Issue 4:4
Atypical Presentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82W6FBedside ultrasound revealed an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) with concern for dissection vs thrombus/hematoma due to an area of echogenicity within the lumen of the vessel, since normal blood vessels (including the aorta) have lumens that are uniformly anechoic. An intimal flap concerning for dissection appears as a hyperechoic stripe within the lumen of the vessel on ultrasound, often with a hypoechoic and/or anechoic area appreciated underneath the flap, indicating a separate area of blood flow. If this visualized area is of significant size, color doppler can be used to confirm blood flow on both sides of the flap. Given his bedside ultrasound findings, the patient underwent emergent computed tomography scan and was found to have an enlarged infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm, with acute intramural hematoma, extending into bilateral common iliac arteries.
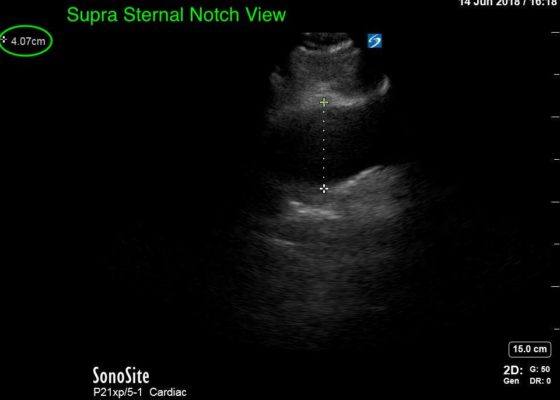
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Measured by Point of Care Ultrasound Suprasternal Notch View
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z64VPoint-of-care cardiac echocardiogram demonstrated a dilated ascending aorta (illustrated in red) measuring approximately 4 cm in the parasternal long axis (PLAX). A dilated aortic arch (illustrated in green) also measuring approximately 4 cm was appreciated using the suprasternal notch view (SSNV). A follow-up computed tomography angiogram (CTA) was performed, validating bedside ultrasound measurements.
Incarcerated Ventral Hernia of T-colon Resulting in Colon Perforation and Intraabdominal Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83W74History of present illness: A 75-year-old female with a remote history of rectal cancer presented to the emergency department with acute right upper abdominal pain. The pain had begun suddenly after lunch. On review of systems, the patient had mild nausea. Initial vital signs were within normal limit. She denied fever, chills, or vomiting. The physical examination revealed a distended,
Ultrasonographic Findings of Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8063SThe ultrasound video clip shows a longitudinal view of the AT during a dynamic exam. While the patient’s foot is gently passively dorsi/plantar flexed, the video demonstrates first a normal Achilles tendon (from the unaffected extremity) without disruption (highlighted by a yellow bracket on screen left). Then it shows an abnormal tendon (the patient’s affected side) with disruption of the typical linear tendon fibers (red arrow identifies area of rupture). Dynamic testing shows the movement of the distal stump of the AT is evident adjacent to hypoechoic fluid that is reactive edema or blood from the acute rupture.
Bezoars: An Interesting Case of Abdominal Pain
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VD1VComputed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and intravenous contrast was ordered to evaluate her symptoms. The CT showed three large collections of ingested material seen as hypodense material with circular rings surrounded by the hyperdense oral contrast (see red outlines). These findings are consistent with bezoars, the largest of which measured 11.5 x 7.8 cm. There was also thickening of the gastric wall (see blue outline), most notably at the pylorus, consistent with partial obstruction.
Medial Subtalar Dislocation: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QP9DOn examination, the patient had a significant deformity to his left foot and ankle. His left foot was pointed medially. His distal left tibia and fibula were visible and palpable upon inspection, with the overlying skin completely intact. There was no neurovascular compromise of the foot. X-ray demonstrated a subtalar dislocation of the left ankle (green arrow) and significant widening of the tibiotalar joint space (yellow arrow). There was associated soft tissue swelling but no acute displaced fractures were identified.
The Elusive Pheo: A Case Report of Pheochromocytoma in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KW63ED work-up: BMP within normal limits (WNL), white blood cell (WBC) 27.4, ECG showed sinus tachycardia, nonspecific ST segment abnormalities, BNP and troponin were within normal limits, HR 146 beats/minute, CT abdomen/pelvis showed a 10-cm-heterogenous enhancing left adrenal mass (anterior-posterior view [shown in red], lateral view [shown in blue]).
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G64HChest X-ray showed an elevated left hemi-diaphragm with superior displacement of a portion of intra-abdominal contents presumed to be the stomach (green arrowheads) with associated rightward mediastinal shift (yellow arrows). The diagnosis was confirmed by CT. Computed tomography imaging of the chest showed a large, left diaphragmatic defect measuring approximately 5.5 cm with herniation of the upper half of the stomach through the defect. The fundus of the stomach (blue arrow) herniated superiorly through the ruptured diaphragm (red arrow).