Trauma
Child Maltreatment Education: Utilizing an Escape Room Activity to Engage Learners on a Sensitive Topic
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J84H1CBy the end of the escape room, the learner should be able to: 1) understand the national and local prevalence of child maltreatment; 2) understand the different types of child maltreatment and common associated presentations; 3) know the local EMS agency reporting requirements; 4) understand when to make base hospital contact with respect to concern for maltreatment; 5) collaborate effectively as a team.
Case Report of a Tongue-Type Calcaneal Fracture
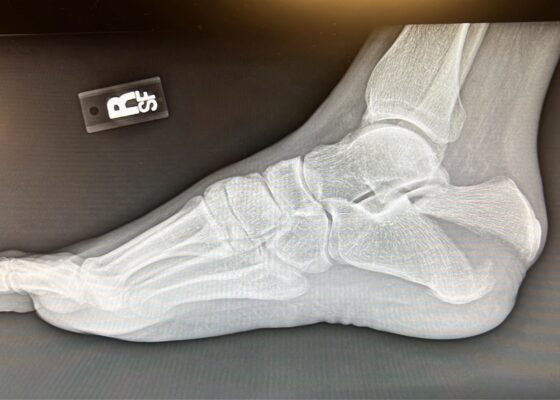
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NH11Examination of the right ankle demonstrated a large deformity of the superior talus with bruising and blanching of the overlying skin in the area of the Achilles tendon (see images 2,3). The remaining bones of the foot were not tender to palpation and the foot was neurovascularly intact throughout with only mild numbness in the area of the tented skin. Completing the trauma exam, the patient had no signs of head injury and no midline spinal tenderness to palpation. Inspection of the remaining long bones and joints showed no other injuries. There were mild skin scrapes on the right flank from the fall. X-rays of the right foot and ankle showed a longitudinal fracture of the calcaneal tuberosity from the articular surface to the posterior surface (see red outline) with extension into the subtalar joint (blue lines) and roughly 1.8 cm displacement between the fracture segments (yellow double arrow). These findings represented a tongue-type calcaneal bone fracture.
A Different Type of Tension Headache: A Case Report of Traumatic Tension Pneumocephalus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DH0GCT head without contrast demonstrated a minimally displaced fracture of the frontal sinuses at the midline underlying his known laceration that involved the anterior and posterior tables of the calvarium. This is seen on the sagittal view and indicated by the blue arrow. There was a small volume of underlying subarachnoid hemorrhage along the falx. There was also extensive pneumocephalus most pronounced along the bilateral anterior frontal convexity associated with the frontal sinus fracture, seen on the axial image and indicated by the red arrow. This pattern of air is commonly referred to as the “Mount Fuji” sign.6 Other intracranial air can also be seen on the sagittal image and is indicated by the white arrow.
Jefferson Fracture and the Classification System for Atlas Fractures, A Case Report
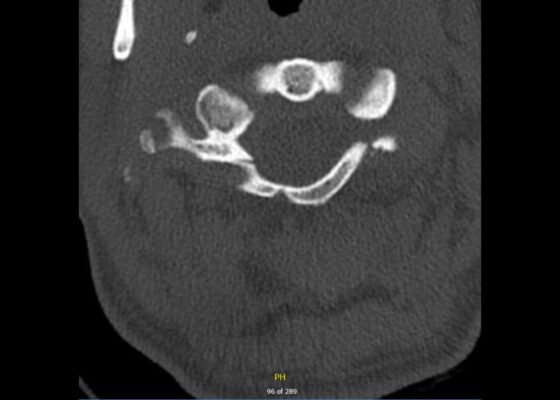
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88P9CComputed tomography (CT) revealed a burst fracture (Jefferson) of the anterior arch (white arrows) and of the posterior arch (yellow arrows) of the first cervical vertebrae (C1). There was also a fracture of the right lateral mass (blue arrow) of C1 with mild lateral subluxation of the lateral masses (curved arrows).
A Case Report of a Transected Carotid Artery Caused by a Stab Wound to the Neck
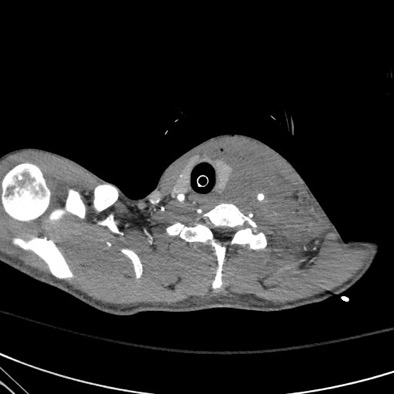
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BP8MThe post intubation chest x-ray (CXR) showed severe rightward displacement of the trachea (purple arrow). The computed tomography angiogram (CTA) showed transection of the left common carotid artery (LCCA), extensive neck hematoma without extravasation and severe tracheal deviation to the right (blue arrow). The intravenous (IV) contrasted chest computed tomography (CT) image showed a lateral contrast projection from the aortic arch at the level of the isthmus (green and pink arrows). There were no other significant injuries reported on the CT scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis.
Posterior Sternoclavicular Dislocation: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8363QChest X-ray revealed an inferiorly displaced right clavicle at the right sternoclavicular joint (blue arrow). A computed tomography angiogram (CTA) of the chest was therefore obtained and revealed a right posterior sternoclavicular dislocation with resultant compression of the left brachiocephalic vein (purple arrow). Even though the right clavicle is displaced, the anatomy of the brachiocephalic vein is such that it is positioned to the right of midline, placing the left brachiocephalic vein posterior to the right clavicle. The right brachiocephalic and common carotid artery were normal in appearance. The CTA also revealed a comminuted fracture of the left anterior second rib at the costochondral junction that had not been previously seen on the x-ray.
Case Report: Traumatic Tension Pneumothorax in a Pediatric Patient
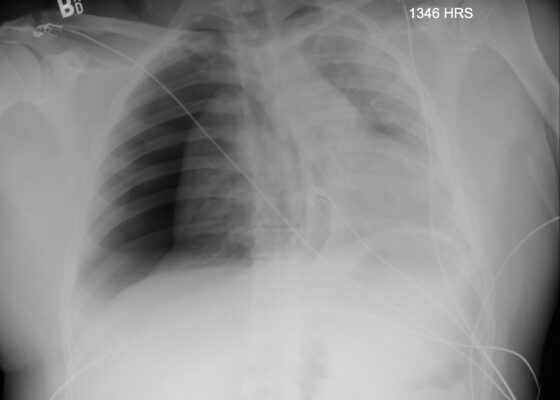
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZD1SChest X-ray demonstrated significant right-sided pneumothorax (with red outline showing border of collapsed right lung) with cardio mediastinal shift to the left (shown by blue arrows) indicative of a tension pneumothorax
Owning the Trauma Bay: Teaching Trauma Resuscitation to Emergency Medicine Residents and Nurses through In-situ Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WK9XABSTRACT: Audience: The following two cases were designed to address learning objectives specific to interns, junior residents, and senior residents in emergency medicine, as well as trauma-certified emergency nurses. Introduction: Traumatic and unintentional injuries account for 5.8 million deaths across the globe each year, with a high proportion of those deaths occurring within the initial hour from the time of