Issue 3:3
Woman Swallows a “Handful of Pills”
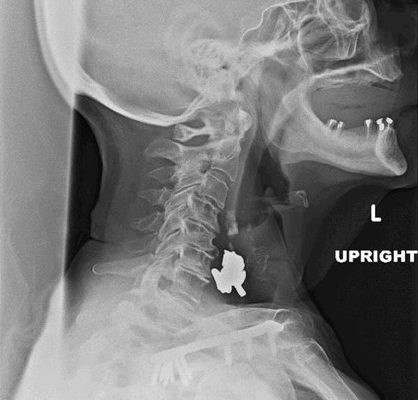
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8V64XSoft tissue lateral X-ray of neck was performed. The lateral soft tissue X-ray of the neck showed a metallic foreign body at the level cricoid.
Lisfranc Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8QD1MThe frontal view of the right foot showed divergent dislocation of the second through fifth metatarsal bones (red outlines) consistent with Lisfranc injury. Though the Lisfranc ligament is not visualized by radiograph, the yellow markings represent the location of the Lisfranc ligament between the medial cuneiform (blue dot) and the base of the second metatarsal bone. The first metatarsal and the medial cuneiform remain congruent. The lateral view shows dorsal dislocation of the midfoot (pink circle) consistent with instability. There is associated extensive midfoot soft tissue swelling.
Incidental Hiatal Hernia on Chest X-ray
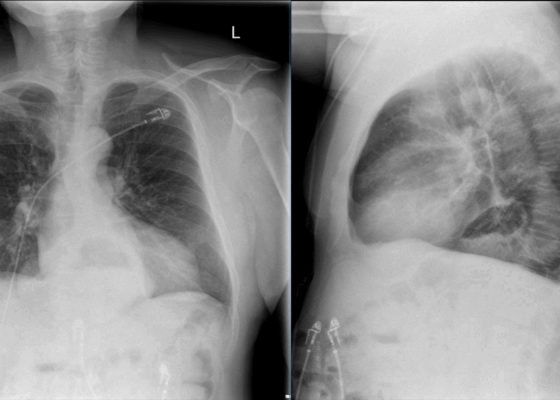
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KP8SThe two-view chest X-ray shows mild opacification of the bilateral lower lobes concerning for pneumonia (red arrows). Incidental retrocardiac opacity with air-fluid level consistent with large hiatal hernia is also observed (green arrow).
Button Battery in Esophagus
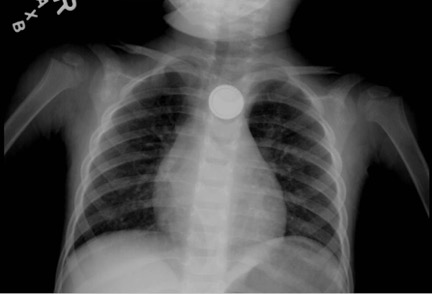
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8FW6VChest radiograph showed the presence of a round radiopaque foreign body in the mid-chest. It was suspected to be in the esophagus rather than in the trachea due to the en-face positioning of the foreign body. The foreign body demonstrated two concentric ring circles concerning for a “double ring” or “halo" sign, which was suggestive of the presence of a button battery rather than a coin.
Pediatric Foreign Body Aspiration
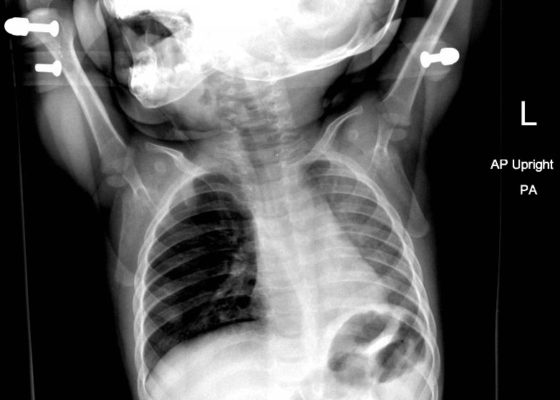
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B648Chest radiograph showed increased radiolucency (red arrow) and flattening of the diaphragm on the right side (blue arrow) consistent with hyperinflation of the right lung, as well as left mediastinal shift (green arrow), indicating obstruction.
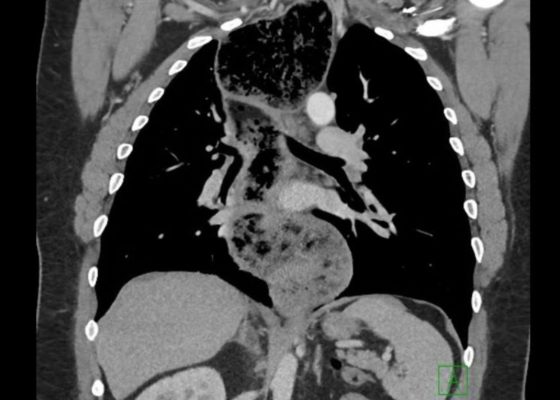
Achalasia: An Uncommon Presentation with Classic Imaging
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J86D2BThe chest X-ray demonstrated a markedly widened mediastinum (red brackets), raising concern for thoracic aortic aneurysm/aortic dissection, which prompted labs and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the chest. The CT revealed a dilated proximal esophagus that narrowed distally (yellow tracing and red arrow), with particulate material, mass-effect on the trachea (purple outline), and bilateral patchy opacities suggesting aspiration. Barium esophagram showed a drastically dilated esophagus filled with contrast (yellow arrow), terminating into the classic “bird’s beak sign” (red arrow) at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Esophageal manometry later confirmed achalasia, proving that widened mediastina can have unexpected etiologies.
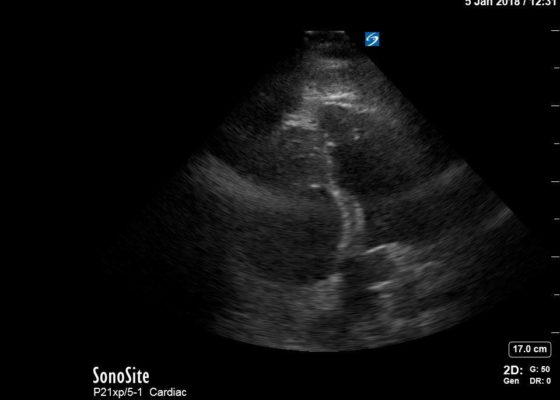
Right Ventricular Dilation in Patient With Submassive Pulmonary Embolism
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82P84Bedside echocardiography four chamber view revealed enlarged right ventricular (RV) to left ventricular (LV) ratio (greater than 1) on apical four-chamber view (see red and blue outlines respectively). The right atrium is not clearly delineated in this image and therefore is not outlined. One can also rule out a large pericardial effusion as the cause of her dyspnea, since there is no large hypoechoic collection surrounding the heart on either four- chamber view or parasternal long view.
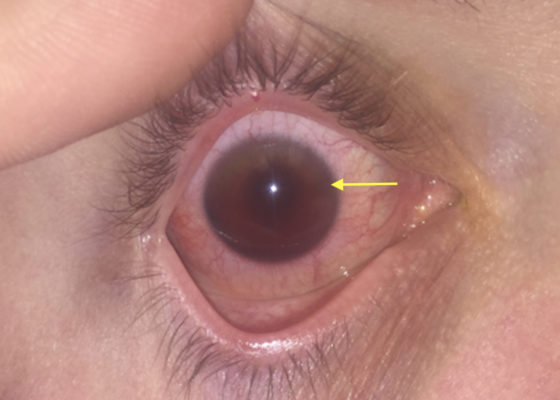
Traumatic Hyphema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8Z04SUpon initial evaluation, the patient had an obvious hyphema in the right eye with associated conjunctival injection. Initially, the bleeding in the anterior chamber was cloudy just above the level of the pupil (yellow arrow), appearing to possibly be a grade II hyphema. There were no other signs of trauma to the eye under Wood’s lamp examination with fluorescein staining. The globe was intact. Intraocular pressure in the affected eye was 19 mmHg and 15 mmHg in the unaffected eye. Extraocular movements were full and intact. The pupil was 4 mm round and reactive to direct and consensual light. Visual acuity was greater than 20/200 in the affected eye compared to 20/25 in the unaffected eye. After an observation period of two hours, with the patient remaining upright, the hyphema had settled down to a rim in the lower anterior chamber (green arrow), a grade I hyphema.