Photograph
A Case Report of Epiglottitis in an Adult Patient
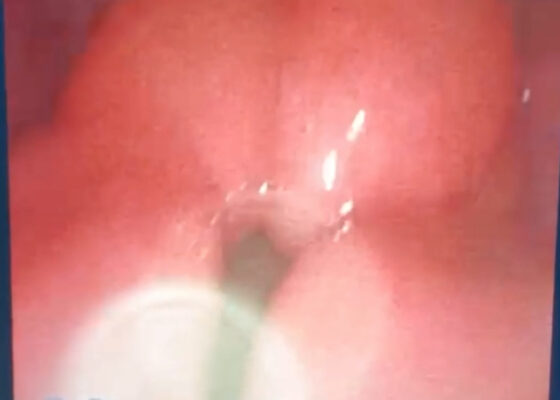
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QM09At the time of presentation to the ED, laboratory results were significant for leukocytosis to 11.8 x 109 white blood cells/L and a partial pressure of carbon dioxide of 52 mmHg on venous blood gas. Computed tomography (CT) of the soft tissue of the neck with contrast showed edematous swelling of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic fold with internal foci of gas (blue arrow) and partial effacement of the laryngopharyngeal airway and scattered cervical lymph nodes bilaterally (Figure 1). Findings were consistent with epiglottitis containing nonspecific air. Additionally, the pathognomonic “thumbprint sign” (yellow arrow) was found on lateral x-ray of the neck (Figure 2). The CT findings as shown in figure 3 illustrate lateral view of the swelling of the epiglottis, gas, and blockage of the airway.
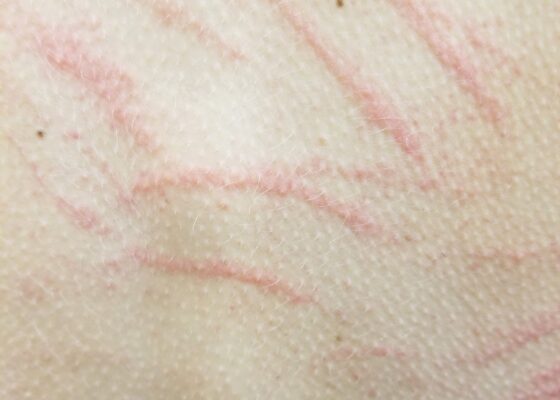
Not Another Presentation of Cellulitis: A Case Report of Erythromelalgia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD2KEpisodic tender, warm, erythematous swelling of the extremity experienced by this patient is typical of erythromelalgia. Erythematous streaking on the volar surface of the left forearm (red arrow) and tender, warm, erythematous blanching swelling was present on the palmar hand (yellow arrow). Most patients with erythromelalgia also have lower extremity involvement including the dorsum or sole of the foot and toes.1
Case Report of a Man with Right Eye Pain and Double Vision
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW7GABSTRACT: A 39-year-old previously healthy male presented with three days of right eye pressure and one day of binocular diplopia. He denied history of trauma, headache, or other neurological complaints. He had normal visual acuity, normal intraocular pressure, intact convergence, and no afferent pupillary defect. His neurologic examination was non-focal except for an inability to adduct the right eye past midline
A Culinary Misadventure: A Case Report of Shiitake Dermatitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X936Close visual examination revealed erythematous linear papules on her upper and lower back. No bullae, drainage, or sloughing of the skin was present. The rest of her body, including palms, soles, and mucosa, was spared.
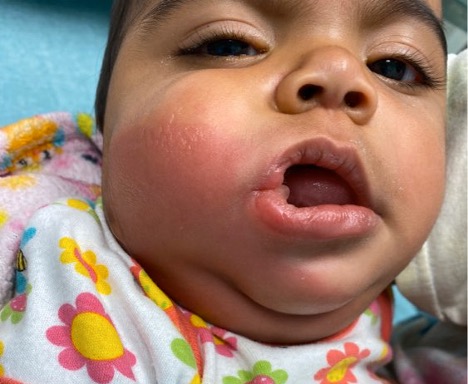
Case Report of Unusual Facial Swelling in an 8-Month-Old
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M06FFacial ultrasound revealed local inflammatory changes such as increased echogenicity and heterogeneity in the soft tissues of the right cheek, suggestive of soft tissue edema. There was evidence of a prominent right parotid gland with increased heterogeneity suggestive of a traumatic injury. Additionally, facial ultrasound demonstrated a 6mm ill-defined anechoic collection within the right cheek without increased doppler flow (green arrow), thought to represent a focal area of edema instead of an abscess.
Auricular Perichondritis after a “High Ear Piercing:” A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WH16On physical examination, there was erythema, swelling, warmth, and general exquisite tenderness of the superior aspect of the left pinna (the outer ear) but excluding the ear canal, lobe, tragus, and crus. There was no facial involvement. There was no fluctuance about the ear and no drainage of fluid. The preauricular lymph nodes were enlarged and tender, but the anterior cervical lymph nodes were not tender. There was no mastoid tenderness, protrusion of the ear, or interruption of the postauricular crease.
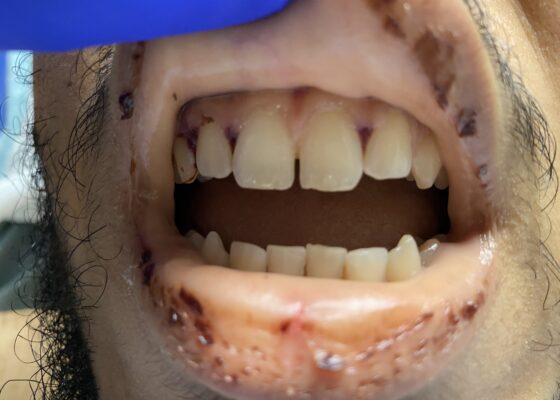
Case Report of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Previously Healthy Adult
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VK9MThe physical exam revealed globalized pallor of his skin as well as conjunctival pallor. Mucous membranes were found to be dry and pale with dried gingival hemorrhages apparent between teeth (image). Additionally, mild hepatosplenomegaly was noted. While in the ED, the patient’s urine was dark reddish-brown, which he then reported had been similarly discolored for the past 7 days.
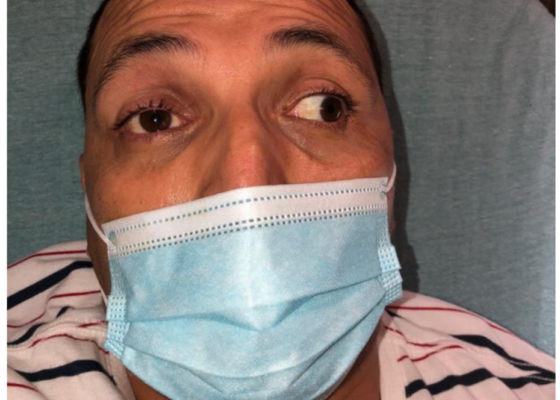
A Case Report of Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Presenting as Cranial Nerve 3 Palsy in a Young Female Patient with Migraines
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QW83Physical exam revealed a right pupil that was dilated compared to the left pupil, though both pupils were reactive. The patient also had impaired medial gaze on the right and ptosis of the right eyelid. Exam was otherwise unremarkable.