Pediatrics
Electrocardiogram Abnormalities Following Diphenhydramine Ingestion: A Case Report
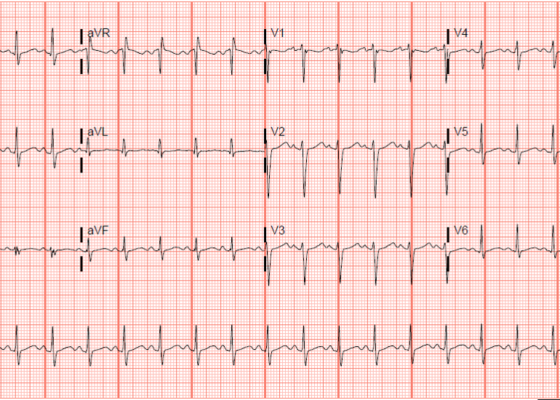
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85H1PThe blue arrow points to one of the terminal R waves in aVR, and the green arrow points to one of the large S waves in lead I, indicating right axis deviation. These findings are pathognomonic for sodium channel blockade. Due to the specific ECG findings and knowledge of diphenhydramine overdose, it was evident that these ECG findings were due to a cardiac sodium channel blockade. Sodium channels are essential within myocardial tissue to ensure the rapid upstroke of cardiac action potential, as well as rapid impulse conduction throughout cardiac tissue. Therefore, sodium channel blockers tend to exhibit significant dysrhythmic properties due to severe conduction disturbances.2 The blockage of the cardiac sodium channels appears as terminal R waves in aVR as well as terminal S waves in lead I due to delaying, and possibly blocking, the electrical conduction pathway of the heart. The orange arrows show resolution of terminal R wave in aVR and terminal S wave in lead I, after administration of sodium bicarbonate.
A Case of Community-Acquired Tuberculosis in an Infant Presenting with Pneumonia Refractory to Antibiotic Therapy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X07MChest radiographs during the initial presentation at seven weeks of life demonstrated right lower lobe (RLL) air space opacity on both PA and lateral views, compatible with pneumonia (referenced by yellow and green arrows, respectively). Repeat chest radiograph performed 12 days after the initial imaging revealed persistent right lower lobe opacity and right hilar fullness, seen as an opacified projection off of the mediastinal border as compared with the prior image, concerning for lymphadenopathy (designated by the aqua arrow). On the third presentation, computed tomography (CT) of the chest with intravenous contrast found persistent right lower lobe consolidation, innumerable 2-3 mm nodules, and surrounding ground glass opacities. This is best visualized as scattered areas of hyperdensity in the lung parenchyma. Axial images confirmed the presence of right hilar as well as subcarinal lymphadenopathy (indicated by white and pink arrows, respectively). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain with IV contrast was performed which showed a punctate focus of enhancement in the left precentral sulcus compatible with a tuberculoma (denoted with red arrow).
Respiratory Distress in the Pediatric ED: A Case-based Self-directed Learning Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T64MEducational Objectives: By the end of this module, learners will be able to: 1) recognize the unique pathophysiology for respiratory distress in the pediatric population and formulate a broad differential; 2) understand the treatment principles for the most common causes of respiratory distress in children; 3) navigate and apply validated clinical decision-making tools for treatment of pediatric respiratory illnesses.
Infant Botulism
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X35WAfter this simulation learners should be able to: 1) develop a differential diagnosis for the hypotonic infant, 2) recognize signs and symptoms of infant botulism, 3) recognize respiratory failure and secure the airway with appropriate rapid sequence intubation (RSI) medications, 4) initiate definitive treatment of infant botulism by mobilizing resources to obtain antitoxin, 5) continue supportive management and admit the patient to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU), 6) understand the pathophysiology and epidemiology of infant botulism, 7) develop communication and leadership skills when evaluating and managing critically ill infants.
Clinical and Radiologic Features of Fulminant Pediatric Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case Report
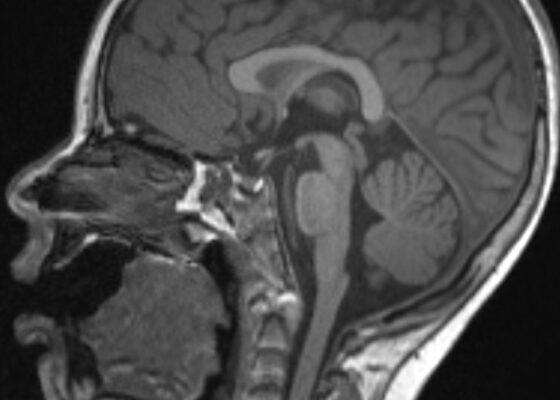
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JW75The neurology service was consulted in the ED and multisequence MRI and MR angiography (MRA) of the brain were obtained without and with IV contrast. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and T2-weighted-Fluid-Attentuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) sequences showed multifocal small areas of diffusion signal abnormality in the brainstem and basal ganglia (red asterisks) suggestive of ischemia. Additional multifocal bilateral supra- and infratentorial foci of signal abnormality including subcortical white matter and deep grey matter were highly concerning for encephalitis or demyelinating disease. MRI was repeated on day 3 and day 7 during evolution of disease.
A Lecture to Teach an Approach and Improve Resident Comfort in Leading Resuscitation of Young Infants in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8H36JBy the end of this lecture, participants should be able to: 1) apply a consistent approach to the initial resuscitation of a critically ill young infant in the emergency department; 2) select appropriate medications and equipment for use in resuscitation of critically ill young infants; 3) describe the components of the Pediatric Assessment Triangle,6 which can be used to identify critically ill infants and children; 4) improve comfort in resuscitating young infants in the emergency department.
An Unusual Case Report of a Toddler with Metastatic Neuroblastoma Mimicking Myasthenia Gravis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G35VWhile still in the ED, MRI with and without gadolinium contrast of the brain, orbits, and cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine were obtained to evaluate for possible CNS lesions including encephalitis, myelitis, or demyelination. Imaging, however, demonstrated multiple unexpected findings: a T1 hypointense, T2 hyperintense and heterogeneously enhancing right adrenal mass measuring 2.7 x 2.1 x 3 cm (yellow asterisk) along with heterogenous enhancement at the clivus, C6, C7, T7, T8, T12, and L3 vertebral bodies (red asterisks). There were otherwise no significant intracranial signal or structural abnormalities and normal orbits.
Not Another Presentation of Cellulitis: A Case Report of Erythromelalgia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD2KEpisodic tender, warm, erythematous swelling of the extremity experienced by this patient is typical of erythromelalgia. Erythematous streaking on the volar surface of the left forearm (red arrow) and tender, warm, erythematous blanching swelling was present on the palmar hand (yellow arrow). Most patients with erythromelalgia also have lower extremity involvement including the dorsum or sole of the foot and toes.1