Neurology
A Case Report of Epidural Hematoma After Traumatic Brain Injury
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R059Non-contrast CT head demonstrated a right sided EDH (red arrow) with overlying scalp hematoma, left-sided subdural hematoma (blue arrow), and bilateral subarachnoid hemorrhages. No skull fractures were noted.
Family Game Show-style Didactic for Teaching Nervous System Disorders during Emergency Medicine Training
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8D357By the end of this didactic exercise the learner will: 1) name 13 important neurologic conditions related to emergency medicine: TPA (tissue plasminogen activator) contraindications/TPA eligibility, optic neuritis, botulism, giant cell (temporal) arteritis, viral encephalitis, neurocysticercosis, rabies, myasthenia gravis, neurosyphilis, status epilepticus, Bell’s palsy, dementia vs. delirium, acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (Guillain-Barré); 2) recognize five pattern words associated with each neurologic condition; 3) understand exam findings, diagnostic tests, and/or treatments for 13 important neurologic conditions.
Primary Measles Encephalitis
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J80S75At the conclusion of the simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) Obtain a relevant focused history, including immunization status, associated symptoms, sick contacts, and travel history. 2) Develop a differential for fever, rash, and altered mental status in a pediatric patient. 3) Discuss management of primary measles encephalitis, including empiric broad spectrum antibiotics and antiviral treatment. 4) Discuss appropriate disposition of the patient from pediatric emergency departments, community hospitals, and freestanding emergency departments, including appropriate time to call for transfer and the appropriate time to transfer this patient during emergency department (ED)workup. 5) Review types of isolation and indications for each.
Novel Emergency Medicine Curriculum Utilizing Self-Directed Learning and the Flipped Classroom Method: Neurologic Emergencies Small Group Module
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J89H0JWe aim to teach the presentation and management of cardiovascular emergencies through the creation of a flipped classroom design. This unique, innovative curriculum utilizes resources chosen by education faculty and resident learners, study questions, real-life experiences, and small group discussions in place of traditional lectures. In doing so, a goal of the curriculum is to encourage self-directed learning, improve understanding and knowledge retention, and improve the educational experience of our residents.
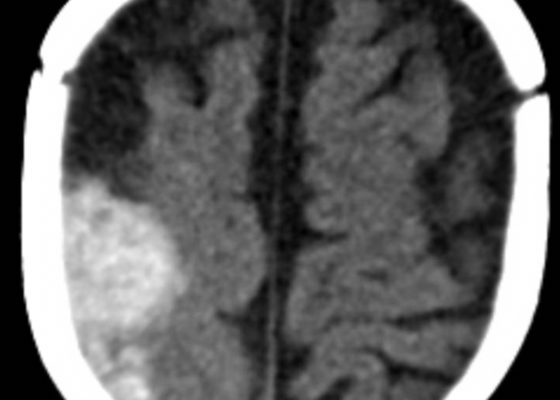
Spontaneous Intracranial Hemorrhage in Severe Hemophilia A: A Rare Cause of Seizure in a Young Child
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8G91DA computed tomography (CT) scan of the head without contrast was obtained out of concern for intracranial pathology due to the patient’s young age and the witnessed focal seizure. The CT showed a 4.2 x 1.2 x 1.5 cm acute extra-axial intracranial right frontoparietal hemorrhage favoring epidural over subdural hemorrhage given its lenticular shape. There was no underlying fracture, herniation or midline shift identified.
Acute Ischemic Stroke
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8R04XBy the end of this simulation session, learners will be able to: 1) recognize a CVA using the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), 2) understand and properly utilize the NIHSS, 3) list appropriate imaging and laboratory orders for a CVA work-up, 4) determine appropriate subspecialty consultation, 5) discuss common stroke syndromes and associated cerebral locations, 6) review indications and contraindications for tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), 7) review hospital specific stroke protocol.
A Woman with Arm Spasms
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8VP88The patient had a witnessed episode of isolated left upper extremity jerking, shown in the video, during which she was completely awake and conversant. Lab results were significant for serum glucose of 1167 mg/dL, no anion gap, and negative serum/urine ketones. She had a computed tomography (CT) of the head that did not show any acute pathology, and underwent a brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without any signs of stroke or other pathology, shown below.
Beware the Devastating Outcome of a Common Procedure
DOI: https://doi.org/10.21980/J8T336Non-contrast head computed tomography (CT) demonstrates multifocal bilateral hypodense lesions (white arrows) representing air emboli. Note the lesions are located in the intra-axial distribution which indicates an underlying vascular origin.