Photograph
Eye-Opener: A Case Report of Eyelid Taping as Presenting Symptom of Myasthenia Gravis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW8GPhysical exam was significant for a very pleasant, well-appearing female in no acute distress, noted to have clear plastic tape attached to her bilateral eyelids and brows (Image 1). When the tape was removed, she had bilateral ptosis, more significantly in the left eye (Image 2). She had no conjunctival injection or pallor. Her airway was patent and protected. She had no neck masses or carotid bruits. Her heart and lung exams were normal, with no evident respiratory distress. Her neurologic exam was further significant for limited extra-ocular movement (EOM). Her most notable deficits were with lateral and upward gaze (Video 1) indicative of weakness at the muscles innervated by cranial nerves III and VI. Her pupillary response was symmetric and brisk bilaterally. She had no additional cranial nerve deficits, slurred speech, or asymmetry in her strength or sensation throughout.
A Case Report on an Elusive Incident of Erythema Multiforme
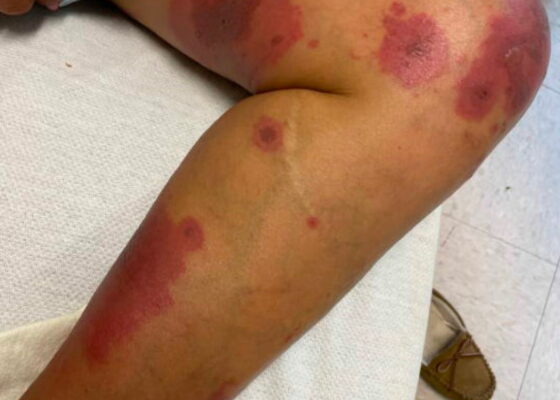
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BM0WHer physical exam was notable for multiple scattered tense vesicles on an erythematous base along the left and right lower extremities and right upper extremity. The lesions were excoriated and in different stages of evolution. No oral, mucosal, or conjunctival lesions were found. Physical exam was otherwise unremarkable.
A Case Report on Dermatomyositis in a Female Patient with Facial Rash and Swelling
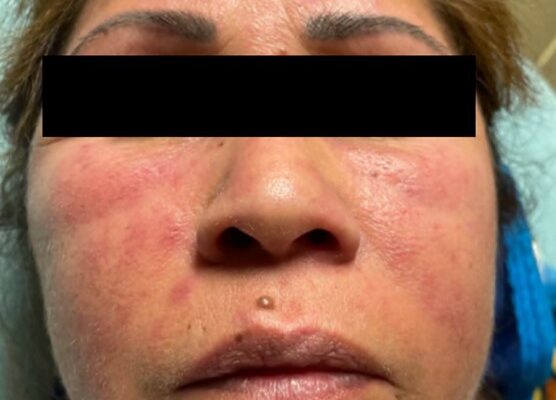
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8506DThe physical exam revealed significant periorbital swelling, facial edema, and a maculopapular rash across the upper chest, symmetrically across the extensor surfaces of the hands and the bilateral arms and thighs. The photograph of her face shows light-red to violaceous macules and patches, with inclusion of the nasolabial folds as well the forehead and upper eyelids with periorbital edema (heliotrope sign). The other rash images show “Shawl sign” (photograph of back showing erythema over the posterior aspect of the upper back), V sign (photograph of chest showing light-red violaceous plaque on mid-chest), Gottron's papules (photograph of hands showing light red scaly papules overlying the right proximal interphalangeal joint [R PIP] and the metacarpophalangeal joint [MCP], and holster sign (photograph of thigh showing light red patches on bilateral lateral thighs). This distribution of rashes is pathognomonic for DM.
A Man With Chest Pain After An Assault – A Case Report
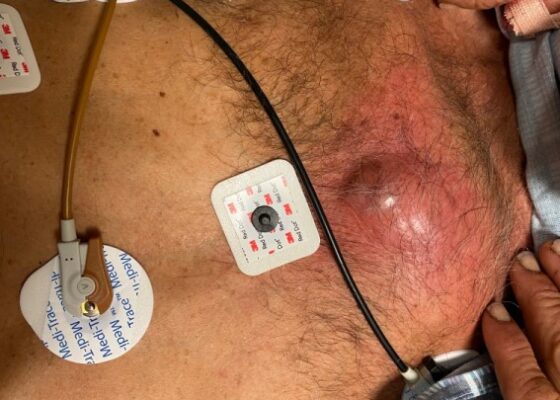
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J93SOn exam, we found a suspected chest wall abscess with surrounding erythema (blue arrow). The patient underwent CT of the chest which showed a comminuted displaced midsternal fracture (yellow arrow) with moderate fluid and air anteriorly (red arrow), consistent with an abscess. His laboratory results had no significant abnormalities.
A Case Report of Lateral Subtalar Dislocation: Emergency Medicine Assessment, Management and Disposition
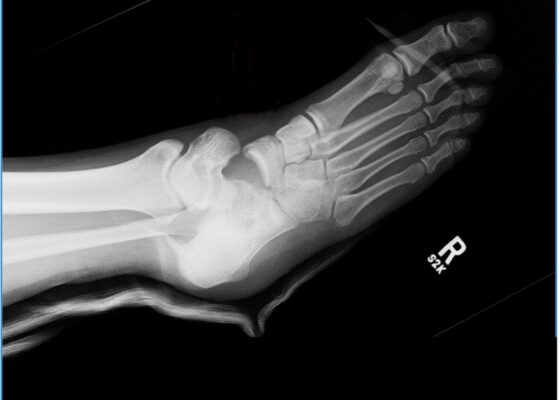
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SS8PIn a lateral subtalar dislocation, the navicular bone (red bone in 3D anatomy image) and the calcaneus (yellow bone in 3D anatomy image) dislocate laterally in relation to the talus (lavender bone in 3D anatomy image). Plain film oblique and lateral X-rays demonstrate the initial dislocation (talus in red, navicular in blue). It is clear in the initial lateral view that there is loss of the talar/navicular articulation (noted by red arrow). The anterior-posterior x-ray is more challenging to discern the anatomy; however, the talus (red dot) is laterally displaced in comparison to the navicular (blue dot).
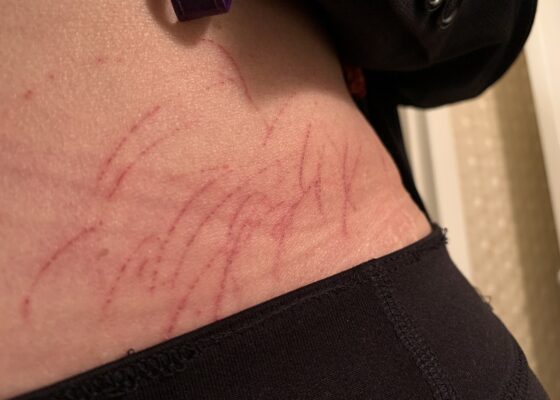
A Case Report of Dermatographia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8P05PPhysical examination was unremarkable except for the urticaria on the right aside of her abdomen (white arrow) with overlying excoriations (stars). Of note, there were no burrows, papules or vesicles in the typical locations including the webs of the fingers, wrists, axillae, areolae, or genitalia. Examination of the linear dermatographia clearly revealed superficial wheals, versus underlying serpiginous lesions.
A Case Report of Acute Compartment Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87061Inspection of the extremity revealed significant swelling with dark discoloration and multiple bullae (pre-operative photograph). Furthermore, notable swelling of the right foot was noted, which felt cold to palpation. Radiographs of pelvis, bilateral knees, tibia, fibula, and feet demonstrated no fractures or dislocations. The bilateral tibia and fibula X-ray revealed soft tissue swelling in the proximal legs, particularly evident in the right leg's AP view, which also showed numerous ovoid radiodensities in the anterior compartment, likely related to soft tissue injury. Post operative images are also provided demonstrating the patients’ four compartment fasciotomies which were loosely closed using staples.
The Clue is in the Eyes. A Case Report of Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DP9MThere was no appreciable esotropia or exotropia noted on straight gaze (yellow arrows). On extraocular muscle examination, patient was noted to have a complete left medial rectus palsy consistent with a left internuclear ophthalmoplegia (red arrow). This was evidence by both eyes easily gazing left (green arrows); however, with rightward gaze, her left eye failed to gaze past midline (red arrow).
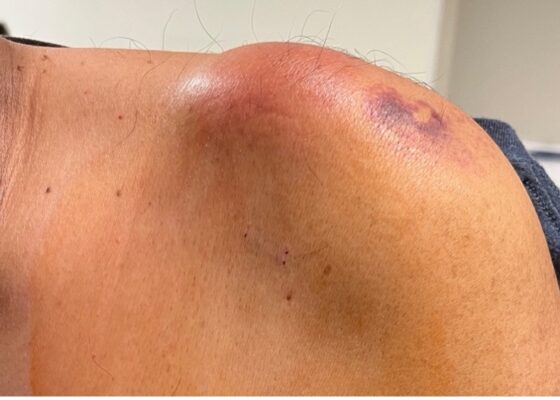
Septic Arthritis of the Acromioclavicular Joint: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP9NMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast was obtained of the shoulder and ankle, and results from both scans showed findings consistent with septic arthritis complicated by intraarticular abscesses. The MRI of the patient’s left acromioclavicular joint is shown as both a T1-weighted sequence in sagittal view and T2-weighted sequence in coronal view. The images show effusion (the dark fluid denoted by the red arrow) with an adjacent fluid collection (blue arrow). A T2-weighted MRI in coronal view of the patient’s right ankle showing multiple effusions (green arrows) and a fluid collection along the medial tibial cortex and subcutaneous tissues (yellow arrow).
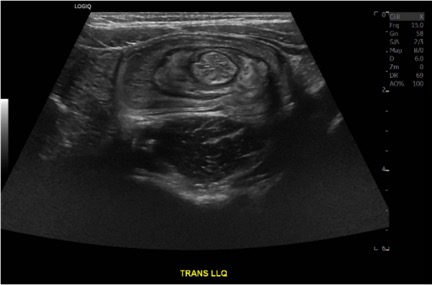
Case Report of a Child with Colocolic Intussusception with a Primary Lead Point
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8564QOn the initial ED visit, an abdominal ultrasound (US) was ordered which showed the classic intussusception finding of a target sign (yellow arrow), or concentric rings of telescoped bowel, on the transverse view of the left lower quadrant (LLQ).