Issue 4:3
Point-of-care Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Bladder Hematoma vs. Hemorrhage
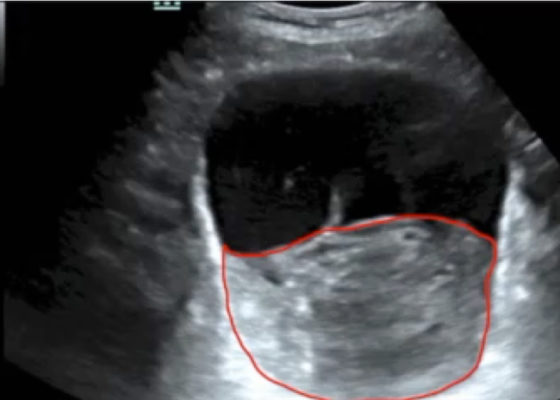
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8092FBladder POCUS demonstrated 500mL of post void residual fluid, indicative of retention. Half of the volume is hyperechoic (red circle); this is likely the bladder wall hematoma. Could also consider sonographic artifact, bladder mass, or cystitis.1-2
Asymptomatic CT Iodinated Contrast Extravasation of the Upper Extremity
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VK87The two radiographs demonstrate extravasation of radiopaque iodinated contrast in the lower left upper extremity with most seen in the left antecubital fossa and left proximal forearm. Extravasation is seen in the subcutaneous and subfascial tissue.
Oral Herpes Zoster
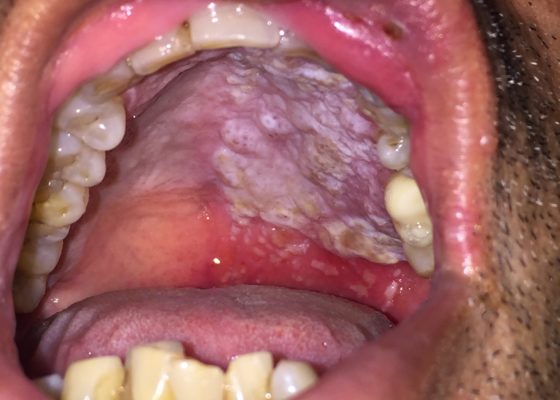
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QS69Physical exam findings revealed vesicular lesions on the lip, hard and soft palates which did not cross the midline. The lesions appeared in the distribution of the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve, consistent with herpes zoster.
Ruptured AAA Presenting with Unresponsiveness and Cardiac Arrest
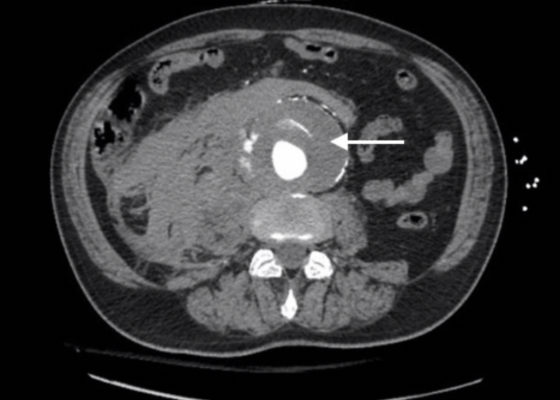
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M34QAxial CT images from the CT chest, abdomen and pelvis revealed a large infra-renal abdominal aortic aneurysm measuring 7.3 x 8.2 x 10 cm with extensive mural thrombus (single white arrow) that has ruptured, with active extravasation (black arrow) of contrast into the aneurysm sac and retroperitoneum with large right retroperitoneal hematoma (multiple white arrows).
Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage in Severe Hemophilia A: A Rare Cause of Seizure in a Young Child
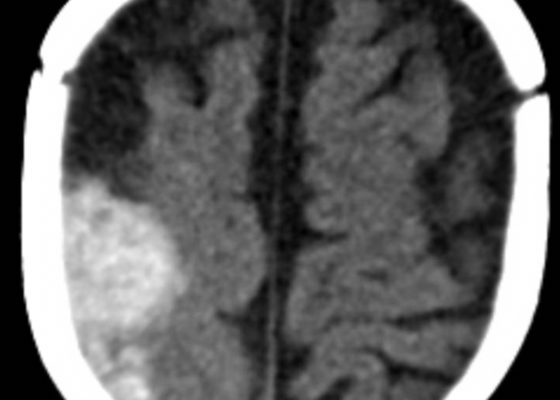
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G91DA computed tomography (CT) scan of the head without contrast was obtained out of concern for intracranial pathology due to the patient’s young age and the witnessed focal seizure. The CT showed a 4.2 x 1.2 x 1.5 cm acute extra-axial intracranial right frontoparietal hemorrhage favoring epidural over subdural hemorrhage given its lenticular shape. There was no underlying fracture, herniation or midline shift identified.
Open Fracture of the Patella
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BK9ZX-ray of the right knee showed evidence of an acute comminuted fracture of the patella (red arrows) with a suprapatellar joint effusion with gas (blue arrow). There was no evidence of joint dislocation or other osseous lesions.
Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Evaluate Intrahepatic Biliary Stent Function
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86S6NThe ultrasound image demonstrates severe intrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation without an obvious intrahepatic obstructive lesion, as pointed out by the white arrows. The hepatic vasculature is well-distinguished from the biliary tree via color flow doppler, as seen by the white arrowheads.
Gastric Volvulus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8335FPoint of care ultrasound of his abdomen showed a large fluid filled structure with well-defined borders containing gastric contents extending from the xiphoid process to the umbilical region. No free fluid was noted on focus assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination. A computed tomography (CT) scan was performed emergently and it was noted that the patient had a significantly distended stomach and gastric volvulus (blue arrows) noted in the area of his paraesophageal/hiatal hernia.