Ultrasound
Thigh Mass Case Report
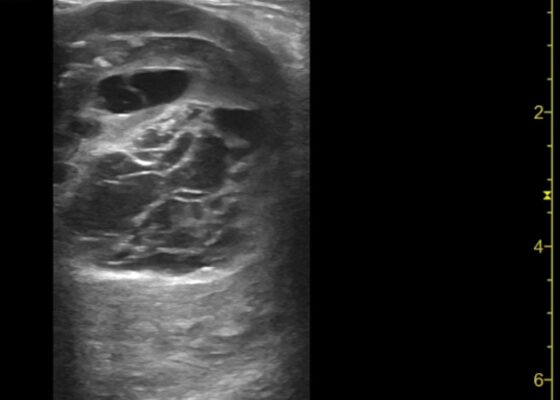
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QD3CPoint-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) demonstrates a large, subcutaneous mass with areas of mixed echogenicity. The mass contains fluid-filled, anechoic areas with internal septations and absent doppler flow. The majority of the mass appears isoechoic to the surrounding tissues with a hyperechoic border. Computed tomography (CT) of his right thigh shows a 16 x 8.1 x 9.5 cm heterogenous, complex mass within his hamstring muscles, inferior to the femur. His lab work was significant for a white blood cell (WBC) of 17.3 (103/µL).
A Case Report of May-Thurner Syndrome Identified on Abdominal Ultrasound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C64KThe patient initially received a venous doppler ultrasound that showed no evidence of a right or left femoropopliteal venous thrombus. Due to the high suspicion of a DVT given the symmetric swelling to the entire limb and acute onset of pain, a CTV was ordered. The transverse view of the CTV showed chronic thrombotic occlusion of the proximal left common iliac vein associated with compression from the right common iliac artery (figure 1, transverse image of CTA), as well as thrombotic occlusion of the left internal iliac vein tributary and corresponding left ascending lumbar vein. Given the previously mentioned clinical context, these features suggested the diagnosis of May-Thurner syndrome.
Vitreous Hemorrhage Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88D3BPoint of care ultrasound (POCUS) revealed hyperechoic material in the vitreous consistent with a vitreous hemorrhage. On the ultrasound images, there is visible hyperechoic debris seen floating in the vitreous as the patient moves his eye. Since the vitreous is typically anechoic (black) in color on ultrasound, turning up the gain on the ultrasound machine makes these findings easier to see and often highlights abnormalities, such as this hemorrhage (see annotated still).
Point-of-Care Ultrasound to Diagnose Molar Pregnancy: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82W7TA transabdominal point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) was initiated to determine whether an abnormality to the pregnancy could be identified. Curvilinear probe was used. Our transabdominal POCUS, in the transverse plane, showed a heterogenous mass with multiple anechoic areas in the uterus. The white arrow on the ultrasound identifies these findings. The classic “snowstorm” appearance was concerning for molar pregnancy.
Unravelling the Mystery of a Continuous Coil: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8PM00A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis with intravenous contrast for evaluation of new onset abdominal pain and distension was obtained in the emergency department. The axial view (CT Image A) shows the coil pack from the prior coil-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration procedure, seen in the left renal vein and gastric varix (red arrow). The path of the coil (yellow arrow) is continuous into the inferior vena cava (CT Image B). It is then seen (CT Image C) situated in the right ventricle (green arrow). Finally, the coil pack is seen in a coronal section, demonstrating its upward path (blue arrow) in the inferior vena cava. (CT Image D). Additional findings included ascites with advanced cirrhosis. As noted in the CT images, a vascular embolization coil was seen within a varix near the junction of the left renal vein. This appeared to have unraveled and extended superiorly into the inferior vena cava and ultimately into the right atrium and right ventricle.
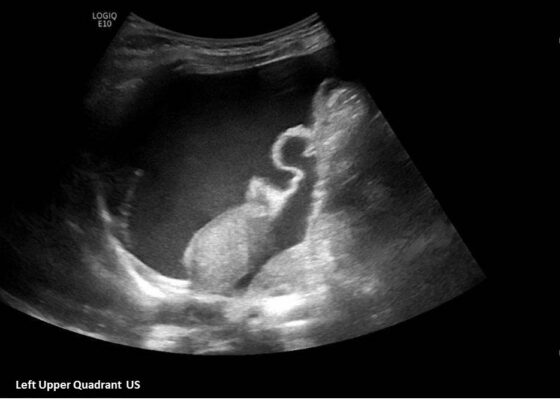
Ovarian Juvenile Granulosa Cell Tumor Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8035HA focused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) exam was performed initially to evaluate for intra-abdominal injury given the clinical picture. A phased-array ultrasound transducer was placed in sagittal orientation along the patient’s right and left flank, demonstrating extensive heterogenous fluid collections in Morrison’s pouch (red arrow), subphrenic space (solid green arrow), and splenorenal recess (dashed green arrow). To further evaluate, a phased-array transducer was placed over her pelvic area in transverse orientation, demonstrating, a large, heterogeneous mass (outlined in yellow arrows). The surgical team was promptly consulted and blood products were ordered. Although there was concern for impending hemorrhagic shock due to patient’s presenting tachycardia, the patient was hemodynamically stable enough for a CT scan of her chest, abdomen, and pelvis. The CT scan showed large-volume ascites, which exerted mass effect on all abdominal organs with centralization of bowel loops. Additionally, there was a large, 6.4 x 6.8 x 10.9-centimeter, midline pelvic mass (outlined in blue arrows).
Ureteral Obstruction and Ureteral Jet Identification—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8206GA point-of-care ultrasound of the urinary tract was performed, evaluating the kidneys and bladder. When imaging her kidneys, right-sided hydronephrosis was noted with a normal appearance to the left kidney. To further evaluate, a curvilinear probe was placed on her bladder with color doppler to assess for ureteral jets. Ureteral jets are seen as a flurry of color ejecting from each of the ureters as urine is released from the ureterovesical junction. In a healthy patient, this finding should be seen ejecting from both ureters every 1-3 minutes as the kidneys continue to filter the blood and create urine to be stored in the bladder. In our patient, however, ureteral jets were only noted on the left side (arrow), which was significant in further verifying our suspicion of right ureteral obstruction.
A Case Report of Glycogenic Hepatopathy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SQ0ZThe ultrasound images reveal hepatomegaly and an increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma that is diffuse. The increased echogenicity can be best appreciated by a comparison to surrounding structures. It is important to note that the increased echogenicity is non-focal and consistent throughout the entire liver in multiple views. These findings can be consistent with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis as well as glycogenic hepatopathy.