Ultrasound
Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room for POCUS Pulmonary: Scan Your Way Out
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RM0MBy the end of performing the Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room, learners will be able to: 1) recognize sonographic signs of A-line, B-line, Barcode sign, Bat sign, Seashore Sign, Plankton sign, Jellyfish Sign, Lung point, lung lockets, and Lung pulse; 2) differentiate sonographic findings of pneumothorax, hemothorax, pneumonia, COVID 19 pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and pleural effusion from normal lung findings; 3) distinguish pneumonia from atelectasis by recognizing dynamic air bronchogram; and 4) recognize indications for performing POCUS pulmonary such as dyspnea, blunt trauma, fall, cough and/or heart failure.
High-Efficiency Ultrasound-Guided Regional Nerve Block Workshop for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84P8RThe objective of this workshop is to provide emergency medicine residents the confidence and skill sets needed to effectively perform five commonly used UGRNBs for conditions encountered in the emergency department. Through this one-day, accelerated workshop, residents will be given an opportunity to sharpen their UGRNB technique prior to applying them in the clinical environment. By the end of this workshop, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the clinical situations in which UGRNBs can be utilized and understand the associated risks, 2) list the commonly used local anesthetic medications and their proper dosing in respect to regional nerve blocks, 3) demonstrate proper ultrasound probe positioning and identify relevant anatomical landmarks for each nerve block on both standardized patients and cadavers, 4) describe the common steps involved to perform each nerve block, 5) perform the five UGRNB techniques outlined in this workshop.
Vitreous Hemorrhage Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88D3BPoint of care ultrasound (POCUS) revealed hyperechoic material in the vitreous consistent with a vitreous hemorrhage. On the ultrasound images, there is visible hyperechoic debris seen floating in the vitreous as the patient moves his eye. Since the vitreous is typically anechoic (black) in color on ultrasound, turning up the gain on the ultrasound machine makes these findings easier to see and often highlights abnormalities, such as this hemorrhage (see annotated still).
Ureteral Obstruction and Ureteral Jet Identification—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8206GA point-of-care ultrasound of the urinary tract was performed, evaluating the kidneys and bladder. When imaging her kidneys, right-sided hydronephrosis was noted with a normal appearance to the left kidney. To further evaluate, a curvilinear probe was placed on her bladder with color doppler to assess for ureteral jets. Ureteral jets are seen as a flurry of color ejecting from each of the ureters as urine is released from the ureterovesical junction. In a healthy patient, this finding should be seen ejecting from both ureters every 1-3 minutes as the kidneys continue to filter the blood and create urine to be stored in the bladder. In our patient, however, ureteral jets were only noted on the left side (arrow), which was significant in further verifying our suspicion of right ureteral obstruction.
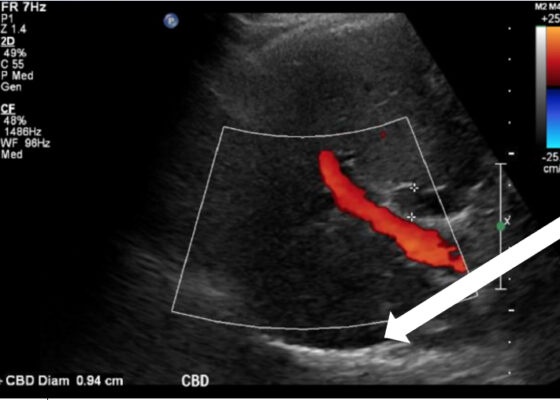
A Case Report on Detecting Porcelain Gallbladder form Wall-Echo-Shadow Sign on Point-of-Care Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8164GPoint-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was performed by the emergency physician. Gallbladder ultrasound (US) should be performed using a curvilinear probe. If the patient’s body habitus does not allow for the use of a curvilinear probe, a phased array probe may be used. To find the gallbladder with ultrasonography, two approaches are commonly used. Many physicians prefer the “subcostal sweep” in which the probe is placed on the xiphoid process in a sagittal plane and swept along the inferior costal margin until the gallbladder is visualized. If this does not adequately locate the gallbladder, the “X minus 7” approach may be used. In this approach, the probe is placed on the xiphoid (X) process in a transverse view and moved 7 centimeters (minus 7) to the patient’s right. This technique is useful for patients with a larger body habitus. If the gallbladder is still not visualized, placing the patient in left lateral decubitus position or asking them to take a deep breath and hold may help the ultrasonographer locate the gallbladder. The US revealed mild hepatic biliary duct dilation with cholelithiasis and sludge, but no additional evidence to suggest cholecystitis. The US image showed a dilated common bile duct at 0.94 cm and calcifications. Visualization of the gallbladder wall is essential in differentiating between a positive wall-echo-shadow (WES) sign and a porcelain gallbladder. While a hypoechoic gallbladder wall is indicative of a WES sign, a hyperechoic wall layer will indicate a calcified gallbladder wall, suggesting a porcelain gallbladder. In image 1, the hyperechoic gallbladder wall can be visualized (white arrow), suggesting the presence of porcelain gallbladder and distinguishing it from a positive WES sign.
An Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia Elective for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TP9BABSTRACT: Audience: This ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia elective is designed for emergency medicine residents. Length of Curriculum: The proposed length of this curriculum is over one week. Introduction: Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia (UGRA) is a useful tool in the emergency department (ED) for managing painful conditions, and many programs have identified that these are useful skills for emergency providers; however, only about
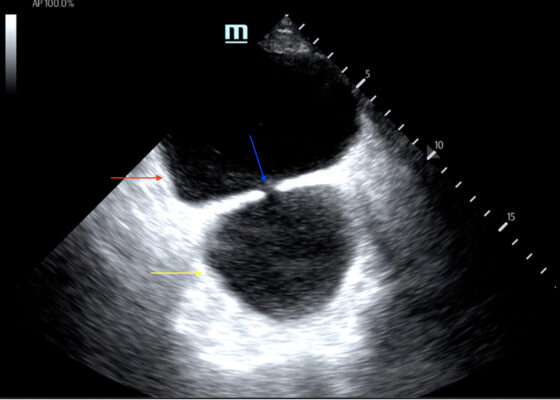
Bladder Diverticulum – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8635COn examination, the patient was alert and oriented but in mild distress. Suprapubic fullness was noted upon abdominal palpation. Point of care ultrasound of the bladder showed two enlarged “bladders” with a central communication. Bedside total bladder volume was measured to be 1288 cm3 (the top “bladder” was measured to be 1011 cm3, while the bottom “diverticulum” was measured to be 277 cm3) by ultrasound.
The POCUS stills of the patient’s bladder demonstrated the bladder (red arrow) and bladder diverticulum (yellow arrow) with a central communication (blue arrow) in the transverse and sagittal views.
Ascending Thoracic Aortic Dissection: A Case Report of Rapid Detection Via Emergency Echocardiography with Suprasternal Notch Views
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WW6WVideo of parasternal long-axis bedside transthoracic echocardiogram: The initial images showed grossly normal left ventricular function, and no pericardial effusion or evidence of cardiac tamponade. However, the proximal aorta beyond the aortic valve was poorly-visualized in this window.