Neurology
Meningococcal Meningitis with Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TH1KBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: (1) manage a patient with altered mental status (AMS) with fever while maintaining a broad differential diagnosis, (2) recognize the risk factors for meningococcal meningitis, (3) manage a patient with worsening shock and perform appropriate resuscitation, (4) develop a differential diagnosis for thrombocytopenia and elevated international normalized ratio (INR) in an altered febrile hypotensive patient with rash, (5) manage the bleeding complications from WFS, (6) discuss the complications of meningococcal meningitis including WFS, and (7) review when meningitis prophylaxis is given.
Case Report: Altered with PRES
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW73On vitals, the patient was found to be consistently hypertensive to the 230s/160s. Point-of-care glucose was within normal limits. Noncontrast CT imaging of the head revealed no acute intracranial hemorrhage or evidence of ischemic stroke, but was remarkable for areas of biparietal subcortical low-attenuation (white arrows), concerning for PRES. Patient subsequently underwent CT angiogram imaging of the head with perfusion which revealed no large vessel occlusion.
A Different Type of Tension Headache: A Case Report of Traumatic Tension Pneumocephalus
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DH0GCT head without contrast demonstrated a minimally displaced fracture of the frontal sinuses at the midline underlying his known laceration that involved the anterior and posterior tables of the calvarium. This is seen on the sagittal view and indicated by the blue arrow. There was a small volume of underlying subarachnoid hemorrhage along the falx. There was also extensive pneumocephalus most pronounced along the bilateral anterior frontal convexity associated with the frontal sinus fracture, seen on the axial image and indicated by the red arrow. This pattern of air is commonly referred to as the “Mount Fuji” sign.6 Other intracranial air can also be seen on the sagittal image and is indicated by the white arrow.
Botulism
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FD0RBy the end of this simulation learners will be able to: 1) develop a differential for descending paralysis and recognize the signs and symptoms of botulism; 2) understand the importance of consulting public health authorities to obtain botulinum antitoxin in a timely fashion; 3) recognize that botulism will progress during the time period antitoxin is obtained. Early indications of respiratory compromise are expected to worsen during this time window.
Secondary learning objectives include: 4) employ advanced evaluation for neurogenic respiratory failure such as physical examination, negative inspiratory force (NIF), forced vital capacity (FVC), and partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2), 5) discuss and review the pathophysiology of botulism, 6) discuss the epidemiology of botulism.
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J85W6CBy the end of the simulation, the learner will be able to: 1) manage an acute seizure 2) discuss imaging modalities to diagnose PRES 3) discuss medical management of PRES.
A Case Report of Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Presenting as Cranial Nerve 3 Palsy in a Young Female Patient with Migraines
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QW83Physical exam revealed a right pupil that was dilated compared to the left pupil, though both pupils were reactive. The patient also had impaired medial gaze on the right and ptosis of the right eyelid. Exam was otherwise unremarkable.
Febrile Seizure Team-based Learning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JD12By the end of this educational session, the learner will: 1) list the characteristics of a simple febrile seizure; 2) discuss the management of a child with a simple vs. complex febrile seizure; 3) discuss the risk factors that correlate with an increased risk of a subsequent febrile seizure; 4) determine when a lumbar puncture should be considered in a febrile child with a seizure; 5) identify when to give anti-epileptics and construct an algorithm for their use; 6) discuss with parents, provide education and return precautions.
Pediatric Seizure Team-Based Learning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8MD22 By the end of this TBL session, learners should be able to: 1) Define features of simple versus complex febrile seizure, 2) Discuss which patients with seizure may require further diagnostic workup, 3) Summarize a discharge discussion for a patient with simple febrile seizures
4) Identify a differential diagnosis for pediatric patients presenting with seizure, 5) Define features of status epilepticus, 6) Review an algorithm for the pharmacologic management of status epilepticus, 7) Indicate medication dosing and routes of various benzodiazepine treatments, 8) Obtain a thorough history in an infant patient with seizures to recognize hyponatremia due to improperly prepared formula, 9) Choose the appropriate treatment for a patient with a hyponatremic seizure, 10) Describe the anatomy of a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt, 11) Relate a differential diagnosis of VP shunt malfunction, 12) Compare and contrast the neuroimaging options for a patient with a VP shunt
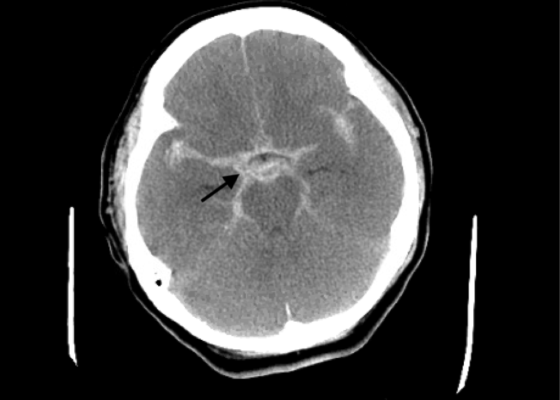
Post-Coital Sudden Cardiac Arrest Due to Non-Traumatic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage—A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8663NThe electrocardiogram demonstrated sinus tachycardia with ST segment elevation in lead aVR (black arrows) and diffuse ST depressions concerning for possible ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Given the events reported and the patient’s neurologic exam without sedation, non-contrast CT of the head was ordered; imaging showed evidence of a large subarachnoid hemorrhage, mostly at the level of the Circle of Willis (black arrow) concerning for an aneurysmal bleed as well as mild generalized white matter density suggestive of cerebral edema.
A Case Report of Epidural Hematoma After Traumatic Brain Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R059Non-contrast CT head demonstrated a right sided EDH (red arrow) with overlying scalp hematoma, left-sided subdural hematoma (blue arrow), and bilateral subarachnoid hemorrhages. No skull fractures were noted.