Ob/Gyn
The EMazing Race: A Novel Gamified Board and Clinical Practice Review for Emergency Medicine Residents
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52075By the end of this 2-hour session, learners will demonstrate their knowledge on the following board-related emergency medicine topics: Ob/GYN – links to 13.7 Complications of Delivery in Core Model of EM 2022, Renal/GU – links to 15.0 Renal and Urogenital Disorders in Core Model of EM 2022 and Splinting – links to 18.1.8.2 Extremity bony trauma, fracture in Core Model of EM 2022.
Critical Care Transport: Blunt Polytrauma in Pregnancy
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81366At the completion of this simulation participants will be able to 1) perform primary and secondary trauma surveys, 2) assess the neurovascular status of a tibia/fibula fracture, 3) appreciate anatomic and physiologic differences in pregnancy, 4) appropriately order analgesia and imaging, 5) recognize and treat hemorrhagic shock, 6) perform an extended focused assessment with sonography in trauma exam (eFAST) in undifferentiated hemorrhage, 7) identify a displaced pelvic fracture and properly apply a pelvic binder, and 8) obtain and interpret fetal heart rate using ultrasound.
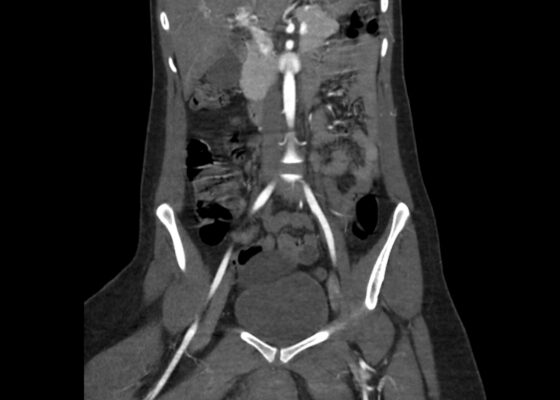
Computed Tomography Findings in Non-Obstetric Vulvar Hematoma: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8194HBedside ultrasound was first used to evaluate for evidence of abscess or cyst formation. Ultrasound demonstrated a hypoechoic area within the right labia without evidence of a cyst or abscess wall. Based on these findings, an angiogram CT of the pelvis was obtained which revealed a vulvar hematoma with evidence of active arterial extravasation. In both the coronal and axial view, there is an asymmetric area of isodensity in the right labia representing a hematoma (blue circled area). Angiography may show areas of active extravasation, which appears as hyperdensity within the area of hematoma (see red arrow in coronal plane).
High-Fidelity Simulation with Transvaginal Ultrasound in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8606QBy the end of the session, learners should be able to 1) recognize the clinical indications for transvaginal ultrasound in the ED, 2) practice the insertion, orientation, and sweeping motions used to perform a TVPOCUS study, 3) interpret transvaginal ultrasound images showing an IUP or alternative pathologies, and 4) understand proper barrier, disinfection, and storage techniques for endocavitary probes.