CT
A Case Report of an Atypical Presentation of Fournier’s Gangrene
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/M5.52203A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis was significant for scrotal fluid and punctate gas locules (red arrow) without discrete evidence of invasion into the adjacent soft tissues, suspicious for Fournier’s gangrene. There was also fluid collection centered around the seminal vesicles suggestive of an abscess.
A Case Report of Facial Swelling and Crepitus Following a Dental Procedure
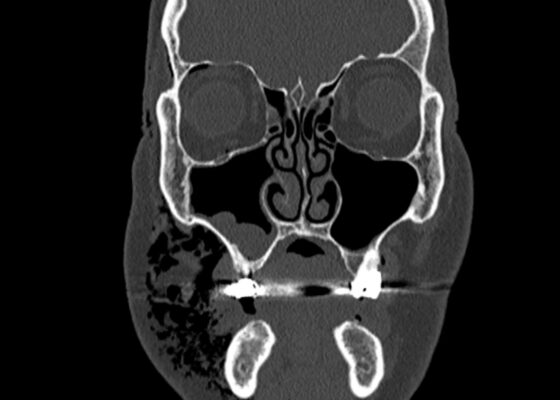
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83W8HGiven the physical exam findings of crepitus on the right neck up to the right lower eyelid, a maxillofacial CT scan without contrast was performed. It revealed diffuse subcutaneous air within the soft tissues of the face and neck and free air within the pre-septal soft tissue of the right eye, appearing as hyperlucent (dark) areas on CT within the soft tissue planes (blue outline). It showed no evidence of post-septal free air. A single-view chest X-ray was also performed and was unremarkable except for incompletely imaged soft tissue gas in the right lower neck (blue outline). On flexible fiberoptic laryngoscopy performed by ENT, the oropharynx appeared diffusely edematous and narrowed.
Case Report: Iatrogenic Bowel Perforation Following Dental Procedure
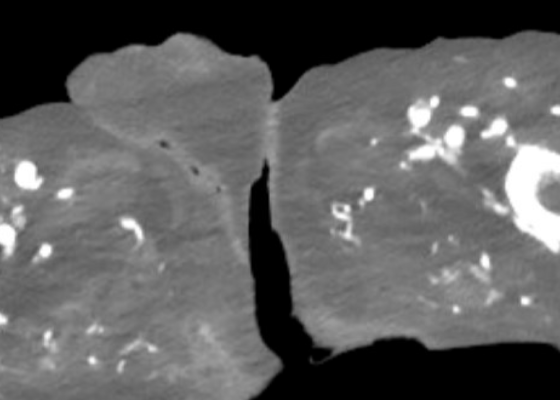
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CD38The patient’s abdominal CT demonstrated a metallic foreign body in the left side of the abdomen within the small bowel, without surrounding induration or abscess. Radiology questioned whether the metallic foreign object perforated the bowel. Seen in the cross-sectional CT image, there is a hyperdense linear structure transversing the small intestinal wall, given that a portion of the structure was located outside of the lumen of the bowel.
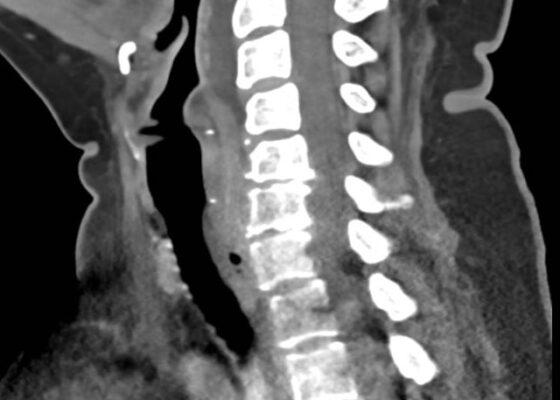
A Case Report of an Unstable C-spine Fracture in the Emergency Department
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8SK90The initial workup in the ED showed an acute displaced fracture of the left occipital condyle (CT-coronal, fracture of the left occipital condyle, red arrow; displacement, orange line), a shattered left lateral mass with involvement of the vertebral canal (CT-axial, red arrow), and malalignment of the craniocervical junction (CT-sagittal, red outline). The CT angiogram head and neck showed a possible irregularity in the left vertebral artery. The CT head without contrast had no significant findings.
A Case Report of Hydropic Gallbladder Presenting as Right Lower Quadrant Abdominal Pain
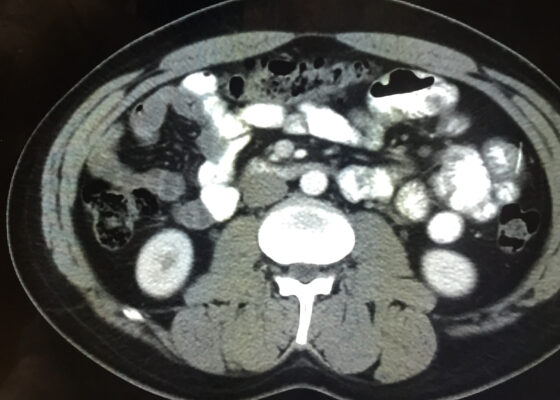
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8DD26Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast was ordered, and general surgery was consulted for the initial working diagnosis of acute appendicitis. However, the CT scan resulted with findings of a markedly distended gallbladder measuring approximately 14.5 x 4 centimeters (cm) with marked gallbladder wall thickening (magenta) and pericholecystic fat stranding (cyan). The appendix was not dilated and had no inflammatory changes or edema. Follow-up right upper quadrant ultrasound confirmed the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis.
A Case Report of Right Atrial Thrombosis Complicated by Multiple Pulmonary Emboli: POCUS For the Win!
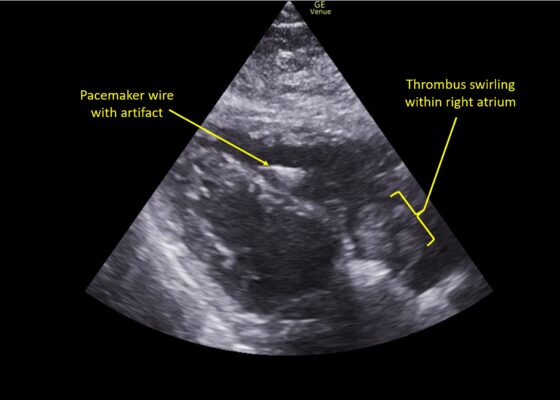
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8TM07Pulmonary POCUS was performed by the ED physician (GE Venue, C1-5-RS 5MHz curvilinear transducer), and lung examination was unremarkable with no pleural effusion, pneumothorax, or infiltrate. Subxiphoid views (GE Venue, 3Sc-RS 4MHz phased-array transducer) were obtained because this patient’s COPD with severe pulmonary hyperexpansion made parasternal and apical 4-chamber views suboptimal. A large thrombus can be seen within the right atrium (movie 1, images 1, 2). This has a serpiginous, rounded appearance and is mobile, appearing to swirl within the right atrium with intermittent extrusion through the tricuspid valve. A pacemaker wire is also visible within the right ventricle as a non-moving, hyperechoic, linear structure with posterior enhancement artifact. Pericardial effusion is not present.
Retropharyngeal Abscess in an Adult Patient Presenting with Neck Fullness and Dysphagia: A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8M36GContrast-enhanced CT soft tissue of the neck showed evidence of a prevertebral/retropharyngeal fluid collection, extending from the odontoid tip to the inferior C4 vertebral body margin, measuring 5.4 x 1.0 x 3.3 centimeters (cm) in size (yellow lines) without gross airway narrowing.
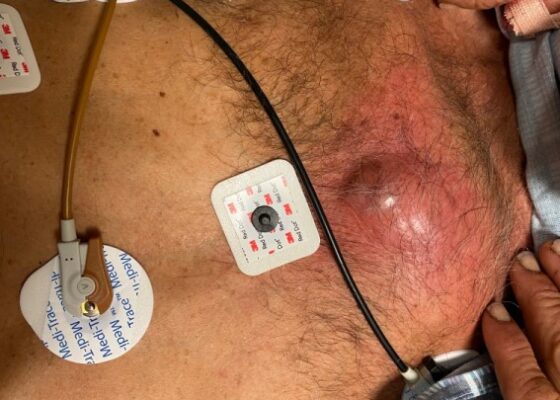
A Man With Chest Pain After An Assault – A Case Report
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8J93SOn exam, we found a suspected chest wall abscess with surrounding erythema (blue arrow). The patient underwent CT of the chest which showed a comminuted displaced midsternal fracture (yellow arrow) with moderate fluid and air anteriorly (red arrow), consistent with an abscess. His laboratory results had no significant abnormalities.