Issue 2:4
Pediatric Toxic Shock Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WK8JBy the end of this simulation session, the learner will be able to: 1) Recognize toxic shock syndrome. 2) Review the importance of a thorough physical exam. 3) Discuss management of toxic shock syndrome, including supportive care and the difference in antibiotic choices for streptococcal and staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome. 4) Appropriately disposition a patient suffering from toxic shock syndrome. 5) Communicate effectively with team members and nursing staff during a resuscitation of a critically ill patient.
Bedside Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Peritonsillar Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8N33NThe first video is an intraoral ultrasound using the high frequency endocavitary probe demonstrating an anechoic fluid collection adjacent to the patient’s enlarged left tonsil. The second video shows real-time ultrasound-guided successful drainage of the PTA.
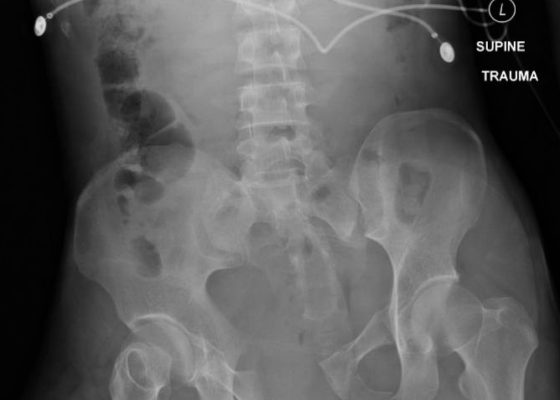
Bilateral Hip Dislocation in Unrestrained Driver
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HD0CThe initial radiograph of the pelvis revealed bilateral hip dislocations. Small bony fragments were noted in the right hip joint, suggestive of an underlying fracture. The sacroiliac joints and the pelvic ring were intact. In the emergency department, bilateral hip reductions were performed using the Captain Morgan technique.1 The post-reduction film showed reduction of the bilateral hip dislocations with extensive comminuted and displaced fractures of the right and left acetabula.
Open Book Pelvic Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CK7HThe initial radiograph of the pelvis shows an open-book pelvic fracture deformity with pubic symphyseal dislocation, left greater than right sacroiliac diastases, and fractures of the left superior and inferior pubic rami, right inferior pubic ramus, and left acetabular anterior column. The additional inlet and outlet radiographs of the pelvis after application of a pelvic binder also show an open book fracture with significant improvement of the widened pubic symphysis.
Oropharynx Ulceration
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87W60The photograph demonstrates an area of ulcerative tissue at the left palatine tonsil without surrounding erythema or purulent drainage. The computed tomography (CT) scan shows a large ulceration of the left soft palate and palatine tonsil (red arrow). There is no evidence of skull base osteomyelitis. There is suppurative lymphadenopathy with partial left jugular vein compression due to mass effect (yellow highlight). There is mild nasopharyngeal airway narrowing with architectural distortion (blue arrow), but no other evidence of airway obstruction.
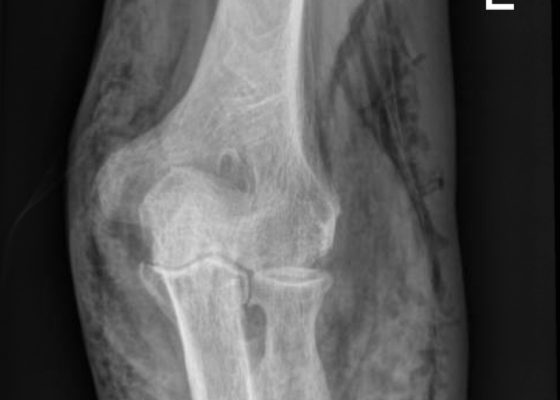
Subcutaneous Emphysema in Non-Necrotizing Soft Tissue Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8432MX-Rays of the elbow revealed diffuse striated lucencies throughout the soft tissue, consistent with extensive subcutaneous air throughout the superficial and deep tissues. There was no evidence of a fracture.
An Elderly Male with Amyand’s Hernia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80D13Ultrasound of the right scrotum shows a right inguinal hernia with an air-containing loop of bowel (white arrow) and a non-compressible appendix (yellow arrow). Coronal and axial views of abdomen-pelvis CT show a right inguinal hernia containing a loop of small bowel (white arrow) and appendix (yellow arrow).
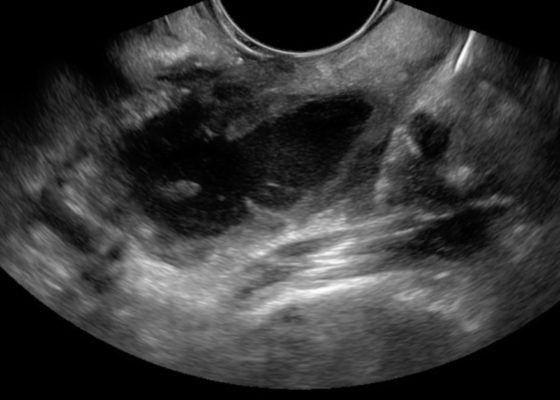
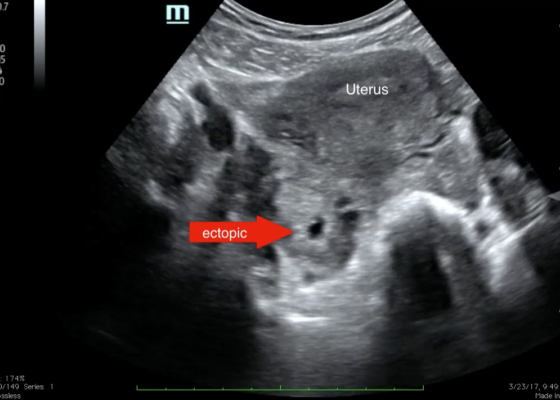
Point-of-care Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VK7VThe transabdominal pelvic ultrasound shows an empty uterus (annotated) with free fluid and a right sided extrauterine gestational sac representing an ectopic pregnancy (red arrow).