Issue 4:3
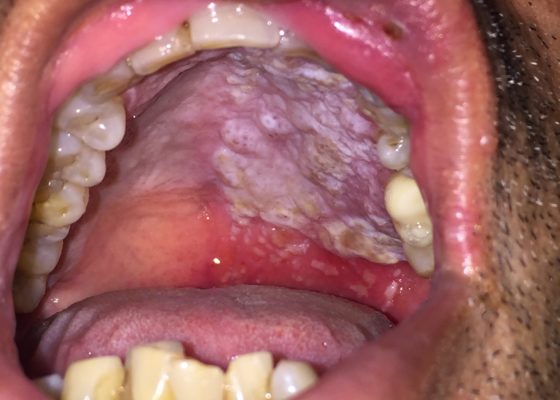
Oral Herpes Zoster
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QS69Physical exam findings revealed vesicular lesions on the lip, hard and soft palates which did not cross the midline. The lesions appeared in the distribution of the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve, consistent with herpes zoster.
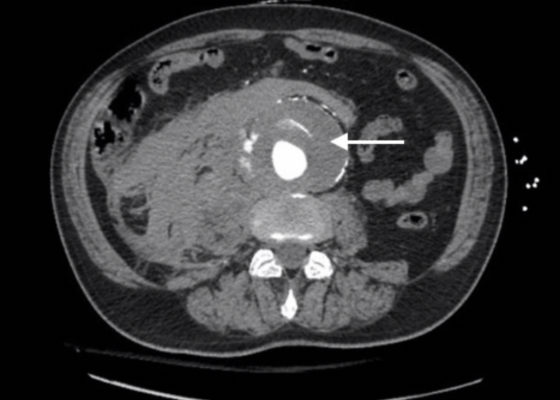
Ruptured AAA Presenting with Unresponsiveness and Cardiac Arrest
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M34QAxial CT images from the CT chest, abdomen and pelvis revealed a large infra-renal abdominal aortic aneurysm measuring 7.3 x 8.2 x 10 cm with extensive mural thrombus (single white arrow) that has ruptured, with active extravasation (black arrow) of contrast into the aneurysm sac and retroperitoneum with large right retroperitoneal hematoma (multiple white arrows).
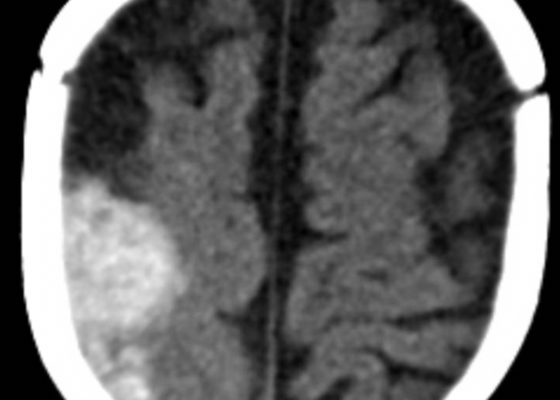
Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage in Severe Hemophilia A: A Rare Cause of Seizure in a Young Child
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G91DA computed tomography (CT) scan of the head without contrast was obtained out of concern for intracranial pathology due to the patient’s young age and the witnessed focal seizure. The CT showed a 4.2 x 1.2 x 1.5 cm acute extra-axial intracranial right frontoparietal hemorrhage favoring epidural over subdural hemorrhage given its lenticular shape. There was no underlying fracture, herniation or midline shift identified.
Open Fracture of the Patella
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BK9ZX-ray of the right knee showed evidence of an acute comminuted fracture of the patella (red arrows) with a suprapatellar joint effusion with gas (blue arrow). There was no evidence of joint dislocation or other osseous lesions.
Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Evaluate Intrahepatic Biliary Stent Function
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86S6NThe ultrasound image demonstrates severe intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation without an obvious intrahepatic obstructive lesion, as pointed out by the white arrows. The hepatic vasculature is well-distinguished from the biliary tree via color flow doppler, as seen by the white arrowheads.
Gastric Volvulus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8335FPoint of care ultrasound of his abdomen showed a large fluid filled structure with well-defined borders containing gastric contents extending from the xiphoid process to the umbilical region. No free fluid was noted on focus assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination. A computed tomography (CT) scan was performed emergently and it was noted that the patient had a significantly distended stomach and gastric volvulus (blue arrows) noted in the area of his paraesophageal/hiatal hernia.
Diagnosis and Treatment of an Anterior Shoulder Dislocation with Bedside Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z924Bedside ultrasound with the transducer placed on the posterior right shoulder revealed an anterior dislocation of the right humerus. This is evident by displacement of the humeral head further away from the posteriorly placed ultrasound transducer, and appears deep to the glenoid cavity. In a posterior shoulder dislocation, the humeral head would appear closer to the transducer (and the near field of the ultrasound image) than the glenoid. Note that a hypoechoic, heterogeneous fluid collection is within the joint space, compatible with a hematoma. A right shoulder X-ray confirmed the anterior dislocation with no evidence of fracture. Under direct ultrasound guidance the glenohumeral joint space was injected with 10 mL of 2% lidocaine as an intraarticular anesthetic block. The right shoulder was reduced using continual traction. Post-reduction ultrasound demonstrated a successful shoulder reduction, depicted by the humeral head being relocated to its anatomical location, adjacent to the glenoid cavity, as noted on the ultrasound image. A hematoma remains present within the joint space. Successful shoulder reduction was further confirmed by X-ray. The patient’s arm was placed in a sling and she was discharged home with orthopedics follow-up.
Brown Recluse Spider Bite
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TK99Examination of the skin revealed erythema and induration on the right lateral leg 12 cm in diameter with a 6 cm area of central necrosis and surrounding petechiae without fluctuance or crepitus. The patient was neurovascularly intact distal to the lesion. Laboratory values were within normal limits, except for an elevated C-reactive protein (5.31 mg/dL, normal range <0.70 mg/dL). The patient was diagnosed with ulceration secondary to envenomation from a brown recluse spider.
Wandering Spleen
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PS7CHistory of present illness: A 7-month-old boy presented for evaluation of an abdominal mass. Two weeks prior, the patient had a fever followed by 24 hours of vomiting and abdominal pain, which self-resolved. His pediatrician noted the mass on exam and referred child to the emergency department (ED). His abdominal exam was significant for a hard mass palpated to the
Levamisole Induced, Cocaine Associated Vasculitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8K35SAn asymmetric pattern of palpable purpura with bullae was noted on bilateral lower extremities with smaller patches on bilateral upper extremities. There was no tenderness or crepitus.