Visual EM
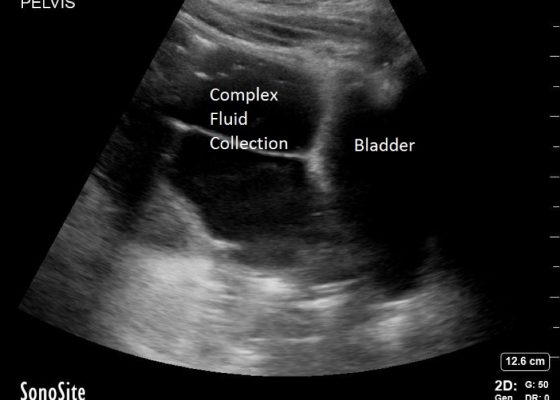
Perforated Gastric Ulcer with Intra-abdominal Abscess
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J82H0CBedside ultrasound revealed a large volume of free fluid in the right upper quadrant and in the pelvis. The fluid appeared complex with multiple septations. Its appearance was not consistent with ascites or acute intra-abdominal free fluid due to striations and pockets.
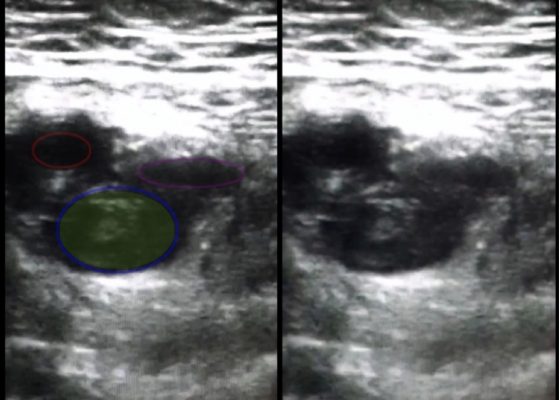
Use of Bedside Compression Ultrasonography for Diagnosis of Deep Venous Thrombosis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J81G94As shown in the still image of the performed ultrasound, a transverse view of the proximal-thigh revealed a visible thrombus (green shading) occluding the lumen of the left common femoral vein (blue ring), which was non-compressible when direct pressure was applied to the probe. Also visible is a patent and compressible branch of the common femoral vein (purple ring) and the femoral artery (red ring), highlighted by its thick vessel wall and pulsatile motion.
Open Pneumothorax
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88036A large chest wound was clinically obvious. A chest radiograph performed after intubation showed subcutaneous emphysema, an anterior rib fracture, and a right-sided pneumothorax. He was then taken to the operating room for further management.
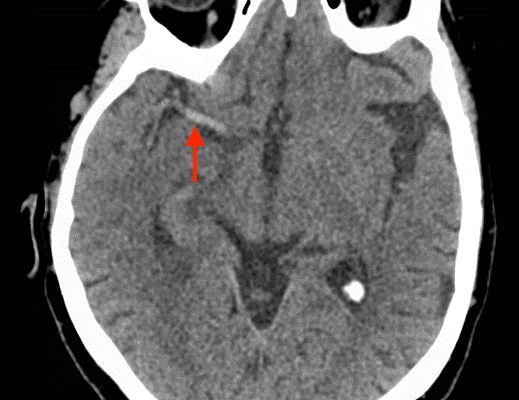
Dense MCA Sign
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8CS66A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan showed a hyperdensity along the right middle cerebral artery (MCA) consistent with acute thrombus. The red arrow highlights the hyperdensity in the annotated image.
Supracondylar Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8492PHistory of present illness: A 15-year-old male presented to the emergency department with right elbow pain after falling off a skateboard. The patient denied a decrease in strength or sensation but did endorse paresthesias to his hand. On exam, the patient had an obvious deformity of his right elbow with tenderness to palpation and decreased range of motion at the
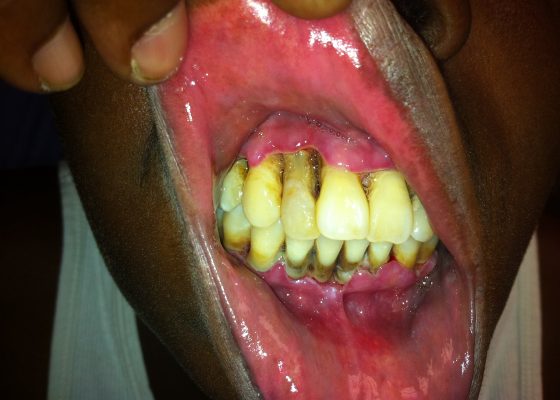
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8S88HPhysical examination revealed inflamed gingiva, ulceration, and soft tissue necrosis (Image 1) along with mandibular lymphadenopathy (not shown). Given her symptoms, poor oral care, and her immunocompromised state, she was given a diagnosis of Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG) or Vincent’s Angina.
Acute Aortic Dissection Presenting Exclusively as Lower Extremity Paresthesias
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NK57Chest x-ray and CT angiogram was performed to evaluate his thoracic and abdominal vasculature. Chest x-ray did not show any significant widening of the mediastinum. The CT angiogram demonstrated an intimal tear along the aortic arch separating a true and false aortic lumen, consistent with an acute aortic dissection. The true lumen (highlighted in blue in images 1-5) can be identified by continuity with an undissected part of the aorta. While the false lumen (highlighted in red in images 1-5) can be identified by its crescent shape and larger cross-sectional area.
Galeazzi Fracture
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8HS39The X-ray showed an acute comminuted fracture of the distal diaphysis of the radius with disruption of the distal radioulnar joint, consistent with a Galeazzi fracture. The patient was then splinted and taken for operative reduction and internal fixation the following day.
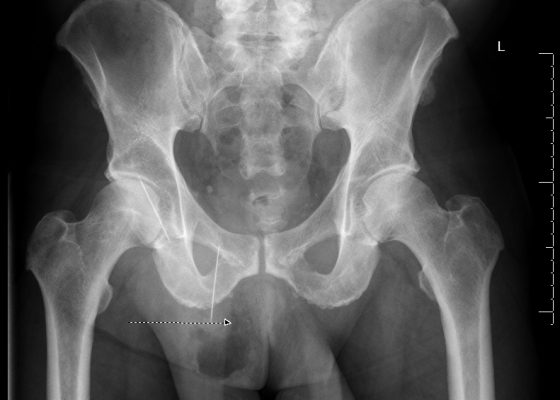
Bowel Perforation complicating an incarcerated inguinal hernia
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D30BThe AP and lateral pelvis x-rays revealed two sewing needles, 60 mm in length, within the soft tissue over the anterior right lower hemipelvis. In addition, the AP view showed emphysema involving the right hemiscrotum (arrow), concerning for perforated bowel.
Infectious Mononucleosis: Pharyngitis and Morbilliform Rash
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J88C7HHer physical exam was significant for bilateral tonsillar exudates, cervical lymphadenopathy, and a morbilliform rash that included the palms (Figure 1-4). Laboratory testing was significant for white blood cell (WBC) count of 16.5 thous/mcl with an elevation in absolute lymphocytes of > 10 thous/mcl. The monospot and EBV (Epstein-Barr virus) panel were positive.