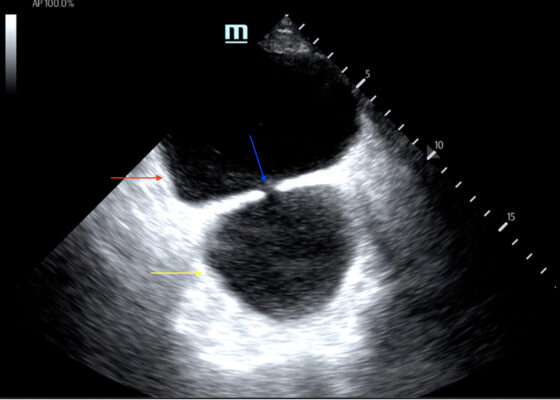
Bladder Diverticulum – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8635COn examination, the patient was alert and oriented but in mild distress. Suprapubic fullness was noted upon abdominal palpation. Point of care ultrasound of the bladder showed two enlarged “bladders” with a central communication. Bedside total bladder volume was measured to be 1288 cm3 (the top “bladder” was measured to be 1011 cm3, while the bottom “diverticulum” was measured to be 277 cm3) by ultrasound.
The POCUS stills of the patient’s bladder demonstrated the bladder (red arrow) and bladder diverticulum (yellow arrow) with a central communication (blue arrow) in the transverse and sagittal views.
Ascending Thoracic Aortic Dissection: A Case Report of Rapid Detection Via Emergency Echocardiography with Suprasternal Notch Views
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WW6WVideo of parasternal long-axis bedside transthoracic echocardiogram: The initial images showed grossly normal left ventricular function, and no pericardial effusion or evidence of cardiac tamponade. However, the proximal aorta beyond the aortic valve was poorly-visualized in this window.
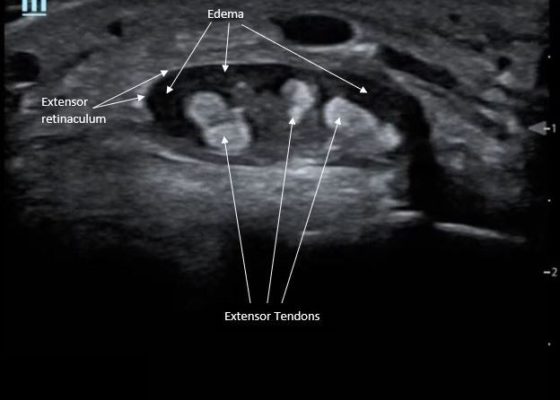
Point-Of-Care Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Extensor Tenosynovitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Q050Point-of-care ultrasound of the dorsal aspect of the left hand reveals a heterogenous hypoechoic fluid collection surrounding the extensor tendons (axial view) within the retinaculum consistent with edema. Longitudinal view shows anechoic fluid within the tenosynovium which is located between the anisotropic extensor tendon and linear hyperechoic synovial sheath. Longitudinal view also shows some cobblestoning, or tissue edema, superficial to the anisotropic extensor tendon. The patient’s contralateral right dorsal hand was scanned in a longitudinal view and shows no cobblestoning or hypoechoic fluid under the synovial sheath. The patient was diagnosed with tenosynovitis, and started on intravenous antibiotics.
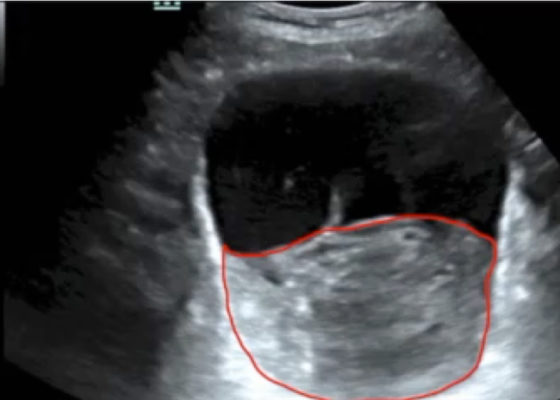
Point-of-care Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Bladder Hematoma vs. Hemorrhage
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8092FBladder POCUS demonstrated 500mL of post void residual fluid, indicative of retention. Half of the volume is hyperechoic (red circle); this is likely the bladder wall hematoma. Could also consider sonographic artifact, bladder mass, or cystitis.1-2
Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Evaluate Intrahepatic Biliary Stent Function
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86S6NThe ultrasound image demonstrates severe intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation without an obvious intrahepatic obstructive lesion, as pointed out by the white arrows. The hepatic vasculature is well-distinguished from the biliary tree via color flow doppler, as seen by the white arrowheads.
Pericardial Clot on Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZH1TFocused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) scan was positive for a clinically significant pericardial effusion as evidenced by the hypoechoic fluid around the myocardium, indicated by the blue arrow in image 2. Findings are also consistent with tamponade process as evidenced by restricted expansion and collapse of the right ventricle during diastole. The hyperechoic floating structure between the pericardium and myocardium, adjacent to the right ventricle, represents a pericardial clot, indicated by the white arrow.The density of the pericardial clot differs from that of the myocardium, thus serving as an additional variable to avoid confusing this as part of the myocardial structure.
Radiolucent Foreign Body Seen on Point-of-Care Ultrasound but not on X-ray
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WS77X-rays of the foot were obtained and no radiopaque foreign body was visualized. Due to high clinical suspicion for retained foreign body, a point-of-care ultrasound was performed by applying a high-frequency linear probe at the area of discomfort. In the long axis an ovoid focus of hypoechogenicity (orange outline) is visualized. Within this finding there is a linear focus (yellow line) of increased echogenicity measuring 1 mm in diameter and 1 cm in length. On short axis view, a rectangle focus (green dot) demonstrating shadowing (blue highlight) is seen.
Low-Cost, Low Fidelity Meat Model to Teach Ultrasound Guided Nerve Blocks
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83G9RUpon completion of this workshop, learners will be able to: 1) Describe the risks and benefits of ultrasound guided nerve blocks. 2) Choose the appropriate nerve to block based on the area that needs anesthesia. 3) Display proficiency in performing an ultrasound guided nerve block on meat models. 4) Verbalize confidence in successfully performing ultrasound guided regional anesthesia. By successfully meeting these objectives, we aim to improve learner confidence and clinical ability in performing ultrasound guided nerve blocks.
Point of Care Ultrasound Illustrating Small Bowel Obstruction
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T637POCUS of the small bowel illustrated significantly dilated loops of bowel (white line), thickened bowel wall (white arrow) and to-and-fro peristalsis, consistent with small bowel obstruction.