Posts by JETem
A Lecture to Teach an Approach and Improve Resident Comfort in Leading Resuscitation of Young Infants in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8H36JBy the end of this lecture, participants should be able to: 1) apply a consistent approach to the initial resuscitation of a critically ill young infant in the emergency department; 2) select appropriate medications and equipment for use in resuscitation of critically ill young infants; 3) describe the components of the Pediatric Assessment Triangle,6 which can be used to identify critically ill infants and children; 4) improve comfort in resuscitating young infants in the emergency department.
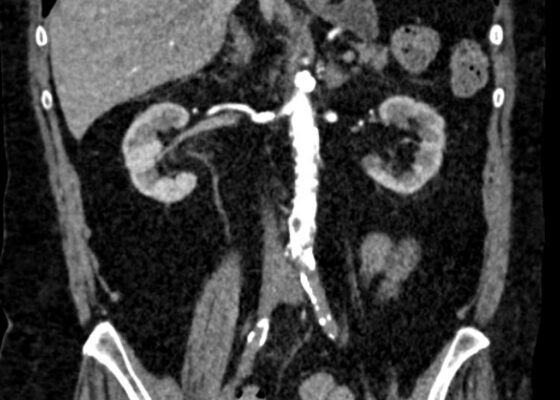
Initial Management and Recognition of Aortoiliac Occlusive Disease, A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87M0ZComputerized tomography with angiography (CTA) of the entire aorta demonstrated an occluded distal infrarenal aorta with extension into the bilateral common femoral arteries (red outline), lack of flow through femoral arteries (yellow outline) and trickle flow reconstituted distally consistent with aortoiliac occlusive disease (blue outline). Some small segments of the proximal celiac axis showed signs of occlusion (purple outline). A short segment of non-specific bowel wall thickening, which may have been related to ischemic changes, was also seen (not seen on images). The included coronal slice shows the extent of the bilateral occlusive burden, with three-dimensional reconstruction emphasizing the same findings.
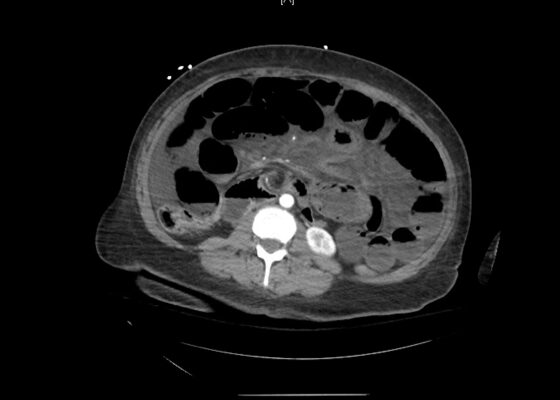
Case Report: It’s a Small Whirl Afterall
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S8GThe CT imaging of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated multiple loops of dilated small bowel with a whirl sign (red arrow) within the mid abdomen and a transition point (green arrow), suspicious for closed loop bowel obstruction and internal hernia.
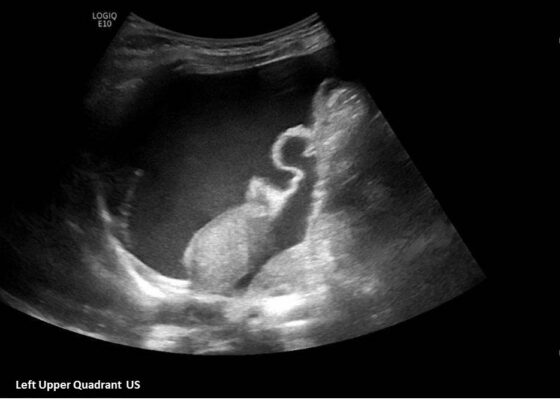
Ovarian Juvenile Granulosa Cell Tumor Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8035HA focused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) exam was performed initially to evaluate for intra-abdominal injury given the clinical picture. A phased-array ultrasound transducer was placed in sagittal orientation along the patient’s right and left flank, demonstrating extensive heterogenous fluid collections in Morrison’s pouch (red arrow), subphrenic space (solid green arrow), and splenorenal recess (dashed green arrow). To further evaluate, a phased-array transducer was placed over her pelvic area in transverse orientation, demonstrating, a large, heterogeneous mass (outlined in yellow arrows). The surgical team was promptly consulted and blood products were ordered. Although there was concern for impending hemorrhagic shock due to patient’s presenting tachycardia, the patient was hemodynamically stable enough for a CT scan of her chest, abdomen, and pelvis. The CT scan showed large-volume ascites, which exerted mass effect on all abdominal organs with centralization of bowel loops. Additionally, there was a large, 6.4 x 6.8 x 10.9-centimeter, midline pelvic mass (outlined in blue arrows).
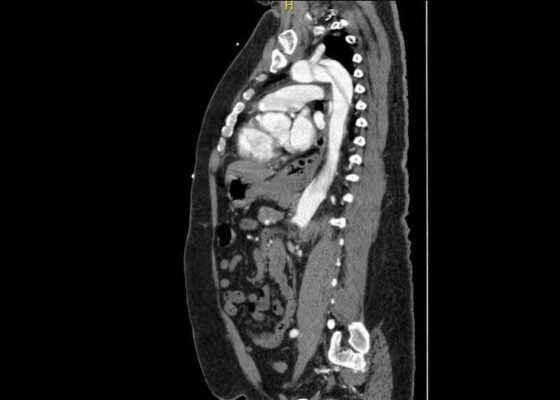
A Case Report of Aortic Dissection Involving the Aortic Root, Left Common Carotid Artery, and Iliac Arteries
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V93KComputed tomography angiography (CTA) of the thoracic and abdominal aorta revealed an aortic dissection of the ascending aorta, with a dissection flap starting from the aortic root/aortic annulus (yellow arrows), extending into the aortic arch (light blue arrowhead) and involving the left common carotid artery (purple arrow), left subclavian artery (pink arrow), extending to the descending aorta (red arrows), and into the bilateral iliacs (green arrows). The true lumen (red star) and false lumen (blue star) created by the dissection flap can best be seen in the axial views.
A Case Report of Epiglottitis in an Adult Patient
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QM09At the time of presentation to the ED, laboratory results were significant for leukocytosis to 11.8 x 109 white blood cells/L and a partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 52 mmHg on venous blood gas. Computed tomography (CT) of the soft tissue of the neck with contrast showed edematous swelling of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic fold with internal foci of gas (blue arrow) and partial effacement of the laryngopharyngeal airway and scattered cervical lymph nodes bilaterally (Figure 1). Findings were consistent with epiglottitis containing nonspecific air. Additionally, the pathognomonic “thumbprint sign” (yellow arrow) was found on lateral x-ray of the neck (Figure 2). The CT findings as shown in figure 3 illustrate lateral view of the swelling of the epiglottis, gas, and blockage of the airway.
An Unusual Case Report of a Toddler with Metastatic Neuroblastoma Mimicking Myasthenia Gravis
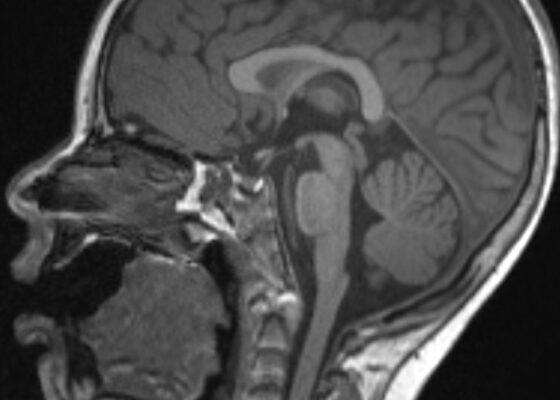
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G35VWhile still in the ED, MRI with and without gadolinium contrast of the brain, orbits, and cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine were obtained to evaluate for possible CNS lesions including encephalitis, myelitis, or demyelination. Imaging, however, demonstrated multiple unexpected findings: a T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense and heterogeneously enhancing right adrenal mass measuring 2.7 x 2.1 x 3 cm (yellow asterisk) along with heterogenous enhancement at the clivus, C6, C7, T7, T8, T12, and L3 vertebral bodies (red asterisks). There were otherwise no significant intracranial signal or structural abnormalities and normal orbits.
Not Another Presentation of Cellulitis: A Case Report of Erythromelalgia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD2KEpisodic tender, warm, erythematous swelling of the extremity experienced by this patient is typical of erythromelalgia. Erythematous streaking on the volar surface of the left forearm (red arrow) and tender, warm, erythematous blanching swelling was present on the palmar hand (yellow arrow). Most patients with erythromelalgia also have lower extremity involvement including the dorsum or sole of the foot and toes.1