Posts by JETem
Mushroom for Improvement Case Report: The Importance of Involving Mycologists
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZW7WThe mushroom displayed here is large and lacks any gills. Small puffball mushrooms can resemble young immature button top Amanita type mushrooms. Opening the Amanita mushroom should reveal apparent gills and quickly differentiate the two- -the puffball mushroom should have a white interior without gills.
A Case Report of a Man with Burning Arm and Leg Weakness
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V659A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) of the head and neck was performed, followed by an MRI of the cervical spine. The CT demonstrated congenital narrowing of the cervical spinal canal, with posterior disc osteophyte complex and disc bulge at C3-4 and C4-5 (arrow). The T2-weighted MRI additionally demonstrated obliteration of the anterior and posterior subarachnoid space at the level of C3-C5, with associated patchy central cord signal abnormality (arrow).
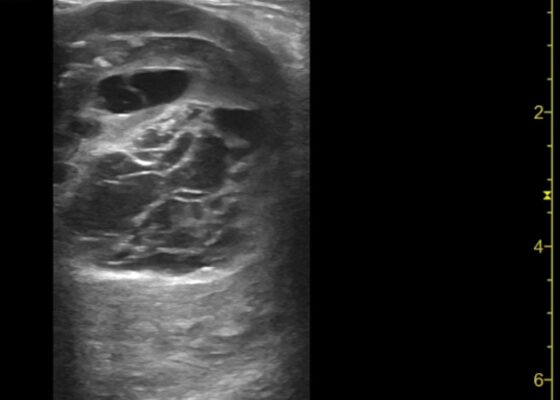
Thigh Mass Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QD3CPoint-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) demonstrates a large, subcutaneous mass with areas of mixed echogenicity. The mass contains fluid-filled, anechoic areas with internal septations and absent doppler flow. The majority of the mass appears isoechoic to the surrounding tissues with a hyperechoic border. Computed tomography (CT) of his right thigh shows a 16 x 8.1 x 9.5 cm heterogenous, complex mass within his hamstring muscles, inferior to the femur. His lab work was significant for a white blood cell (WBC) of 17.3 (103/µL).
Inferior STEMI Electrocardiogram in a Young Postpartum Female with Sickle Cell Trait with Chest Pain – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KP95ECG shows evidence of ST segment elevation in the inferolateral leads with reciprocal change in a bigeminy pattern. The ECG pattern seen in this patient demonstrates ST elevations in the inferior leads (II, III, and avF) as well as the precordial leads V4-V6. Reciprocal changes can also be seen in leads I and avL. Though this STEMI pattern is typically associated with occlusion of the right coronary artery in 80% of cases, it may also be caused by occlusion of the left circumflex artery. This may explain this patient’s cardiac catheterization findings of vasospasm in the left circumflex coronary artery.
Transverse Myelitis in Naloxone Reversible Acute Respiratory Failure—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B659Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine without contrast was obtained and revealed increased signal throughout the spinal cord from C-1 to the conus medullaris with mild expansion consistent with transverse myelitis.
Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room for POCUS Pulmonary: Scan Your Way Out
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8RM0MBy the end of performing the Zombie Cruise Ship Virtual Escape Room, learners will be able to: 1) recognize sonographic signs of A-line, B-line, Barcode sign, Bat sign, Seashore Sign, Plankton sign, Jellyfish Sign, Lung point, lung lockets, and Lung pulse; 2) differentiate sonographic findings of pneumothorax, hemothorax, pneumonia, COVID 19 pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and pleural effusion from normal lung findings; 3) distinguish pneumonia from atelectasis by recognizing dynamic air bronchogram; and 4) recognize indications for performing POCUS pulmonary such as dyspnea, blunt trauma, fall, cough and/or heart failure.
High-Efficiency Ultrasound-Guided Regional Nerve Block Workshop for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84P8RThe objective of this workshop is to provide emergency medicine residents the confidence and skill sets needed to effectively perform five commonly used UGRNBs for conditions encountered in the emergency department. Through this one-day, accelerated workshop, residents will be given an opportunity to sharpen their UGRNB technique prior to applying them in the clinical environment. By the end of this workshop, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the clinical situations in which UGRNBs can be utilized and understand the associated risks, 2) list the commonly used local anesthetic medications and their proper dosing in respect to regional nerve blocks, 3) demonstrate proper ultrasound probe positioning and identify relevant anatomical landmarks for each nerve block on both standardized patients and cadavers, 4) describe the common steps involved to perform each nerve block, 5) perform the five UGRNB techniques outlined in this workshop.
Cyanide Poisoning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80W76After the completion of this simulation, participants will have learned how to: 1) identify clues of smoke inhalation based on a physical examination; 2) identify smoke inhalation-induced airway compromise and perform definitive management; 3) create a differential diagnosis for victims of fire cyanide poisoning, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide; 4) appropriately treat cyanide poisoning; 5) demonstrate the importance of preemptively treating for cyanide poisoning; 6) perform an initial physical examination and identify physical marks suggesting the patient is a fire and smoke inhalation victim; and 7) familiarize themselves with the Cyanokit and treatment with hydroxocobalamin.