Respiratory
Saddle Pulmonary Embolus
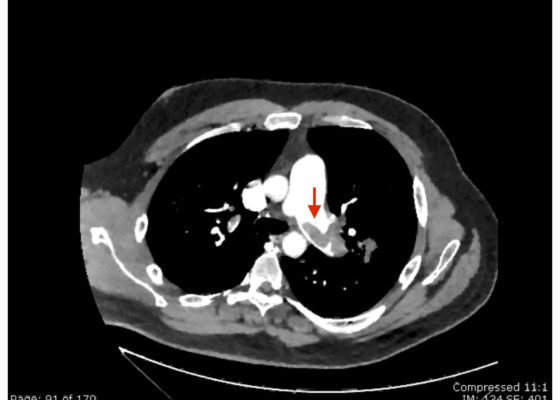
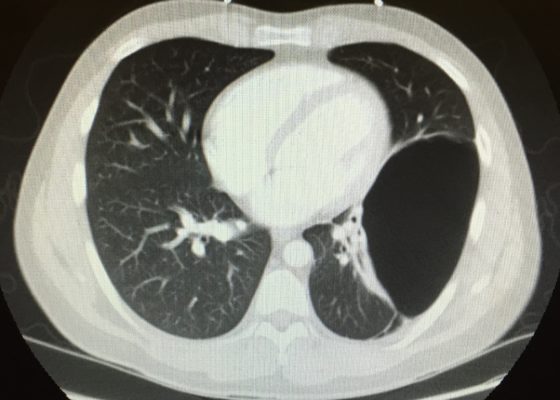
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8N63PAn electrocardiogram (ECG) showed evidence of right heart strain with an incomplete right bundle branch block, S1Q3T3 (see red arrow [S1], blue arrow [Q3], and black arrow [T3]), and ST-segment elevation in the septal leads (green arrows). Bedside echocardiography showed a dilated right ventricle with ventricular wall akinesis (red arrow) sparing the apex (purple arrow), which is known as McConnell’s Sign. It also showed a mobile hyperechoic mass (yellow arrow). These ultrasound findings were concerning for pulmonary embolism (PE), so computed tomography (CT) angiogram of the chest was ordered and confirmed massive bilateral obstructive filling defects (red arrows) consistent with saddle pulmonary embolism. Additionally, noted is flattening of the interventricular septum (blue arrow) consistent with right heart strain. Laboratory studies were notable for a troponin-I of 0.29 ng/mL, a B-type natriuretic peptide of 792.3 pg/mL, lactic acid of 5.30 mmol/L, and a creatinine of 2.0 mg/dL, consistent with end organ dysfunction. All other lab work was within normal limits.
Pediatric Airway Team Based Learning
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8KH01This cTBL covers a variety of pediatric airway emergencies. Therefore, by the end of this cTBL, the learner will be able to: 1) List the signs and symptoms associated with airway foreign body obstructions. 2) State the appropriate management of upper and lower airway foreign bodies. 3) Discuss the symptoms, signs, and management of bacterial tracheitis. 4) Discuss a step-wise algorithm for emergency asthma treatment in the emergency department setting. 5) Identify the potential complications of tonsillectomy and the acute management of post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage.
Subcutaneous Emphysema After Chest Trauma
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8864NPlain film anteroposterior (AP) radiography of the chest shows left-sided subcutaneous emphysema (red arrow) with overlapping muscle striations of the pectoralis major (green arrow). After chest tube placement (blue arrow), AP chest radiography shows persistent left-sided subcutaneous emphysema (red arrow). CT of the chest shows pneumomediastinum (blue arrow), left apical pneumothorax (pink arrow), and subcutaneous emphysema (red arrow) at the level of T2. At the level of T6, rib fractures can be visualized on the CT (yellow arrow). At the level of T8, left sided pneumothorax is also seen (pink arrow) as the absence of lung tissue on CT.
Croup
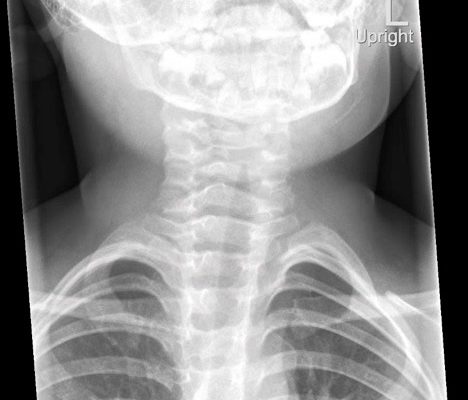
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W05JThe anteroposterior X-ray reveals the classic steeple sign (blue outline) indicative of subglottic edema leading to tracheal narrowing, consistent with croup. The lateral x-ray shows narrowing of the subglottic region (green outline and arrows).
Bullous Emphysema
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8W62GThe upright chest X-ray shows a large lucent area in the left lower lung field without lung markings, with associated curvilinear opacities (yellow arrows) consistent with a large air-filled bulla. The bulla is large enough to compress adjacent lung tissue as shown by the visible pleural line (blue line). The discontinuity of the pleural line and presence of lung markings superiorly makes these findings more consistent with bulla than pneumothorax. The chest computed tomography (CT) confirmed a large left hemithorax bulla.
The Role of Chest X-Ray and Bedside Ultrasound in Diagnosing Pulmonary Bleb versus Pneumothorax
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8MP7QThe patient was evaluated with bedside ultrasound for concern of possible pneumothorax. Imaging of the left lung with M-mode demonstrated a “sea shore” sign showing a wavy pattern below the pleural line caused by lung sliding as well as “comet tail” artifact caused by from the deep pleura. However, there was no lung sliding on the right shown by a lack of “comet tail” artifact and a “bar code” sign where M-mode shows straight lines throughout the image, this is caused by lack of motion below the pleura. This lack of lung sliding is consistent with possible pneumothorax or bleb.
A two-view chest X-ray (CXR) revealed absent lung parenchyma in the right lung similar to a large pneumothorax (see red outline). Electronic medical record chart review revealed previous CXRs with similar findings. This patient was determined to have an acute COPD exacerbation with chronic blebs, but no pneumothorax.
Pediatric Foreign Body Aspiration
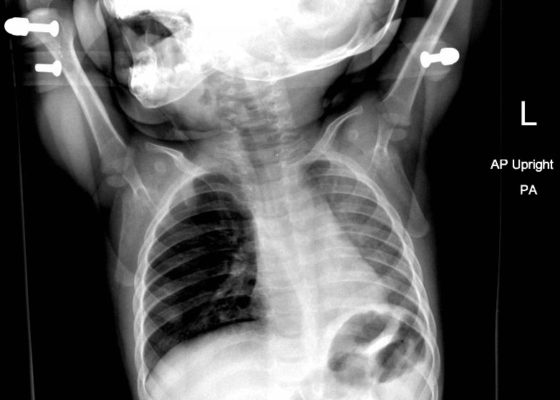
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8B648Chest radiograph showed increased radiolucency (red arrow) and flattening of the diaphragm on the right side (blue arrow) consistent with hyperinflation of the right lung, as well as left mediastinal shift (green arrow), indicating obstruction.
Spontaneous Pneumomediastinum: Hamman Syndrome
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8NS72The initial CT scans showed extraluminal gas surrounding the distal esophagus as it traversed the posterior mediastinum, concerning for possible distal esophageal perforation that prompted surgery and GI consultations. There was no evidence of a drainable collection or significant fat stranding. The image also showed an intraluminal stent traversing the gastric antrum and gastric pylorus with no indication of obstruction. Circumferential mural thickening of the gastric antrum and body were consistent with the patient’s history of gastric adenocarcinoma. The shotty perigastric lymph nodes with associated fat stranding, along the greater curvature of the distal gastric body suggested local regional nodal metastases and possible peritoneal carcinomatosis.
The thoracic CT scans showed extensive pneumomediastinum that tracked into the soft tissues of the neck, which given the history of vomiting also raised concern for esophageal perforation. There was still no evidence of mediastinal abscess or fat stranding. Additionally, a left subclavian vein port catheter, which terminates with tip at the cavoatrial junction of the superior vena cava can also be seen on the image.