Open Fracture of the Patella
History of present illness:
The patient is a 53-year-old male brought in by ambulance to the emergency department (ED) as a trauma activation status post motor vehicle accident. The patient was the restrained driver of a vehicle that suffered a head-on-collision with another vehicle at freeway speeds. The patient was noted to have seatbelt markings across his chest and lower abdomen as well as a puncture wound to his right knee with instability of the patella on exam. Intravenous antibiotics and tetanus shot were administered in the ED.
Significant findings:
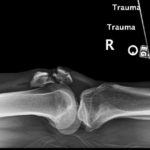
X-ray of the right knee showed evidence of an acute comminuted fracture of the patella (red arrows) with a suprapatellar joint effusion with gas (blue arrow). There was no evidence of joint dislocation or other osseous lesions.
Discussion:
The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body with many important functions. It helps in the mechanics of knee extension, protects the knee joint, and helps in providing nourishment for the articular cartilage and distal femur.1 Patella fractures account for about 1% of all skeletal injuries in children and adults.1 Most fractures of the patella result from direct forceful trauma, such as a fall onto a flexed knee or the knee hitting the dashboard during a motor vehicle accident.2 A patella fracture should be included in the differential whenever a patient presents with an acutely swollen knee and patella pain following direct or indirect trauma to the anterior knee.
Examination in a patient with a patella fracture may reveal a knee joint effusion or hemarthrosis and focal tenderness of the patella.1 The patient may be unable to extend the knee against gravity.1
Initial evaluation with radiographs includes anterior posterior (AP) view with the patient in the supine position with knee extended; lateral view with patient in the supine position and knee flexed at a 30-degree angle, and sunrise (axial) viewwith the patient in the supine position and the knee flexed.2 The radiograph for the sunrise view is taken with the x-ray beam tangential to the patella parallel to the long axis of the lower extremity.2 The lateral view is most sensitive for assessing displacement.2The sunrise view may not be necessary in the setting of a large effusion or severe pain, and is unnecessary if the fracture can be diagnosed on other views.2
Operative repair is recommended in the following circumstances:3
- Displaced fractures; fracture with greater than 2mm of articular step off
- Diastasis; fracture with greater than 3mm of fragment separation
- Comminuted fractures, with or without displacement of the articular surface
- Disruption of the extensor mechanism
- Persistent neurovascular deficits
- Any open fracture
Hospital course:
The patient in this case was found to have an open knee fracture and was urgently taken to the operating room. Per orthopedics, the patient’s patella was highly comminuted with over 6 fracture fragments noted and underwent open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). Patient improved during the course of his hospital stay. He remained on intravenous antibiotics for 3 days post-op for the open fracture. No major complications with the knee were noted. Per orthopedics, the patient was to be weight-bearing as tolerated with a knee immobilizer on the right lower extremity and follow up outpatient in two weeks.
Topics:
Trauma, patella fracture, X-ray.
References:
- Harris, RM. Fracture of the patella and injuries to the extensor mechanism. In: Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, eds. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002:1775.
- Melvin JS, Mehta S. Patellar fractures in adults. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2011;19(4):198-207.
- DeLee, J, Drez, D. Patellar fractures in the adult. In: DeLee JC, Drez D, eds. Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: Principles and Practice. 2nd Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Company; 2003:1760.
This research was supported (in whole or in part) by HCA Healthcare and/or an HCA Healthcare affiliated entity. The views expressed in this publication represent those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the official views of HCA Healthcare or any of its affiliated entities.