Latest Articles
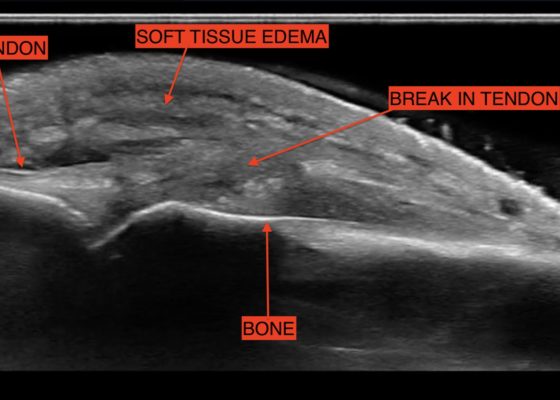
Fight Bite with Tendon Laceration
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8MP7QThe video shows a water bath ultrasound of the right 4th digit, demonstrating soft tissue swelling with a hypoechoic region along the tendon consistent with edema and tendon disruption (see video and annotated still image).
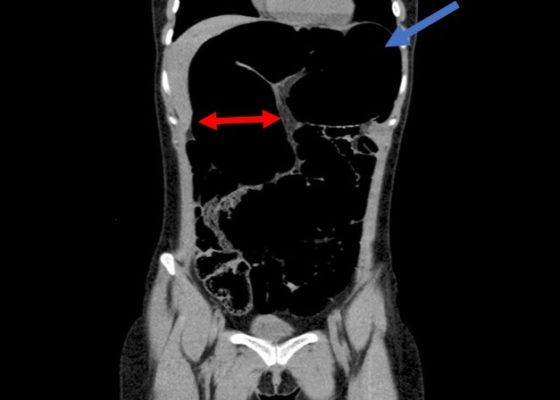
Recurrent Sigmoid Volvulus in a Young Female
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8GW5SComputed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis was obtained revealing a colonic volvulus in the left mid to upper abdomen (blue arrow) involving the distal transverse colon and descending colon, with gaseous colonic distention to 8.5 cm (red arrow). The characteristic “whirl pattern” is also present (yellow arrow). These findings are suggestive of a high-grade colonic obstruction. It was without evidence of pneumoperitoneum, pneumatosis, or drainable collection. Of note, a 3.6 cm dermoid tumor is also observable in the left adnexa (green arrow).
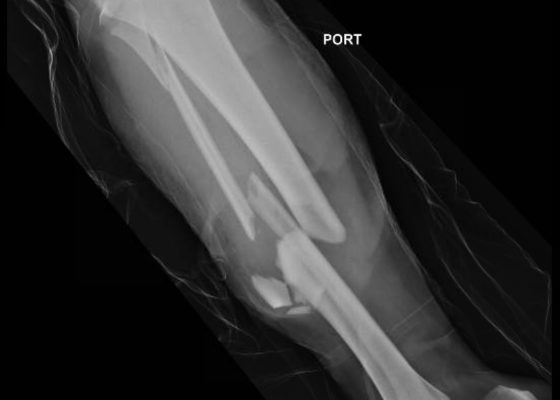
Bilateral Tibia/Fibula Fractures in Automobile versus Pedestrian Accident
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8C636Plain film shows severely comminuted and displaced mid tibia/fibula fractures of bilateral lower extremities (red arrows) and comminuted right fibular head (blue arrow) and proximal shaft fracture (yellow arrow).
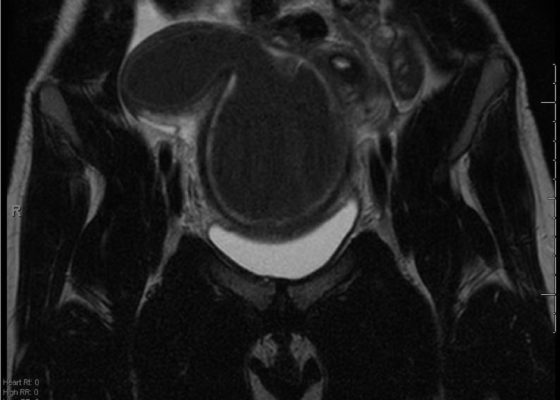
A Rare Cause of Pelvic Pain in a Teenage Girl
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J87D0WDue to pain out of proportion to her exam, an ultrasound of her pelvis was obtained and showed a blood-filled distended uterus, or hematometrocolpos (white arrow), with a 4.9 cm right ovarian cyst (blue arrow). A pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) then revealed an obstructed right hemi-vagina, normal left uterus and vagina and ipsilateral renal agenesis (red arrow) with normal left kidney (double arrow) consistent with obstructed hemivagina, ipsilateral renal agenesis (OHVIRA) syndrome. The patient underwent surgical repair with complete resolution of symptoms.
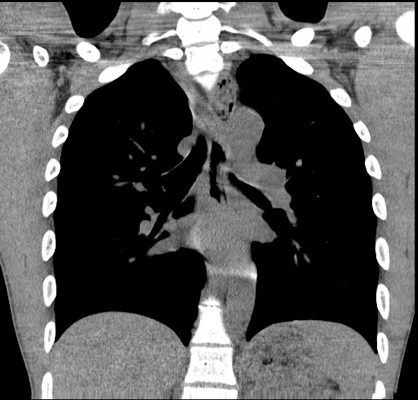
Acute Dysphagia in a 25-Year-Old Male
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J83P8FAfter an unremarkable chest radiograph was obtained, a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest was obtained due to possible co-ingestion of bones to rule out perforation. The CT scan demonstrated focal distention of the mid-esophagus due to an impacted food bolus (white arrow). An aberrant right subclavian artery (yellow arrow) was located just distal to the impaction site with partial compression of the esophagus (red arrow).
Dorsally-Displaced Metacarpal Dislocation-Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8ZW54A two-view radiograph of the right hand was obtained which revealed a dorsal dislocation of the distal fourth and fifth metacarpals (see red and blue outline, respectively) with a concomitant fracture of the distal fifth metacarpal (see yellow line) and avulsion fracture of the lateral aspect of the hamate (see green line). After reduction the fourth and fifth metacarpal dislocations are resolved; however, the distal fifth metacarpal fracture (yellow line) and avulsion fracture of the lateral aspect of the hamate (green line) are still visible.