X-Ray
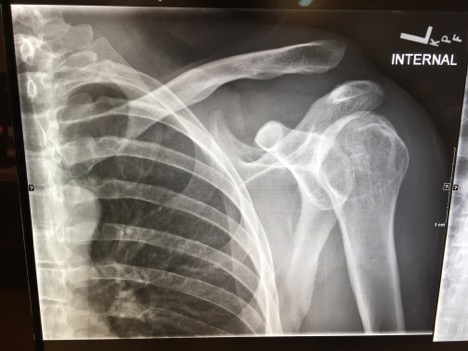
Acromioclavicular joint separation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C91GHistory of present illness: A 30-year-old male was brought in by ambulance to the emergency department as a trauma activation after a motorcycle accident. The patient was the helmeted rider of a motorcycle traveling at an unknown speed when he lost control and was thrown off his vehicle. He denied loss of consciousness, nausea, or vomiting. The patient’s vital signs
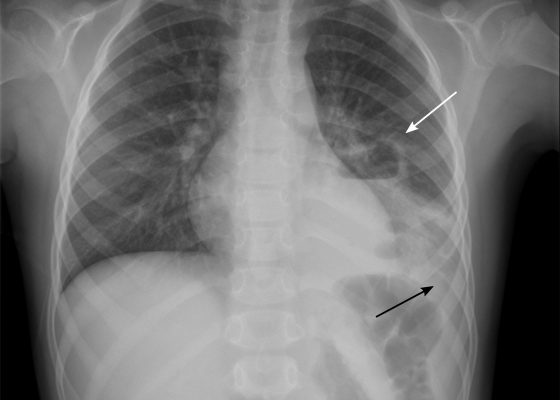
Pediatric Pulmonary Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83S6QUpright posterior-anterior plain chest films show a left lower lobe consolidation with an air-fluid level and a single septation consistent with a pulmonary abscess (white arrows). A small left pleural effusion was also present, seen as blunting of the left costophrenic angle and obscuration of the left hemidiaphragm (black arrows).
Scaphoid Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80344The anteroposterior (AP) plain film of this patient demonstrates a full thickness fracture through the middle third of the scaphoid (red arrow), with some apparent displacement (yellow lines) and subtle angulation of the fracture fragments (blue line).
Acute comminuted intertrochanteric hip fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QK9CHistory of present illness: A 69-year-old male presented to the emergency department (ED) with left hip pain after he was rear-ended on his bicycle by a vehicle traveling 10-15 miles per hour. He had normal vital signs. On exam, his left lower extremity was externally rotated and shortened with trochanteric point tenderness. His pelvis was stable. His lower extremity compartments
Pneumomediastinum After Cervical Stab Wound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87P79Anteroposterior (AP) chest X-ray showed subcutaneous emphysema of the neck, surrounding the trachea (red arrows), right side greater than left, and a streak of gas adjacent to the aortic arch (white arrow). Computed tomography angiogram (CTA) of the neck showed air outside of the trachea, positive for pneumomediastinum (blue arrows).
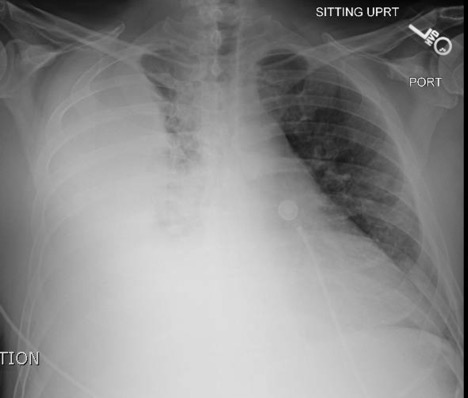
Empyema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86P9RThe chest X-ray shows a large fluid collection in the right lung demonstrated by the opacification that blunts the costophrenic angle on the right side. There is also a meniscus present, which is generally indicative of fluid. Chest computed tomography (CT) demonstrated an infiltrate with a mixture of densities within the same collection, consistent with a loculated effusion and concerning for an empyema.
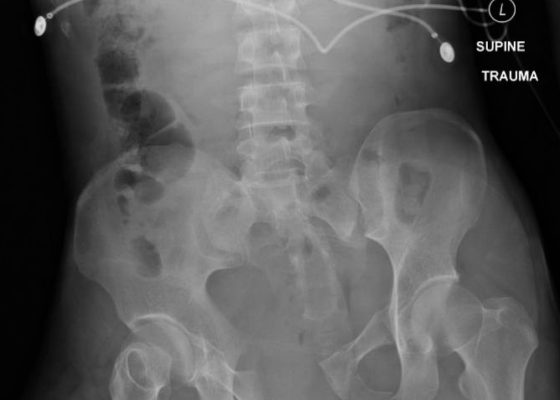
Bilateral Hip Dislocation in Unrestrained Driver
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HD0CThe initial radiograph of the pelvis revealed bilateral hip dislocations. Small bony fragments were noted in the right hip joint, suggestive of an underlying fracture. The sacroiliac joints and the pelvic ring were intact. In the emergency department, bilateral hip reductions were performed using the Captain Morgan technique.1 The post-reduction film showed reduction of the bilateral hip dislocations with extensive comminuted and displaced fractures of the right and left acetabula.
Open Book Pelvic Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CK7HThe initial radiograph of the pelvis shows an open-book pelvic fracture deformity with pubic symphyseal dislocation, left greater than right sacroiliac diastases, and fractures of the left superior and inferior pubic rami, right inferior pubic ramus, and left acetabular anterior column. The additional inlet and outlet radiographs of the pelvis after application of a pelvic binder also show an open book fracture with significant improvement of the widened pubic symphysis.