Pediatrics
Case Report of Incarcerated Gastric Volvulus and Splenic Herniation in Undiagnosed Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in an Infant
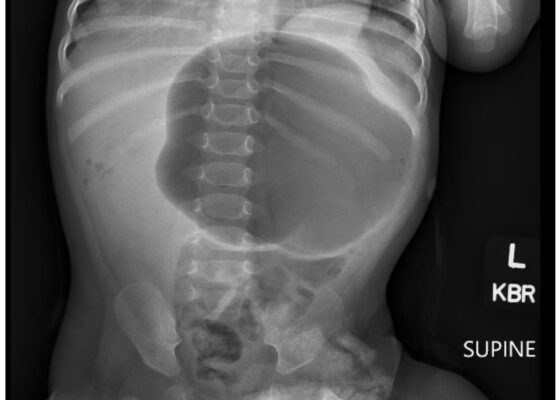
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VD27An upper gastrointestinal series (UGI) showed an enteric tube with its tip in the stomach and side-port in the esophagus. There was a large amount of air in the stomach and a small volume of scattered distal bowel gas. The tip of an enteric tube was seen in the stomach (red arrow). Contrast partially filled the stomach, and the greater curvature was visualized superior to the lesser curvature in the left upper quadrant (blue arrow). The body of the stomach was herniated into the right chest through a Bochdalek hernia (blue star). There was a large amount of air in the stomach and a small volume of scattered distal bowel gas. These findings were consistent with mesenteroaxial gastric volvulus.
Beware of the Pediatric Limp: A Case of Mycoplasma Associated Acute Transverse Myelitis
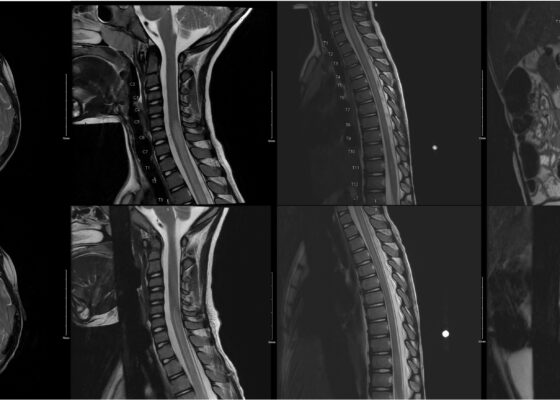
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QQ1QAn MRI with contrast, T2 sequence was performed. In Figures a-d, the MRI of the patient’s brain and spinal cord on admission shows abnormal signals in the patient’s pons (lack of symmetrical gray-white differentiation on cross-section) along with hyperintensity (sagittally shown as brightness in what should be homogenously intense spinal cord) and significant central cord edema (with swelling seen as increased width) starting from C5 and continuing to the conus medullaris around L1/L2.
A Simulation and Small-Group Pediatric Emergency Medicine Course for Generalist Healthcare Providers: Gastrointestinal and Nutrition Emergencies
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WH2KThe aim of this curriculum is to increase learners’ proficiency in identifying and stabilizing acutely ill pediatric patients with gastrointestinal medical or surgical disease or complications of malnutrition. This module focuses on the diagnosis and management of gastroenteritis, acute bowel obstruction, and deficiencies of feeding and nutrition. The target audience for this curriculum is generalist physicians and nurses in limited-resource settings.
Case Report of a Child with Colocolic Intussusception with a Primary Lead Point
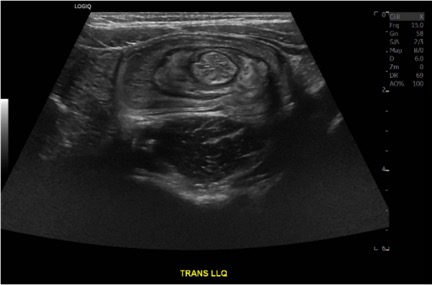
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8564QOn the initial ED visit, an abdominal ultrasound (US) was ordered which showed the classic intussusception finding of a target sign (yellow arrow), or concentric rings of telescoped bowel, on the transverse view of the left lower quadrant (LLQ).
Adolescent with Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Hypothermia and Pneumomediastinum
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FP8JBy the end of the simulation, learners will be able to: 1) develop a differential diagnosis for an adolescent who presents obtunded with shortness of breath; 2) discuss the management of diabetic ketoacidosis; 3) discuss management of hypothermia in a pediatric patient; 4) discuss appropriate ventilator settings in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis; and 5) demonstrate interpersonal communication with family, nursing, and consultants during high stress situations.
Little Patients, Big Tasks – A Pediatric Emergency Medicine Escape Room
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89W70By the end of this small group exercise, learners will be able to: 1) demonstrate appropriate dosing of pediatric code and resuscitation medications; 2) recognize normal pediatric vital signs by age; 3) demonstrate appropriate use of formulas to calculate pediatric equipment sizes and insertion depths; 4) recognize classic pediatric murmurs; 5) appropriately diagnose congenital cardiac conditions; 6) recognize abnormal pediatric electrocardiograms (ECGs); 7) identify life-threatening pediatric conditions; 8) demonstrate intraosseous line (IO) insertion on a pediatric model; and 9) demonstrate appropriate use of the Neonatal Resuscitation Protocol (NRP®) algorithms.
Point-Of-Care Ultrasound Use for Detection of Multiple Metallic Foreign Body Ingestion in the Pediatric Emergency Department: A Case Report
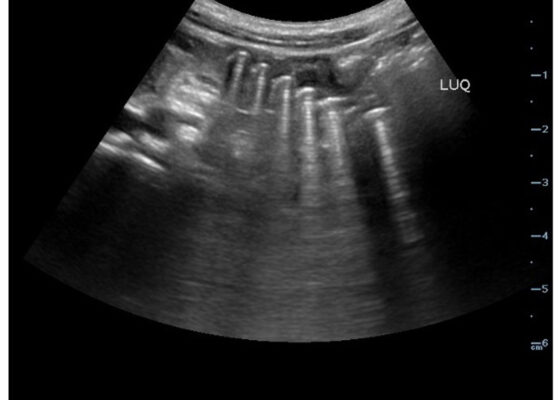
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83D2DBedside POCUS was performed on the patient’s abdomen using the curvilinear probe. The left upper quadrant POCUS image demonstrates multiple hyperechoic spherical objects with shadowing and reverberation artifacts concerning multiple foreign body ingestions. Though the patient and mother initially denied knowledge of foreign body ingestion, on repeated questioning after POCUS findings, the patient admitted to his mother that he ate the spherical magnets he received for his birthday about one week ago. The patient swallowed these over the course of two days. The presence of multiple radiopaque foreign bodies was confirmed with an abdominal X-ray.
Child Maltreatment Education: Utilizing an Escape Room Activity to Engage Learners on a Sensitive Topic
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84H1CBy the end of the escape room, the learner should be able to: 1) understand the national and local prevalence of child maltreatment; 2) understand the different types of child maltreatment and common associated presentations; 3) know the local EMS agency reporting requirements; 4) understand when to make base hospital contact with respect to concern for maltreatment; 5) collaborate effectively as a team.