Dermatology
An Appy That Needs Epi: An Atypical Presentation of Anaphylaxis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80H14At the conclusion of the simulation, learners will be able to: 1) demonstrate ability to efficiently review patient records to optimize patient care and identify relevant details to current presentation, 2) rapidly assess a patient when there is a change in clinical status, 3) recognize the need to start resuscitative fluids for undifferentiated hypotension, 4) identify anaphylaxis, 5) demonstrate the medical management of anaphylaxis, 6) utilize the I-PASS framework to communicate with the inpatient team during the transition of care.
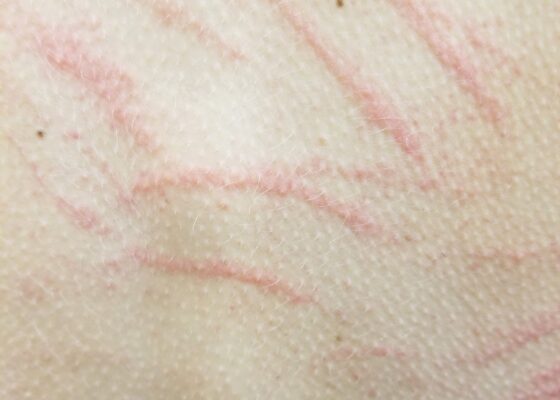
Not Another Presentation of Cellulitis: A Case Report of Erythromelalgia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BD2KEpisodic tender, warm, erythematous swelling of the extremity experienced by this patient is typical of erythromelalgia. Erythematous streaking on the volar surface of the left forearm (red arrow) and tender, warm, erythematous blanching swelling was present on the palmar hand (yellow arrow). Most patients with erythromelalgia also have lower extremity involvement including the dorsum or sole of the foot and toes.1
A Culinary Misadventure: A Case Report of Shiitake Dermatitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8X936Close visual examination revealed erythematous linear papules on her upper and lower back. No bullae, drainage, or sloughing of the skin was present. The rest of her body, including palms, soles, and mucosa, was spared.
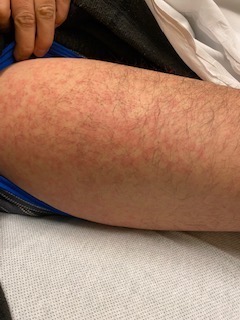
Case Report of COVID-19 Positive Male with Late-Onset Full Body Maculopapular Rash
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86W72The images demonstrate a diffuse, flat, maculopapular exanthema along the torso, bilateral upper and lower extremities, and neck without edema consistent with reported cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19. There are no surrounding bullae, vesicles, or draining. On palpation, there was blanching of the rash. Sensation to light touch was intact in all extremities. The findings were also apparent on the face with no mucosal involvement.
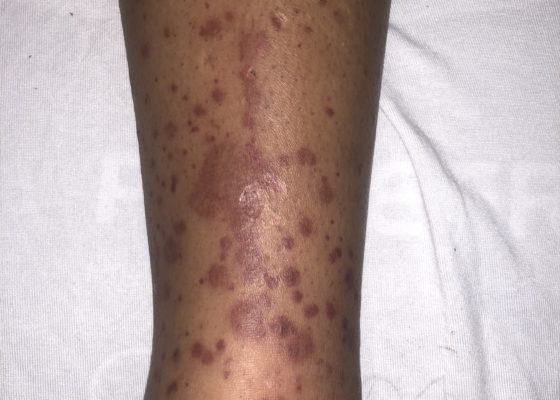
Henoch-Schönlein Purpura in the Adult
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QH08The images show a raised, palpable, purpuric rash on the lower extremities, surrounded by a mild, 1+ non-pitting edema. Several of the lesions are exfoliated with serous discharge. There is no surrounding erythema, fluctuance, or lymphangitis to suggest cellulitis. There was no tenderness to palpation; however, pruritus was exacerbated on palpation.
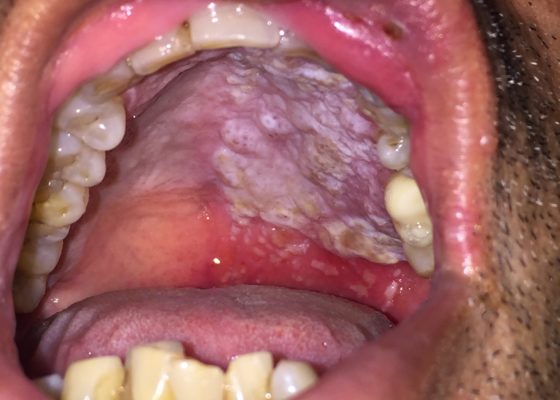
Oral Herpes Zoster
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QS69Physical exam findings revealed vesicular lesions on the lip, hard and soft palates which did not cross the midline. The lesions appeared in the distribution of the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve, consistent with herpes zoster.
Levamisole Induced, Cocaine Associated Vasculitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8K35SAn asymmetric pattern of palpable purpura with bullae was noted on bilateral lower extremities with smaller patches on bilateral upper extremities. There was no tenderness or crepitus.
Suspicious Skin Lesion in an 11-Year-Old Male
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8JK9TThe patient had a 5 cm ulcerative lesion with raised borders and a yellow, “fatty” center. There was no active drainage, site tenderness, or lymphadenopathy.