MRI
Septic Arthritis of the Acromioclavicular Joint: A Case Report
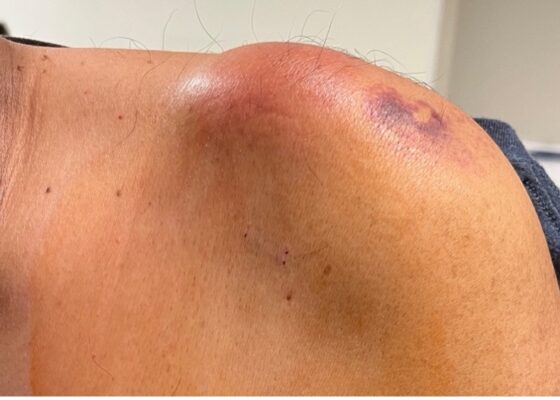
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP9NMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast was obtained of the shoulder and ankle, and results from both scans showed findings consistent with septic arthritis complicated by intraarticular abscesses. The MRI of the patient’s left acromioclavicular joint is shown as both a T1-weighted sequence in sagittal view and T2-weighted sequence in coronal view. The images show effusion (the dark fluid denoted by the red arrow) with an adjacent fluid collection (blue arrow). A T2-weighted MRI in coronal view of the patient’s right ankle showing multiple effusions (green arrows) and a fluid collection along the medial tibial cortex and subcutaneous tissues (yellow arrow).
A Case Report of Invasive Mucormycosis in a COVID-19 Positive and Newly-Diagnosed Diabetic Patient
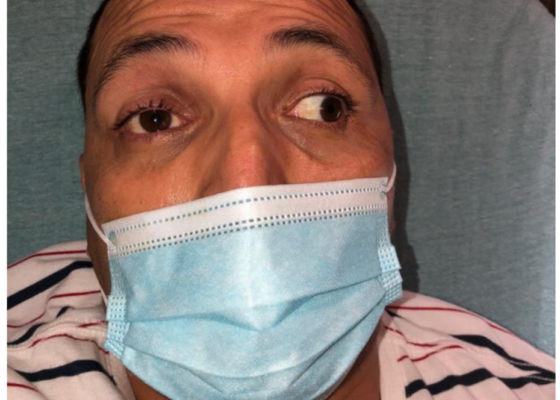
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81M1GOn physical exam, when the patient was asked to try and look to her right, the right eye failed to move laterally/abduct (blue arrow). Additionally, when asked to look straight ahead, the eye was slightly adducted (red arrow). There was a lack of motion of the right eye in abduction when the patient was asked to look to her right (yellow arrow).
A Case of Community-Acquired Tuberculosis in an Infant Presenting with Pneumonia Refractory to Antibiotic Therapy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X07MChest radiographs during the initial presentation at seven weeks of life demonstrated right lower lobe (RLL) air space opacity on both PA and lateral views, compatible with pneumonia (referenced by yellow and green arrows, respectively). Repeat chest radiograph performed 12 days after the initial imaging revealed persistent right lower lobe opacity and right hilar fullness, seen as an opacified projection off of the mediastinal border as compared with the prior image, concerning for lymphadenopathy (designated by the aqua arrow). On the third presentation, computed tomography (CT) of the chest with intravenous contrast found persistent right lower lobe consolidation, innumerable 2-3 mm nodules, and surrounding ground glass opacities. This is best visualized as scattered areas of hyperdensity in the lung parenchyma. Axial images confirmed the presence of right hilar as well as subcarinal lymphadenopathy (indicated by white and pink arrows, respectively). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with IV contrast was performed which showed a punctate focus of enhancement in the left precentral sulcus compatible with a tuberculoma (denoted with red arrow).
A Case Report of a Man with Burning Arm and Leg Weakness
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V659A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) of the head and neck was performed, followed by an MRI of the cervical spine. The CT demonstrated congenital narrowing of the cervical spinal canal, with posterior disc osteophyte complex and disc bulge at C3-4 and C4-5 (arrow). The T2-weighted MRI additionally demonstrated obliteration of the anterior and posterior subarachnoid space at the level of C3-C5, with associated patchy central cord signal abnormality (arrow).
Transverse Myelitis in Naloxone Reversible Acute Respiratory Failure—A Case Report
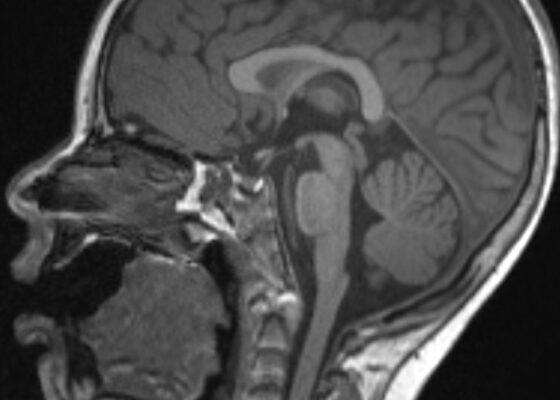
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B659Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine without contrast was obtained and revealed increased signal throughout the spinal cord from C-1 to the conus medullaris with mild expansion consistent with transverse myelitis.
Clinical and Radiologic Features of Fulminant Pediatric Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JW75The neurology service was consulted in the ED and multisequence MRI and MR angiography (MRA) of the brain were obtained without and with IV contrast. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and T2-weighted-Fluid-Attentuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) sequences showed multifocal small areas of diffusion signal abnormality in the brainstem and basal ganglia (red asterisks) suggestive of ischemia. Additional multifocal bilateral supra- and infratentorial foci of signal abnormality including subcortical white matter and deep grey matter were highly concerning for encephalitis or demyelinating disease. MRI was repeated on day 3 and day 7 during evolution of disease.
An Unusual Case Report of a Toddler with Metastatic Neuroblastoma Mimicking Myasthenia Gravis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G35VWhile still in the ED, MRI with and without gadolinium contrast of the brain, orbits, and cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine were obtained to evaluate for possible CNS lesions including encephalitis, myelitis, or demyelination. Imaging, however, demonstrated multiple unexpected findings: a T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense and heterogeneously enhancing right adrenal mass measuring 2.7 x 2.1 x 3 cm (yellow asterisk) along with heterogenous enhancement at the clivus, C6, C7, T7, T8, T12, and L3 vertebral bodies (red asterisks). There were otherwise no significant intracranial signal or structural abnormalities and normal orbits.
Case Report of a Man with Right Eye Pain and Double Vision
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW7GABSTRACT: A 39-year-old previously healthy male presented with three days of right eye pressure and one day of binocular diplopia. He denied history of trauma, headache, or other neurological complaints. He had normal visual acuity, normal intraocular pressure, intact convergence, and no afferent pupillary defect. His neurologic examination was non-focal except for an inability to adduct the right eye past midline
A Boy with Rash and Joint Pain Diagnosed with Scurvy: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89H1XHis lower extremity magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings showed abnormal signals in his knees, which were most consistent with scurvy. The white arrows on the T1-weight sequence indicate hypointensity (decreased signal or darker region) of the knees. The white arrows in the T2-weighted short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence indicate hyperintensity (increased signal or brighter region) in an MRI of the knees.
Erectile Dysfunction as a Presenting Symptom for Renal Cell Carcinoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8563BThe MRI showed extensive spondylotic changes suggestive of malignancy (red arrows) with severe spinal canal stenosis at the lumbar spine L3-L4 (purple arrows) level contributing to clumping of cauda equina nerve roots and severe bilateral neuroforaminal narrowing with diffuse disc bulges abutting the exiting nerve roots at multiple levels. Findings also showed a hypo-attenuated tumor (blue arrow) and hyper-attenuated loculated tumor (green arrow) consistent with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
1›
Page 1 of 2