Photograph
A Case Report of an Atypical Presentation of Fournier’s Gangrene
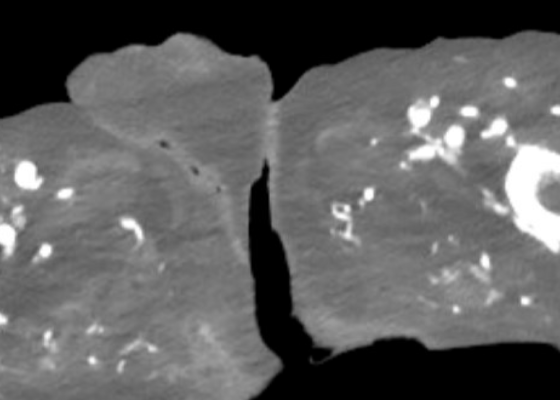
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/M5.52203A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis was significant for scrotal fluid and punctate gas locules (red arrow) without discrete evidence of invasion into the adjacent soft tissues, suspicious for Fournier’s gangrene. There was also fluid collection centered around the seminal vesicles suggestive of an abscess.
Case Report of a Dermatologic Reaction to Wound Closure Strips and Liquid Adhesive
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8.52256The patient removed the splint, and the wound were notable for erythematous bullae (blue arrow), blisters (yellow arrow), and skin maceration (red arrow) in the distribution under the wound closure strips. Of note, there was no surrounding erythema with poorly defined borders.
Case Report of Post-Operative Uvular Necrosis Following Intubation
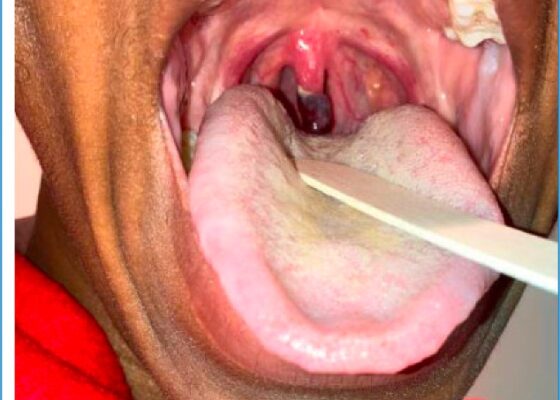
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8065JThe distal portion of her uvula was necrotic with a clear demarcation approximately halfway up the uvula. She had no trauma to the anterior oropharyngeal structures, tonsils, or adenoids. There were no lesions to the hard or soft palate. She had no carotid bruits or thrills, and no tenderness over the anterior portion of the neck.
Case Report: Iatrogenic Bowel Perforation Following Dental Procedure
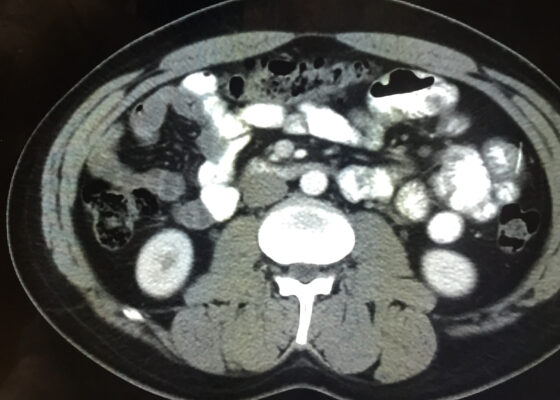
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CD38The patient’s abdominal CT demonstrated a metallic foreign body in the left side of the abdomen within the small bowel, without surrounding induration or abscess. Radiology questioned whether the metallic foreign object perforated the bowel. Seen in the cross-sectional CT image, there is a hyperdense linear structure transversing the small intestinal wall, given that a portion of the structure was located outside of the lumen of the bowel.
Eye-Opener: A Case Report of Eyelid Taping as Presenting Symptom of Myasthenia Gravis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NW8GPhysical exam was significant for a very pleasant, well-appearing female in no acute distress, noted to have clear plastic tape attached to her bilateral eyelids and brows (Image 1). When the tape was removed, she had bilateral ptosis, more significantly in the left eye (Image 2). She had no conjunctival injection or pallor. Her airway was patent and protected. She had no neck masses or carotid bruits. Her heart and lung exams were normal, with no evident respiratory distress. Her neurologic exam was further significant for limited extra-ocular movement (EOM). Her most notable deficits were with lateral and upward gaze (Video 1) indicative of weakness at the muscles innervated by cranial nerves III and VI. Her pupillary response was symmetric and brisk bilaterally. She had no additional cranial nerve deficits, slurred speech, or asymmetry in her strength or sensation throughout.
A Case Report on an Elusive Incident of Erythema Multiforme
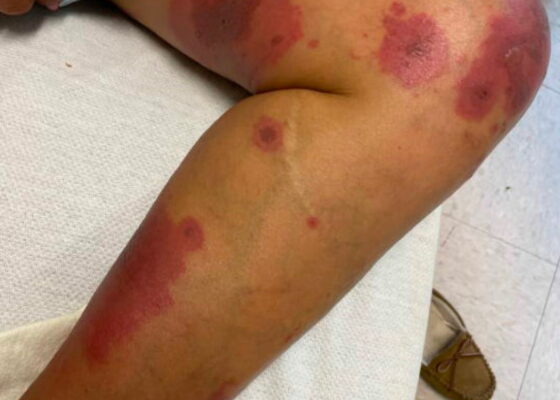
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8BM0WHer physical exam was notable for multiple scattered tense vesicles on an erythematous base along the left and right lower extremities and right upper extremity. The lesions were excoriated and in different stages of evolution. No oral, mucosal, or conjunctival lesions were found. Physical exam was otherwise unremarkable.
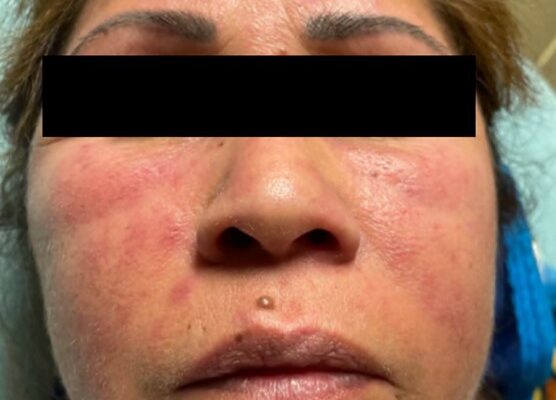
A Case Report on Dermatomyositis in a Female Patient with Facial Rash and Swelling
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8506DThe physical exam revealed significant periorbital swelling, facial edema, and a maculopapular rash across the upper chest, symmetrically across the extensor surfaces of the hands and the bilateral arms and thighs. The photograph of her face shows light-red to violaceous macules and patches, with inclusion of the nasolabial folds as well the forehead and upper eyelids with periorbital edema (heliotrope sign). The other rash images show “Shawl sign” (photograph of back showing erythema over the posterior aspect of the upper back), V sign (photograph of chest showing light-red violaceous plaque on mid-chest), Gottron's papules (photograph of hands showing light red scaly papules overlying the right proximal interphalangeal joint [R PIP] and the metacarpophalangeal joint [MCP], and holster sign (photograph of thigh showing light red patches on bilateral lateral thighs). This distribution of rashes is pathognomonic for DM.
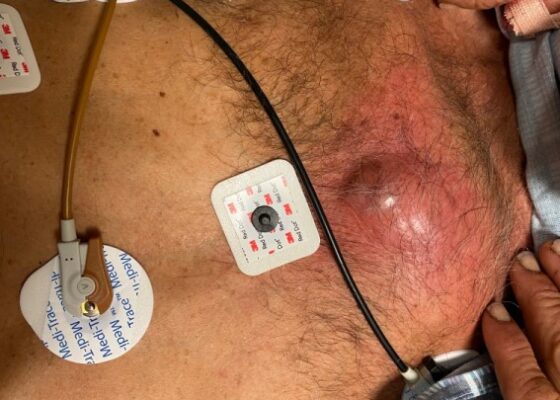
A Man With Chest Pain After An Assault – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J93SOn exam, we found a suspected chest wall abscess with surrounding erythema (blue arrow). The patient underwent CT of the chest which showed a comminuted displaced midsternal fracture (yellow arrow) with moderate fluid and air anteriorly (red arrow), consistent with an abscess. His laboratory results had no significant abnormalities.