Issue 3:1
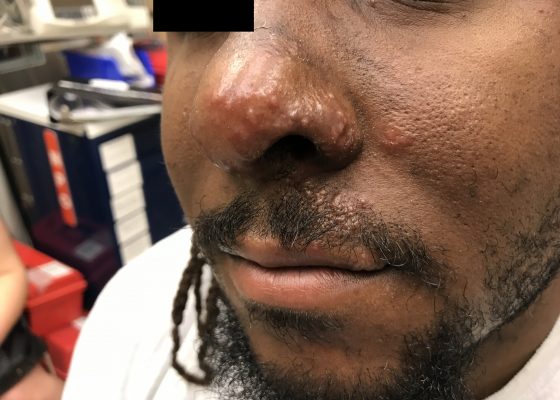
Hutchinson’s Sign
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8N040The unilateral distribution of vesicular lesions over the patient's left naris, cheek, and upper lip are consistent with Herpes zoster reactivation with Hutchinson's sign. Hutchinson's sign is a herpes zoster vesicle present on the tip or side of the nose.1 It reflects zoster involvement of the 1st branch of the trigeminal nerve, and is concerning for herpes zoster ophthalmicus.1 Herpes zoster vesicles may present as papular lesions or macular vesicles on an erythematous base.2,3 Emergent diagnosis must be made to prevent long-term visual sequelae.4
Viridans streptococci Intracranial Abscess Masquerading as Metastatic Disease
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CH05A non-contrast CT (Figure 1) revealed a large hypoattenuating left parietal lesion. When the CT was enhanced with intravenous contrast (Figure 2), the same lesion showed peripheral rim enhancement, suggestive of a brain abscess.
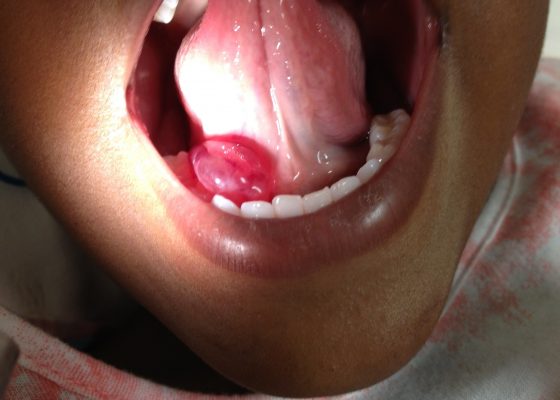
A Sublingual Mass in a 5-Year-Old Male
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8H622Oral ranula. On oral inspection he had a 3 x 1.5 cm, soft, non-tender, mobile, cystic, sublingual mass on the right aspect of the floor of his mouth that did not move with swallowing (Image 1). There was mild associated submandibular swelling on the right side of his face.
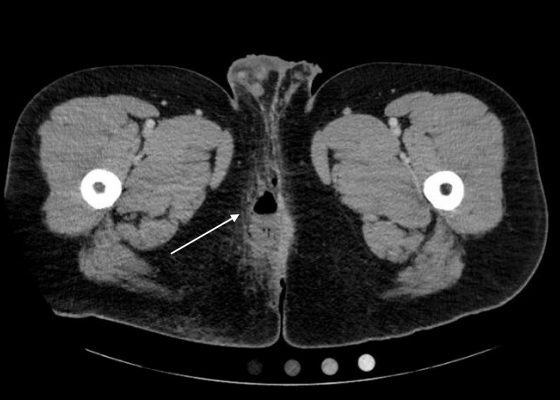
Pneumomediastinum After Cervical Stab Wound
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87P79Anteroposterior (AP) chest X-ray showed subcutaneous emphysema of the neck, surrounding the trachea (red arrows), right side greater than left, and a streak of gas adjacent to the aortic arch (white arrow). Computed tomography angiogram (CTA) of the neck showed air outside of the trachea, positive for pneumomediastinum (blue arrows).
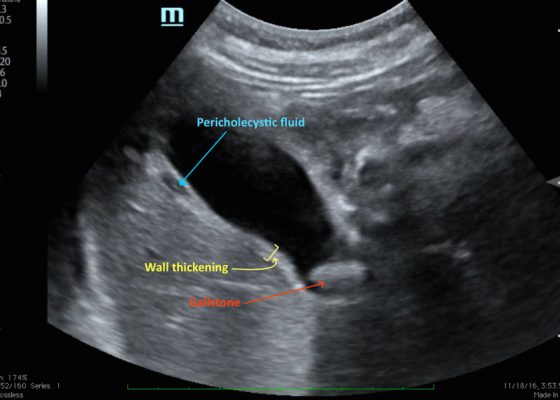
A Case of Acute Cholecystitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8405QBedside point-of-care ultrasound revealed a distended gallbladder, thickened gallbladder wall, pericholecystic fluid, and a stone in the neck of the gallbladder indicative of acute cholecystitis.
Computed Tomography and Ultrasound Diagnosis of Spontaneous Subcapsular Renal Hematoma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8062DBedside ultrasound was performed and demonstrated a hypoechoic area within the left kidney (images not shown). The non-contrast computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis shows a significantly enlarged left kidney and a region of high-attenuation encapsulating the left kidney, concerning for acute hemorrhage.
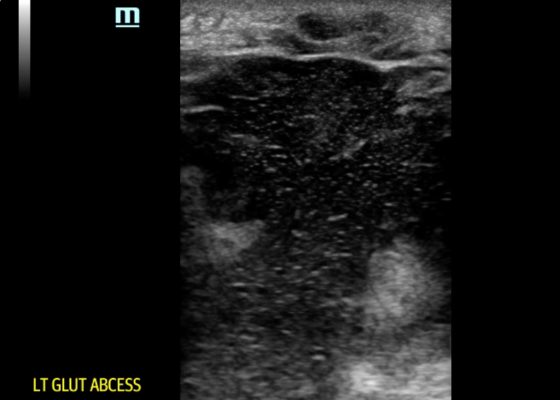
Point-of-care Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of a Gluteal Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VH1WPOCUS reveals a large, hypoechoic soft tissue abscess with debris and tracks extending to the bottom of the image. Furthermore, when compressed, movement of the abscess contents is appreciated. There is also superficial cobble-stoning consistent with overlying cellulitis and soft tissue edema.
Perianal Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QP81Computed Tomography (CT) of the Pelvis with intravenous (IV) contrast revealed a 5.7 cm x 2.4 cm air-fluid collection in the right perianal soft tissue along the right gluteal cleft, with surrounding fat stranding, consistent with a perianal abscess with cellulitis.