Latest Articles
Owning the Trauma Bay: Teaching Trauma Resuscitation to Emergency Medicine Residents and Nurses through In-situ Simulation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8WK9XABSTRACT: Audience: The following two cases were designed to address learning objectives specific to interns, junior residents, and senior residents in emergency medicine, as well as trauma-certified emergency nurses. Introduction: Traumatic and unintentional injuries account for 5.8 million deaths across the globe each year, with a high proportion of those deaths occurring within the initial hour from the time of
Simulated Mass Casualty Incident Triage Exercise for Training Medical Personnel
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82H1RBy the end of this exercise, learners should be able to (1) recite the basic START patient categories (2) discuss the physical exam signs associated with each START category, (3) assign roles to medical providers in a mass casualty scenario, (4) accurately categorize patients into triage categories: green, yellow, red, and black, and (5) manage limited resources when demand exceeds availability.
Necrotizing Fasciitis and Mediastinitis after Wisdom Tooth Extraction: A Case Report
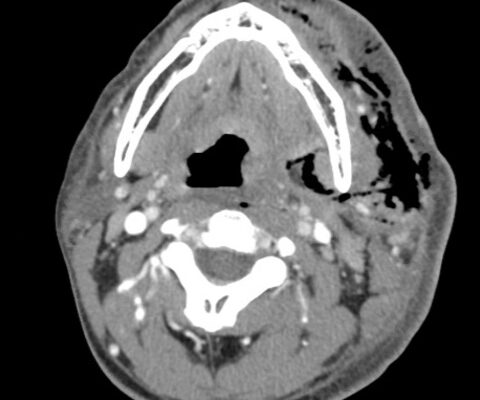
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XW7KComputer tomography (CT) imaging of soft tissues of the neck and of the chest/abdomen/pelvis revealed extensive swelling and subcutaneous air (see red arrows) on the left side of the face and neck extending to the left shoulder, as well as parapharyngeal/retropharyngeal spaces and posterior/superior mediastinum.
Adult Clavicular Fracture Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FM0TThe patient's chest and clavicular radiographs showed a comminuted displaced acute fracture of the right mid-clavicle (green, blue, yellow). The clavicular fracture was also visible on the chest computed tomography (CT). The remainder of his trauma workup was negative for acute findings.
Case Report of Distal Radioulnar Joint and Posterior Elbow Dislocation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89S6KRadiographs of the left elbow and wrist were obtained. Left elbow radiographs showed simple posterolateral dislocation of the olecranon (red) without fracture of the olecranon (red) or trochlea (blue). Left wrist lateral radiographs demonstrated DRUJ dislocation with dorsal displacement of the distal ulna (green) without fracture or widening of the radioulnar joint (purple). Post-reduction radiographs demonstrated appropriate alignment of the elbow with the trochlea seated in the olecranon and improved alignment of the DRUJ.
Bladder Diverticulum – A Case Report
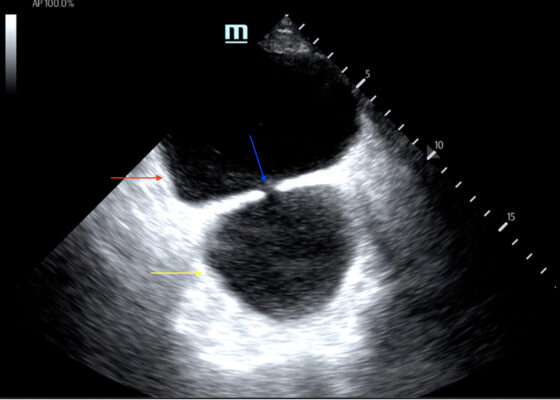
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8635COn examination, the patient was alert and oriented but in mild distress. Suprapubic fullness was noted upon abdominal palpation. Point of care ultrasound of the bladder showed two enlarged “bladders” with a central communication. Bedside total bladder volume was measured to be 1288 cm3 (the top “bladder” was measured to be 1011 cm3, while the bottom “diverticulum” was measured to be 277 cm3) by ultrasound.
The POCUS stills of the patient’s bladder demonstrated the bladder (red arrow) and bladder diverticulum (yellow arrow) with a central communication (blue arrow) in the transverse and sagittal views.
A Case Report of Ogilvie’s Syndrome in a 58-year-old Quadriplegic
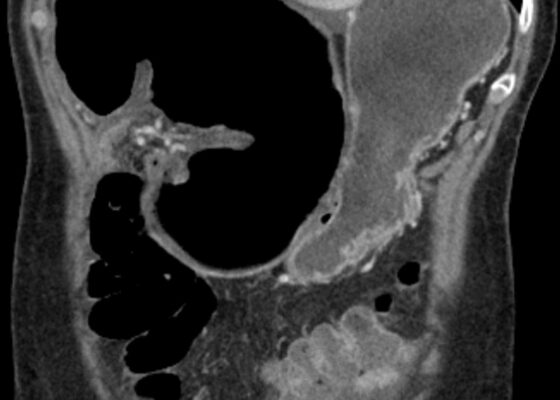
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82922Plain radiograph of the patient's abdomen revealed a gaseous distention of the colon. This is demonstrated as noted in the abdominal x-ray as gaseous distention, most notably in the large bowel (arrows) including the rectal region (large circle). Follow up computed tomography (CT) scan affirmed severe pancolonic gaseous distention measuring up to 11.2 cm, compatible with colonic pseudo-obstruction as noted by the large red arrows. No anatomical lesion or mechanical obstruction was observed, as well as no evidence of malignancy or other acute process.
Cecal Volvulus Diagnosed with a Whirl Sign: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8XM05The CT image demonstrates a “whirl sign” (red arrow) which is indicative of a volvulus. This image occurs when bowel, mesentery and vasculature rotate around a transition point causing an image similar to a hurricane on a weather map. When seen on a CT scan, a whirl sign suggests a high likelihood of either a closed loop bowel obstruction or volvulus in the cecum, sigmoid or midgut. In any of the cases, seeing a whirl sign strongly increases the need for emergent surgical management.
Paroxysmal Ventricular Standstill—A Case Report of all Ps and no QRS in Ventricular Asystole
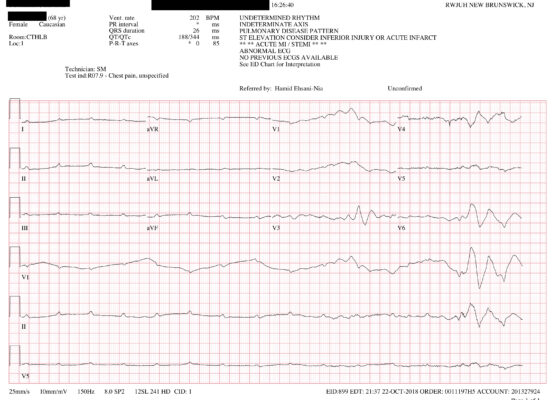
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SS79In route, it was proposed that this patient was suffering from a dysrhythmia due to the transient episodes of syncope with lack of ventricular activity on telemetry. Upon close examination of the rhythm strips as well as the ECG, P waves can be visualized without any accompanying QRS complexes lasting multiple seconds (ED ECG blue arrows). Additionally, the rhythm has an intrinsic rate of 100 beats per minute and has a consistent morphology with no evidence of ventricular activity due to the lack of QRS complexes. As a result, the rhythm likely originates in the atria with no passage of impulses into the ventricles through the atrioventricular (AV) node versus an accelerated ventricular rhythm where QRS complexes would be seen.8 These rhythm strips demonstrate an example of VS. There is preserved native atrial automaticity, with an intact sinoatrial (SA) node, with a complete lack of ventricular electrical activity